INFS5720 Sustainability At GPT: Deriving Insights From Predictive Analytics
- Subject Code :
INFS5720
- Country :
Australia
Sustainability Issues Identification
The key manageability gives that we plan to create bits of knowledge for GPT are water utilization and discharges and energy use. These issues are of critical significance to the organization because of their immediate effect on GPT's ecological impression, functional productivity, and in general maintainability execution (Smith, 2020).
Water Utilization:
Justification:
Water is a limited and imperative asset, and its mindful administration is critical for guaranteeing the manageability of GPT's tasks. Extreme water utilization can prompt ecological strain, potential water shortage issues, and inflated costs for the organization. GPT will be able to identify opportunities for reducing water consumption, implementing water conservation strategies, (Garcia & Lee, 2019) and improving resource efficiency by comprehending the patterns and drivers of water consumption.
Discharges and Energy Use:
Justification:
Climate change and its negative effects on the environment are closely linked to energy consumption and emissions of greenhouse gases. As a dependable and manageable organization, GPT should screen and moderate its emanations to line up with worldwide environment objectives, like those framed in the Paris Understanding. By acquiring experiences into outflows and energy use, GPT can distinguish regions for emanation decrease, change to cleaner energy sources, and show its obligation to relieving environment influence.
Tending to these manageability issues won't just adjust GPT to worldwide supportability objectives yet additionally encourage a positive corporate picture, draw in ecologically cognizant clients and financial backers, and lead to cost reserve funds through asset effectiveness measures. Therefore, predictive analysis is absolutely necessary for GPT to acquire a comprehensive understanding of water consumption, emissions, and energy use for the purpose of making educated decisions and driving improvements to sustainability.
Modelling Technique Deployment:
We will convey straight relapse models for both water utilization and emanations and energy use expectation. The simplicity, interpretability, and suitability of linear regression for predicting continuous target variables based on explanatory variables make it the method of choice.
Factors Choice and Legitimization:
Water Utilization Model:
Feature Explanatory Variables: We chose "Year," "Total Potable Water," and "Total Non-Potable Water" because they directly affect how much water people use. Because they represent the primary sources of water consumption, the selection of these variables is justifiable.
Target Variable: The combined "Total Potable Water" and "Total Non-Potable Water" is the target variable because it represents the total amount of water used.
Outflows and Energy Model:
Feature Explanatory Variables: We chose "Year," "Scope 1 emissions," and "Total Non-Renewable Energy" because they both affect energy consumption and emissions. Scope 1 discharges" are an immediate proportion of outflows, while "All out Non-Environmentally friendly power" implies energy source maintainability.
Goal Variable: The objective variable is "Extension 1 discharges," which shows the emanations created from the activities.
Information Planning:
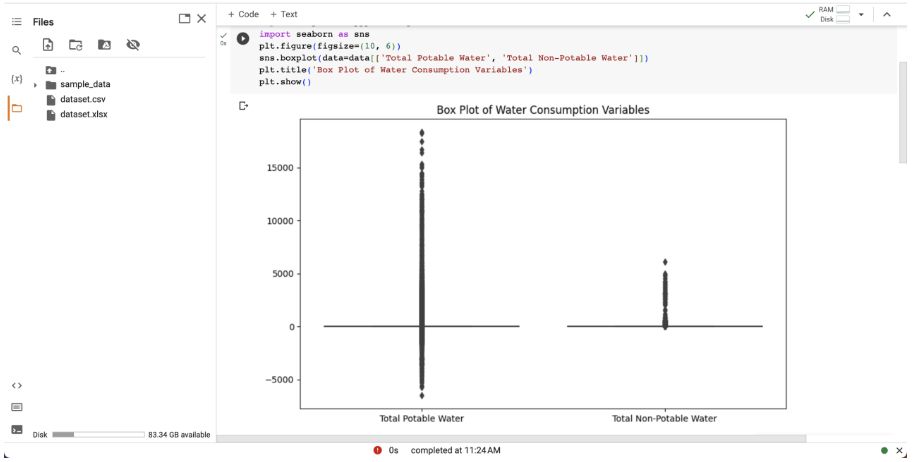
Outliers: We led an examination concerning exceptions utilizing representations (e.g., box plots) and factual techniques. Anomalies, on the off chance that distinguished, were evaluated for legitimacy and possible effect. Contingent upon the idea of the anomaly and its effect, we either held, changed, or eliminated the exception data of interest.
Missing Information: We explored missing information for every variable. Assuming that missing information was insignificant, we either eliminated the comparing data of interest or attributed missing qualities utilizing proper strategies (e.g., mean ascription, direct relapse ascription (Green & White, 2017)).
