Create a Wikipedia style website about the disease targeting an audience of "Bioscience Entrepreneurs.
Wiki page instructions General considerations
Before you start work on this assignment, read the assessment criteria and mark scheme (see Moodle page). This describes what we would like to see at the end. This is a bit like us asking you to bake a pie and telling you what we expect at the end (e.g. taste, appearance, size etc.). A good cook will be able to produce a nice tasting pie within the allotted time, but an inexperienced cook will struggle without a recipe. More importantly, even a good cook will do better with a recipe. I have therefore reflected on the process and compiled a recipe here. Obviously, there are many ways you can make a pie, so feel free to adapt my recipe.
There are three major stages to write your assignment:
Stage 1: Research the topic and create an overall structure/framework
Stage 2: Write and assemble the page
Stage 3: Challenge, revise, proof
Stage 1: Research Strategy
Strategy for researching a disease (or other scientific topics)
When you start researching, dont just rely on what you already know. Instead apply a defined strategy to make sure you avoid omissions and dont miss aspects you may have not thought of. I therefore suggest you follow these 7 steps for researching your topic:
- Starting information collection
- Expand search
- Establish different axes*
- Choose and complete grids**
- Analyse and restructure
- Evaluate and conceptualise
- Drill down on a/some chosen subtopic/s
* By axis I mean different ways you can categorise a topic
** By grid I mean a matrix based on two or more axes
- Starting information collection
Start with a few generic sources such as a Wikipedia and Goggle search with just the disease name. From this you will probably learn some basic information about: Signs and Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Different disease subtypes
- Risk factors and pathobiology
- Treatment/management
Do this step even if you think you already have a good understanding of the topic.
- Expand search
Importantly, step 1 will equip you with basic concepts, disease subcategories and keywords to expand your search. Now use more complex search terms to find specialist review articles in PubMed or Google Scholar. Focus on recent reviews from reputable journals and spend some time reading at least 3-5 articles.
- Establish different axes
Having established a broader knowledge about the topic, ask yourself how you can slice the topic, keeping in mind what we have covered in this module. For example, if the disease has several subtypes, e.g. osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout arthritis, this would be one axis of slicing arthritis. This process may require some further research. Axes you should consider are:
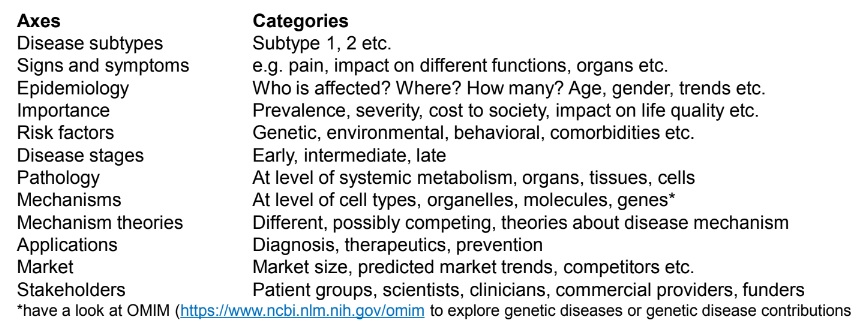
In your Wiki page you should considered most of the different axes mentioned above at least on a superficial level.
- Choose and complete grids
In this step you should use different axes to create grids. For example, a grid might have in the x-axis the different disease subtypes and in the y-axis mechanisms. Obviously, it does not make sense to complete all 66 possible axis combinations from the previous slide. Some axis/categories may be less important for your specific topic or you may also want to add further axes and/or categories. But exploring different axis combinations and completing the grids (possibly by further research) will allow you to cover the topic more broadly and help you to avoid omissions. Also, the choice of axis combinations will influence the flavour of your wiki page.
- Evaluate and conceptualise
After you have researched and thought about your topic broadly and from different angles you now need to start evaluating what is important. Also, are there unexpected connections or are there gaps in the published literature you have not previously appreciated? Furthermore, you should try to see whether any new concepts or insights have emerged from your search. This is academically the most challenging as well as the most creative step. Discovering novel/original connections or different ways of thinking about topics is truly rewarding but is hard to achieve. It cant be forced and you should allow sufficient time to immerse yourself in the topic for this process to occur naturally.
6. Analyse and restructure
Now you need to start reducing complexity, focus on specific key characteristics that emerged from step 5 and reduce the multidimensional grid space into a linear narrative. So, whilst you have been expanding the information space from step 1-4, step 6 is now all about reducing and distilling the information.
- Drill down on a/some chosen subtopic/s
Steps 1-6 ensure you have explored your topic from different viewpoints and have no major omissions, which should allow you to create a comprehensive overview. By definition, this work will be a bit superficial because the main aim is to achieve breadth, not depth. Nevertheless, to introduce more gravity, you ought to explore a particular subtopic further (mechanisms, therapy or diagnosis are usually well suited to this), using a similar approach as described in steps 1-6. At this stage you may need to delve into some primary literature. This should only be a minor part of the overall assignment but should be a specific point of interest and something thats relevant for the overall narrative.
Stage 2: Write and assemble the page Tips
- A lot of people make the mistake of starting at stage 2. Make sure you have properly researched the topic before you start writing your text and creating figures/diagrams. Ideally you already have a structure with subtitles and sub subtitles from stage 1.
- Invest sufficient efforts into figures and diagrams. They have two main usages. Firstly, they can be used to draw the attention of the reader (as in the usage of clickbait). Secondly, they can be extremely effective in communicating complex structures, relationships, processes etc. without the need of much text. Consider the balance of information in the text vs the figures.
- Think carefully whether you want to include a piece of information within your wiki page or whether it would be more appropriate to have it externally via a link.
- Avoid non-obvious acronyms and specialist terms, they make reading tedious for the non-specialist.
Stage 3: Challenge, revise, proof Tips
- Challenge your overall content and focus. Are there bits that are not really necessary? Dont be afraid of deleting, nobody likes doing it (after all youve spent time writing this content) but succinctness is important to engage the reader (in particular in a business environment). Ideally ask someone else for their opinion.
- Assess the overall structure. Does it make sense and does it flow logically? Dont be afraid of making rearrangements. Often the first structure can be improved upon.
- Look at the overall balance. Are all paragraphs of appropriate length? Are you happy with your choice of figures/diagrams and links?
- Proof read the final product (including figure legends)!
Keep in mind, it is very likely that you will need to do similar research exercises at some point in your future career (besides your MSc thesis). You can apply the strategy outlined here to any topic.

