HOTL2011 Global Aviation
- Subject Code :
HOTL2011
Introduction
Bonza Airlines is a low-cost carrier in Australia. Founded in October 2021, Bonza has managed to thrive in the Australian aviation industry, with more plans for the future (Dye, 2023). This report will analyse the case of Bonza Airlines by reviewing its current business model, stakeholder involvement, and potential risks that could impact the companys success and sustainability in the future.
Bonza Airlines Business Overview Table
|
Business Name |
Bonza Airlines |
|
Business Ownership |
777 Partners |
|
Bonza CEO |
Tim Jordan |
|
Head Office Location |
Sunshine Coast, Queensland, Australia |
|
Flights Commenced |
27 |
|
Flight Routes Currently Operational |
Cairnes Rockhampton Newcastle Whitsunday Coast Rockhampton Townsville Toowoomba Townsville, Whitsunday Coast, Melbourne Mackay, Rockhampton, Gladstone, Bundaberg, Whitsunday Coast, Port Macquarie, Toowoomba (ACCC 2023) |
|
Types of Aircrafts Bonza Fly |
1 |
|
Names of Two of the Aircrafts |
Boeing 737 Max 8 (Bonza Aviation Pty. Ltd. 2022) |
|
Bookings are made via |
FlyBonza (Bonzas mobile app) (Bonza Aviation Pty. Ltd. 2022) |
Table 1: Overview of Bonza Airlines
Business Model of Bonza Airlines
Bonza Airlines operates on a Low-Cost Carrier (LCC) business model, which enables the company to offer low fares to create opportunities and increase demand among flyers. Bonza operates flights on a point-to-point network model by focusing on unexplored and under-utilised routes between domestic as well as regional cities. Operating as a low-cost carrier means that Bonza does away with all unnecessary services and facilities like in-flight entertainment and free meals, further enabling them to gain a competitive edge over other airline companies in terms of cost (Budd & Ison 2020). While Bonza focuses on low operating costs to offer flight seats at much lower rates, the fleet structure also has an equal impact on low-cost offerings. Low-cost carriers like Bonza adopt a mixed strategy along with a cost-focus strategy to minimise all possible costs for the business and its passengers (Bonza Aviation Pty. Ltd. 2022). Due to comparatively higher airline fares, Bonza enjoys a competitive advantage by letting flyers save money on their travels, especially on domestic routes. The use of smaller aircraft by the company further helps reduce costs and increase efficiency as Bonza would need only one set of spare parts as compared to Full-Service Cost (FSC) airlines that need various components for different kinds of aircraft (Budd & Ison 2020). However, LCC models come with a set of disadvantages, especially when it comes to offering additional services to improve flyers experience. Flyers cannot avail of additional seating space, luxury services like business class travel, rescheduling and cancellation services, or enjoy any kind of free (in-flight) meals and/or entertainment. There is also a high chance of hidden costs like service charges, taxes and limited payment modes, which may add up to result in high flyer costs despite Bonza being an LCC (Fontanet-Prez, Vzquez & Carou 2022). Bonza as an LCC operates from smaller airports located at a distance from the main city, which may increase transportation costs (Budd & Ison 2020).
Stakeholder Assessment Matrix
|
Stakeholder Name |
Stakeholders Importance |
Stakeholder advantages |
Stakeholder disadvantages |
Stakeholders Influence |
Justification for Influence Rank |
|
|
Passengers |
Generate revenues and increase profits for Bonza |
Customer satisfaction will increase retention and reputation of Bonza; passenger demands increase revenues (Australian Government 2023) |
Negative reviews, customer complaints or grievances, loss of future business, reputation damage |
Extremely High |
Bonzas main source of revenue generation is through passengers, directly or indirectly as their purchase decisions can impact business performance and profitability in the long run |
|
|
Employees |
Contribution to smooth operations |
Employees can increase operational efficiency, business performance, innovation |
Employees non-compliance with policies and regulations increases operational and safety risks |
High |
Daily operations are directly affected by employees productivity, performance and perceptions of the company |
|
|
Investors |
Provide funds or capital for Bonzas operations in return for profits |
Extension of financial support from investors allows Bonza to utilise technologies, improve strategies, and remain competitive (ACCC 2023) |
Pressure from investors may restrict Bonzas growth, increasing conflicts, and lack of funds result in financial instability |
High |
Investors or shareholders have indirect impacts; however, they could directly impact Bonza operations and financial positions |
|
|
Regulatory Bodies/Authorities like the CASA |
Regulatory authorities like CASA improve security, and operational and safety standards (CASA n.d.) |
Ensures compliance to prevent accidents, and passenger risks, and build public trust |
Stringent regulations may increase Bonza business costs |
Extremely High |
Regulatory bodies have a high and direct impact on Bonzas ability to operate in Australia; non-compliance may result in legal risks and termination of flying operations (Australian Government 2023) |
|
Table 2: Stakeholder Assessment Matrix
Required Approvals for Bonza Airlines
To start operating in Australia, Bonza needs to adhere to the regulations of the Civil Safety Authority (CASA) in Australia.