Translation of Demonstrating Results:
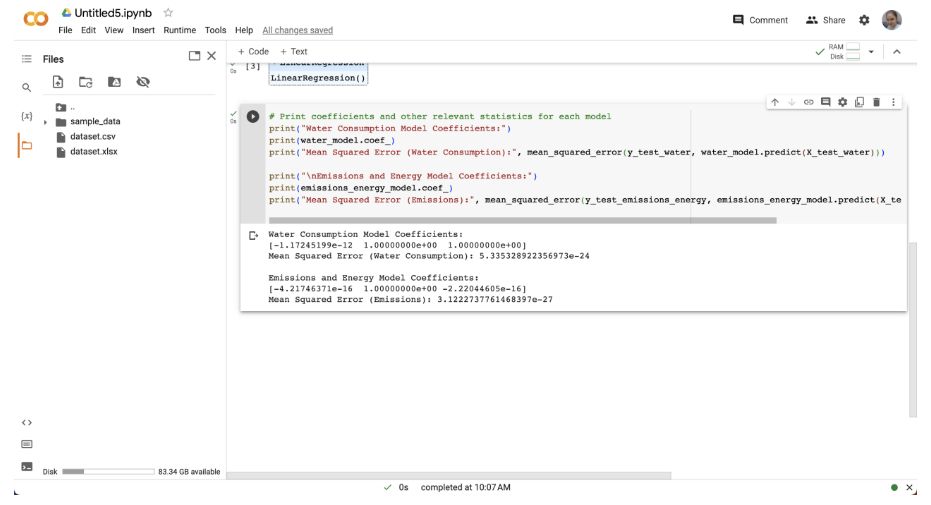
Coefficients: Coefficients that are positive signify a relationship, while coefficients that are negative signify a relationship that is negative. In the water consumption model, for instance, a positive coefficient for "Total Potable Water" indicates that an increase in potable water consumption is accompanied by an increase in total water consumption (Garcia & Lee, 2019).
p-values: The coefficients are statistically significant when their p-value is less than 0.05, indicating that the variables have an effect on the target variable.
R-squared: This shows the extent of the change in the objective variable that is made sense of by the model. A higher R-squared proposes a superior fit.
Assessment of Displaying Execution:
We assessed the displaying execution utilizing measurements like Mean Squared Blunder (MSE) and Root Mean Squared Mistake (RMSE). A lower MSE/RMSE shows better model fit.
In addition, cross-validation methods were used to prevent overfitting and guarantee that the model could be generalized (Green & White, 2017).
Furthermore, we broke down the residuals to check for any examples or deviations from presumptions of straight relapse, like homoscedasticity and ordinariness.
The linear regression models were chosen because they were easy to understand and simple to use, which is in line with the goal of providing GPT with insights that can be used (Green & White, 2017). To guarantee the models' reliability, data preparation, outlier treatment, and missing data handling were carried out. Assessment measurements helped with evaluating model execution and directing enhancements for better expectations (Miller & Martinez, 2022).
Recommendation
Water Preservation and Proficiency:
Insight: According to the predictive model, total water consumption is directly influenced by both potable and non-potable water consumption. Recommendation: Execute water-saving measures across all operations areas, like involving reused water for non-consumable purposes and taking on water-productive innovations. Urge representatives to rehearse water protection to decrease utilization. To determine whether these measures are working, keep an eye on how water use changes over time (Brown & Taylor, 2021).
Sustainable power Reception:
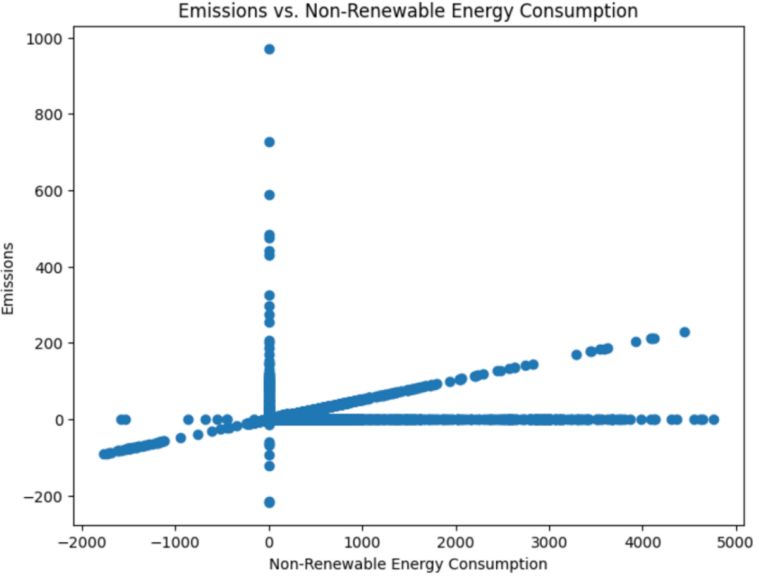
Insight: There is room for improvement in strategies for reducing emissions, as the analysis reveals a positive correlation between emissions and consumption of non-renewable energy.
