BIOL2343:LMonogenic Disorder Case Study
- Subject Code :
BIOL2343
- Country :
Australia
Case Study:
Tay-Sachs disease is an autosomal recessive disorder affecting the central nervous system. Homozygous recessive individuals with the disorder have progressive degeneration of the central nervous system, which is usually fatal. A couple has been referred to a medical clinic for genetic counseling in regard to their present pregnancy. Both the couples families have a history of Tay-Sachs disease. After consultation with the couple, a pedigree of the family has been constructed (Figure 1). The couple is individuals VI2 and VI3 on the pedigree.
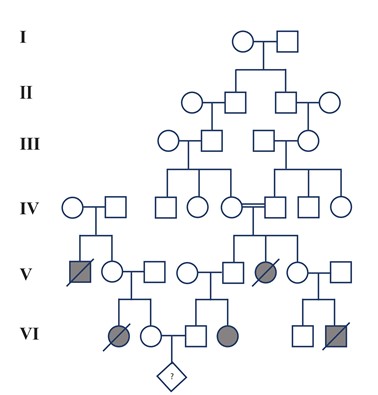
Question 1.What is the probability of the couple (individuals VI2 and VI3 on the pedigree) having a child with Tay-Sachs disease? Show calculations.
The couple decide to have an amniocentesis for prenatal genetic diagnosis to test for the presence of a mutation in the Tay-Sachs gene in their unborn child. Tay-Sachs disease is caused by the absence of an enzyme called hexosaminidase A which is encoded by the gene hexA. Without text, a fatty substance builds up on the nerve cells in the body. A region of DNA encompassing the Hexa gene has been amplified using PCR from the amniocentesis and cloned into the pCR2.1-TOPO vector (Figure 2).

The recombinant plasmid has been digested with a variety of restriction enzymes and these digests have been analyzed by gel electrophoresis. The gel photo is shown in Figure 3. Use the gel photo of the restriction fragments to answer the following questions (hint: use the second gel photo of the DNA ladder (Figure 4) to first identify the sizes of the ladder bands on the first gel (Figure 3)):
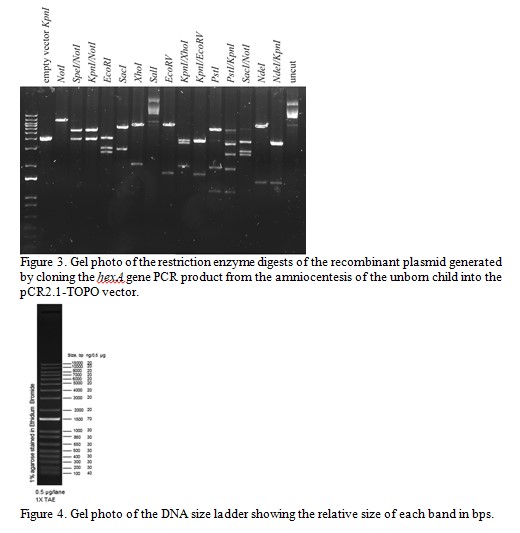
Question 2.What is the total size of the recombinant plasmid and what is the size of the PCR insert? Explain how you calculated these.
Question 3.One researcher in the team wants to digest the recombinant plasmid with the restriction enzyme EcoRI to subclone the entire PCR insert into a different vector. Explain why this would/would not be an appropriate choice of enzyme to use for this purpose.
Question 4.Which combination of two restriction enzymes can be used to cut out the entire PCR insert (without cutting within the insert)?
The M13 Reverse primer and M13 Forward (-20) primer were used to sequence (Sanger sequencing) the PCR product cloned into pCR2.1-TOPO. A segment of the sequencing chromatogram is shown in Figure 5.
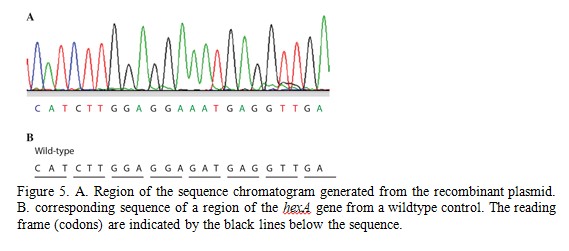
Question 5.What type of DNA mutation is present in the fetus? Does this cause a mutation in the HexA protein and if so, what is this? (hint: use the genetic code to translate the DNA sequence)
Question 6.Can you identify if the fetus is homozygous or heterozygous for a mutation in hexA? Explain how you determined this and would you expect the fetus to have Tay-Sachs disease?
The researchers want to confirm that the mutated hexA gene can still produce a protein product. They aim to clone the hexA gene into another vector containing the gene GFP and then observe if a GFP::HexA fusion protein is produced. A map of the GFP vector pcDNA3.1 NT-GFP-TOPO is shown in Figure 6. Analyze the vector map and answer the following questions.
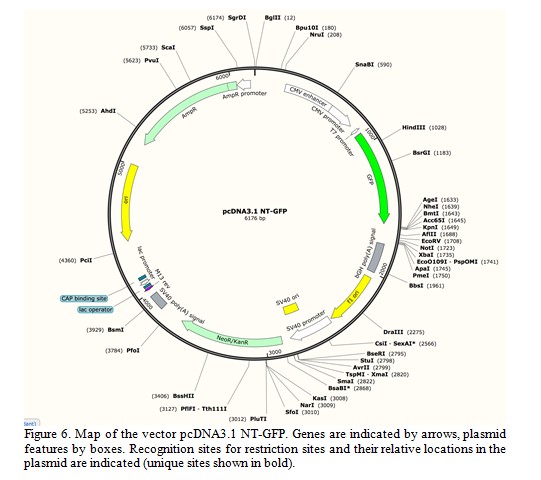
Question 7.Which restriction enzyme/s will cut the plasmid within the open reading frame (ORF) of the GFP gene?
Question 8.Which combination of two restriction enzymes could be used to cut out the smallest possible fragment of the plasmid that contains the CMV enhancer and GFP but not the bGH poly(A) signal? What is the size of this fragment?
Question 9.The combination of BsrG1 and KpnI cannot be used to cut out the entire (intact) GFP gene from the vector. Why?
Question 10.What is the expected sizes of the restriction fragment/s generated from a double digestion of this plasmid with both HindIII and PfoI?
Question 11.Describe how you would sub-clone the KpnI/NotI fragment from the recombinant clone into the vector pcDNA3.1 NT-GFP (Figure 6).
* Include the steps on generating the recombinant molecule, amplifying the recombinant plasmid in bacteria and how you would select for the recombinant clone in E. coli. Include explanations/justification of why you would perform each step.
Note: You do not have the sequence or any primers so you cannot use PCR.
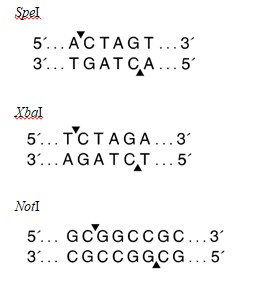
Question 12.Use the restriction enzyme recognition sites listed below to explain if it is possible to sub-clone the SpeI/NotI fragment from the recombinant clone into the vector pcDNA3.1 NT-GFP digested with XbaI/NotI.