- Bonza would need to obtain an Air Operator Certification (AOC) by catering to all necessary operational and safety standards of the CASA (CASA 2023)
- The CASA outlines security and environmental regulations for all airlines that Bonza will need to comply with (CASA 2023)
- Bonza will need approval to operate its specific aircraft type/s (CASA 2023; Budd & Ison 2020)
- Route plans for Bonzas point-to-point route operations will need to be submitted to the CASA for approval (CASA 2023)
- Bonza needs to draft and submit various documentation on operations and training, such as Operations and Training Manuals, Maintenance Control Manual, and other regulatory-compliance manuals to the CASA (CASA 2023; Budd & Ison 2020)
- To ensure the maintenance of high safety and security standards, the CASA requires all airlines to implement robust systems for the identification, assessment and mitigation of safety risks (CASA 2023; Fontanet-Prez, Vzquez & Carou 2022)
- The CASA outlines personnel licensing requirements for airlines to ensure all involved personnel have the necessary certifications and licenses to operate (CASA 2023; Budd & Ison 2020)
Potential Threats/Risks to Bonza Airlines
Entry of Low-Cost Carrier Airlines: The current feasibility of low-cost carrier airline models may witness the entry of more future low-cost carriers in the Australian market. The relatively high competition in the Australian aviation industry may make it challenging for Bonza to attract flyers unless a clear differentiation strategy is adopted by the company (Budd & Ison 2020).
Economic Risks: The COVID-19 pandemic decreased the global passenger traffic in the aviation industry, and continues with a slow growth and recovery for the Australian aviation industry (Fig. 1). Ineffective measures for the regulation of the aviation industry during pandemics and other unforeseen economic challenges might make it difficult for Bonza to continue with their low-cost pricing strategy (ACCC 2023).
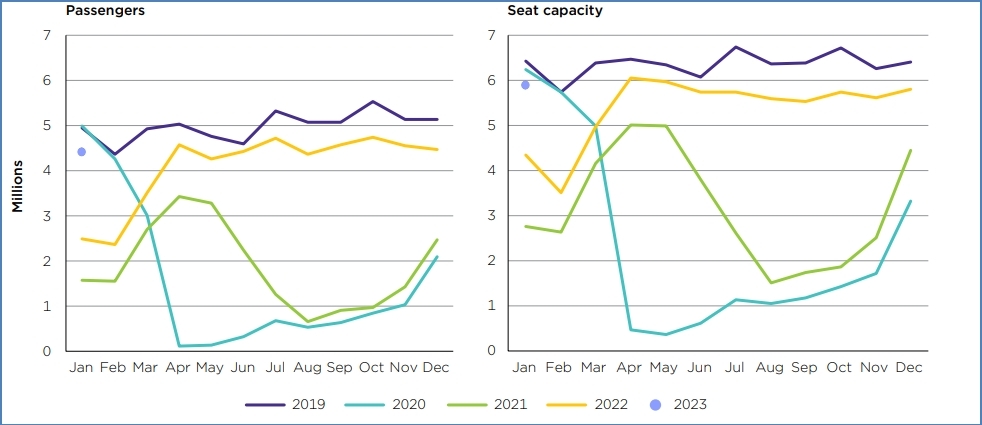
Fig. 1: ACCC Data from Jetstar, Qantas, Rex and Virgin Australia (ACCC 2023)
Stringent Aviation Regulations: The COVID-19 pandemic also resulted in increasing consumer complaints about delayed and cancelled flights, both domestic and international, which impacted consumer service and protection (Fontanet-Prez, Vzquez & Carou 2022). The Australian government puts forth the Airline Customer Advocate (ACA) that supports customers with their complaints and grievances with domestic/international airlines (Airline Customer Advocate n.d.). As such, the increasing concerns of customers regarding the safety and timely operations of airlines would require Bonza to comply with stringent/stricter regulations to protect Australian consumers, especially in terms of providing quality service and effective management and resolution of customer complaints (Australian Government, 2023; ACCC 2023).