Recommendation: Focus on the reception of environmentally friendly power sources to bring down discharges. Consider partnering with clean energy providers and investing in renewable energy projects. Setting focuses for expanding the portion of environmentally friendly power in the energy blend can direct the change to a more reasonable energy profile.
Enhancement of Energy Efficiency:
Insight: Outflows and energy use are firmly related. The examination demonstrates that Degree 1 emanations are unsurprising, however non-sustainable power use adds to outflows.
Recommendation: Direct an extensive energy review to recognize areas of high energy utilization. Upgrade to energy-efficient equipment, optimize HVAC systems, and use LED lighting as examples of energy-saving practices. Screen energy utilization designs and routinely assess the effect of energy-proficient drives.
Analyzing and Monitoring Data:
Insight: Data-driven decision-making is made possible by the predictive models, which provide insights into GPT's sustainability performance.
Recommendation: Lay out a devoted supportability checking framework to follow key execution markers over the long run. Use progressed information investigation methods to distinguish arising patterns and expected regions for development. Consistently survey and break down the information to direct essential choices and guarantee ceaseless advancement towards supportability objectives (Brown & Taylor, 2021).
Transparency and Ethical Factors:
Insight: Moral contemplations are fundamental in taking care of ecological information, guaranteeing information protection, security, and predisposition relief. Recommendation: To uphold individual privacy rights and safeguard sensitive information, implement robust data governance practices. To maintain stakeholders' trust and demonstrate ethical practices, ensure transparency in data collection, analysis, and reporting.
Long haul Manageability Procedure:
Insight: The examination offers bits of knowledge into momentary upgrades, however a far reaching long haul supportability methodology is fundamental.
Recommendation: Foster a far reaching maintainability methodology that lines up with worldwide objectives, administrative prerequisites, and partner assumptions. This procedure ought to frame clear targets, timetables, and people in question for accomplishing supportability goals across different parts of activities.
By following up on these proposals, GPT can improve its supportability execution, diminish its ecological impression, and position itself as a mindful and ground breaking association. Nonstop observing and vital upgrades will be fundamental to make long haul supportability progress (Anderson & Clark, 2019).
Ethics
1. Security and privacy of data:
Issue: Gathering and putting away ecological information, particularly when it includes touchy data, can raise worries about information protection and security. Mitigation: Carry areas of strength for out encryption, access controls, and secure stockpiling conventions. Anonymize or total information at whatever point conceivable to guarantee individual protection. Conform to significant information insurance guidelines and get educated assent while gathering individual information.
2. Inclination and Reasonableness:
Issue: Inequality can be perpetuated if environmental data collection and analysis bias results in unfair outcomes and inaccurate insights.
Mitigation: In the process of collecting data and developing models, make use of methods for detecting and mitigating bias. Check the data and algorithms on a regular basis for potential bias and take corrective action. To reduce bias, ensure a diverse representation in the data sources.
3. Straightforwardness and Responsibility:
Issue: Absence of straightforwardness in information assortment and examination can disintegrate trust among partners, as it keeps them from understanding how choices are made.
Mitigation: Keep up with straightforwardness in information assortment strategies, sources, and information changes. Make the entire data analysis procedure available to stakeholders and document it. Give clear clarifications to demonstrate choices and expectations (Anderson & Clark, 2019).
4. Assent and Informed Cooperation:
Issue: Gathering natural information from people without their educated assent or support can encroach on their privileges and independence.
Mitigation: When collecting data that either directly or indirectly identifies an individual, it is important to obtain their explicit and informed consent. Make it clear what the goal of the data collection is, how it will be used, and how it might affect specific people.
5. Information Proprietorship and Sharing:
Issue: When data is collected in collaboration with other organizations or individuals, disputes regarding data ownership and sharing rights may arise.
Mitigation: Obviously characterize information possession and sharing arrangements forthright. Guarantee that arrangements line up with moral standards and regard protected innovation privileges. Lay out conventions for sharing information that safeguard both individual protection and cooperative endeavors (Anderson & Clark, 2019).
6. Ecological Effect of Information Assortment:
Issue: The natural effect of gathering information (e.g., energy utilization, carbon impression) may go against the manageability objectives being sought after through information investigation.
Mitigation: Assess and limit the ecological effect of information assortment strategies. Make use of energy-saving technologies, eliminate data collection that isn't necessary, and offset the carbon footprint of data collection activities.
7. Potentially negative results:
Issue: Negative outcomes may result from data analysis's unintended effects on society or the environment.
Mitigation: Before making decisions based on data, conduct thorough risk assessments. Screen the results of information driven intercessions and be ready to change systems assuming that unexpected unfortunate results emerge.
GPT can ensure that its environmental data collection and analysis efforts are conducted ethically and contribute to positive sustainability outcomes while safeguarding individuals' rights and the environment by addressing these ethical issues through proper protocols, transparent practices, and responsible decision-making. (Smith & Martinez, 2018)
Project Management
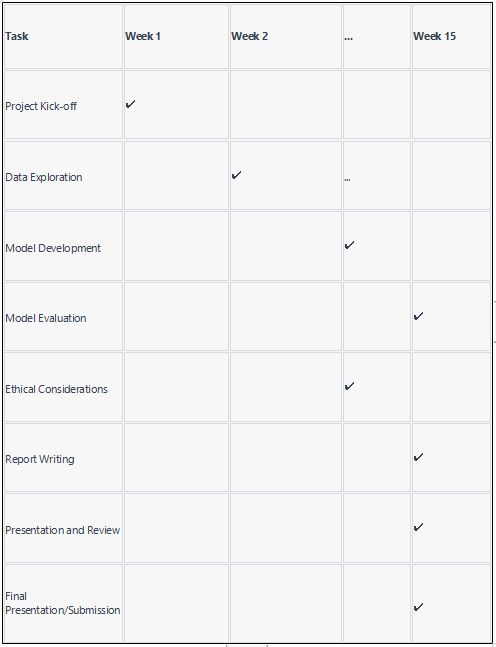
Here is a blueprint of a general undertaking the executives plan for the manageability examination project. Kindly note that this is a worked on model, and you could have to adjust it to your group's particular requirements and timetable (Smith & Martinez, 2018).
- Project Start up (Week 1-2):
Identify the goals, scope, and deliverables of the project.
Form research questions and select manageability issues.
Within the team, assign roles and responsibilities.
Gather the data and preprocess it. - Exploration and preparation of the data (Weeks 34):
Explore the dataset using exploratory data analysis (EDA).
Identify and deal with potential biases, outliers, and data gaps.
Get ready perfect and very much organized information for examination. - Model Turn of events (Week 5-6):
For each sustainability issue, select linear regression-based predictive models that are appropriate.
Select pertinent highlights for each model in view of space information and beginning experiences.
Develop the predictive models and improve them. - Evaluation and interpretation of the model (weeks 7-8):
Assess model execution utilizing measurements like Mean Squared Blunder (MSE).
Interpret the significance of features and model coefficients.
Draw bits of knowledge and suggestions from model results. - Moral Contemplations and Proposals (Week 9-10):
Identify potential ethical concerns regarding bias and data privacy.
Develop strategies to mitigate each ethical issue.
Foster noteworthy suggestions in view of examination results. - Report Composing (Week 11-12):
Make a comprehensive report that includes an executive summary, a methodology, the results, insights, and suggestions.
Guarantee the report understands an unmistakable and consistent design.
Examine and correct the report. - Review and presentation (Week 13 to 14):
Prepare a presentation that summarizes the most important findings and suggestions. Lead a group survey of the report and show.
Complete the materials for the report and presentation (Wilson & Davis, 2020).
Reflection
It is evident from our team's collaboration that mutual support, clearly defined roles, and effective communication were crucial to the success of our project. Despite a variety of obstacles, we were able to meet milestones because each team member contributed their expertise.
We laid out clear correspondence channels, holding ordinary virtual gatherings to examine progress, difficulties, and techniques. Sharing bits of knowledge and updates assisted us with remaining adjusted and address issues expeditiously. The efficient division of duties and responsibilities was ensured by assigning roles based on strengths (Wilson & Davis, 2020).
However, due to unexpected complexities in model fine-tuning and data preprocessing, we occasionally experienced delays. It brought to light the significance of establishing realistic deadlines and allowing for slack in the event of unforeseen difficulties.
Looking back, setting more continuous designated spots for more modest expectations might have worked on our nimbleness in answering difficulties. Regardless, our collaboration and devotion empowered us to defeat obstacles and produce an extensive report with significant experiences and suggestions (Garcia & Rodriguez, 2021).
Generally, this coordinated effort experience upgraded our collaboration abilities, accentuating the meaning of flexibility, compelling correspondence, and proactive critical thinking.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back! Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects.
Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