Rising Fuel Costs: According to Kaye and Akhand (2023), Australian airline Qantas Airways may be forced to increase fares as a result of rising fuel prices. As a result of the tight oil supply, Bonza may be compelled to either cancel their flights or increase fares slightly for passengers, which can negatively affect their competitive advantage in the Australian aviation industry.
Review of Bonzas Business Model
The current LCC business model of Bonza Airlines has a chance of being sustainable in the future (Figure 2), but it would need to navigate through increasing regulatory standards and customer expectations. Post the COVID-19 pandemic, despite reduced disposable incomes, customers have started prioritising safety and quality of service due to frequent issues of flight cancellation and rescheduling (Fontanet-Prez, Vzquez & Carou 2022). The same would increase pressure on Bonza to improve customer experience and provide additional services to attract and retain frequent passengers. According to a study by Amicarelli et al. (2021), Customer Relationship Management (CRM) would be paramount for Bonza to ensure they remain sustainable in the future, but the same would also mean increasing overall business costs. Bonza would eventually be required to improve customer service by handling their grievance better. Additionally, growing environmental concerns put added pressure on LCCs like Bonza to reduce their carbon emissions by investing in biofuels and e-fuels, which could also increase operational costs (ACCC 2023; Budd & Ison 2020; Gssling 2020). The lack of business-class products may further make it challenging for Bonza to attract long-haul passengers.
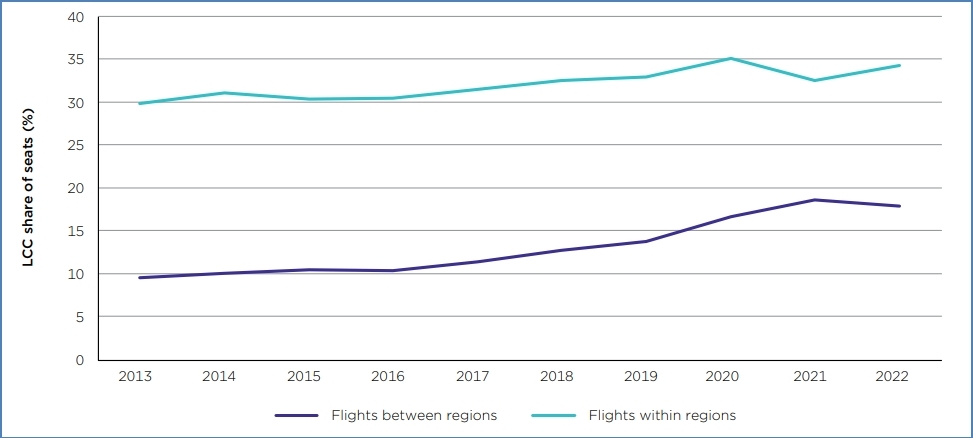
Figure 2: Share of Seats Globally by LCCs: 2013 to 2022 (ACCC 2023)
To become sustainable in the future, Bonza may be required to merge its LCC model with other effective business models/strategies to maintain its competitive edge. Customers will look for a unique proposition value especially in low-cost carrier airlines due to the highly competitive aviation sector in Australia that currently includes several LCC players operating successfully (ACCC 2023).
Conclusion
Bonza Airlines as a low-cost carrier has huge prospects to succeed in the aviation industry, considering the success of several other LCCs in Australia. However, Bonza is faced with economic and regulatory risks that govern the Australian aviation industry along with the existence of high levels of competition. To become sustainable in the future, Bonza may need to modify its business model, reassess pricing strategies, and implement stronger standards for customer safety as well as experience in the future.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back! Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects.
Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

