ACCT6005 Company Accounting
- Subject Code :
ACCT6005
- University :
Torrens University Exam Question Bank is not sponsored or endorsed by this college or university.
- Country :
Australia
Module 1.1: Practice all case studies under Module 1.1
Module 1.2:Question 10.4 Acquisition analysis and journal entries
On 1 July 2019, John Ltd acquired all the issued shares of Robert Ltd for $153 000. At this date the equity of Robert Ltd was recorded as follows:

All the identifiable assets and liabilities were recorded at amounts equal to their fair values.
Required
(a) Prepare the acquisition analysis at 1 July 2019, and consolidation worksheet entries at 1 July 2019 and 1 July 2020 assuming John Ltd paid $153 000 for the shares in Robert Ltd. (b) Prepare the acquisition analysis at 1 July 2019, and consolidation worksheet entries at 1 July 2019 and 1 July 2020 assuming John Ltd paid $148 000 for the shares in Robert Ltd. (c) Prepare the acquisition analysis at 1 July 2019, and consolidation worksheet entries at 1 July 2019 assuming John Ltd paid $145 000 for the shares in Robert Ltd and at that date Robert Ltd had recorded goodwill of $4000.
Module 2 Intragroup transactions
- Why is it necessary to make adjustments for intragroup transactions?
- In making consolidation worksheet adjustments, sometimes tax-effect entries are made. Why?
- Why is it important to identify transactions as current or prior period transactions?4.Where an intragroup transaction involves a depreciable asset, why is depreciation expense adjusted?
- What is meant by realisation of profits?
Question 11.1 Intragroup transactions
Koala Ltd owns all of the shares of Kangaroo Ltd. In relation to the following intragroup transactions, all parts of which are independent unless specified,prepare the consolidation worksheet adjusting entries as at 30 June 2019. Assume an income tax rate of 30%.
(a) In April 2019, Koala Ltd sells inventory to Kangaroo Ltd for $12 000. This inventory had previously cost Koala Ltd $8 000, and it remains unsold by Kangaroo Ltd at the end of the period.
(b) All the inventory in (a) is sold to Cockatoo Ltd, an external party, for $16 500 on 19 June 2019.
(c) Half the inventory in (a) is sold to Galah Ltd, an external party, for $7 200 on 20 June 2019. The remainder is still unsold at the end of the period.
(d) Koala Ltd, in January 2019, sold inventory for $8 000. This inventory had been sold to it by Kangaroo Ltd in the previous year. It had originally cost Kangaroo Ltd $4 800 and was sold to Koala Ltd for $9 600.
Question 11.2 Intragroup transactions
Numbat Ltd owns all of the shares of Goanna Ltd. In relation to the following intragroup transactions, all parts of which are independent unless specified, prepare the consolidation worksheet adjusting entries as at 30 June 2019. Assume an income tax rate of 30%.
(a) On 1 July 2018, Numbat Ltd sold an item of plant costing $15 000 to Goanna Ltd for $18 000. Numbat Ltd had not charged any depreciation on the plant before the sale. Both entities depreciate assets at 10% p.a. on cost.
(b) On 1 January 2017, Goanna Ltd sold a new tractor to Numbat Ltd for $30 000. This had cost Goanna Ltd $24 000 on that day. Both entities charged depreciation at the rate of 10% p.a. on cost.
(c) On 1 July 2018, Numbat Ltd sold an item of machinery to Goanna Ltd for $9 000. This item had cost Numbat Ltd $6 000. Numbat Ltd regarded this item as inventory whereas Goanna Ltd intended to use it as a non-current asset. Goanna Ltd charges depreciation at the rate of 10% p.a. on cost.
(d) In February 2018, Numbat Ltd sold inventory to Goanna Ltd for $9000, at a mark-up of 20% on cost. One-quarter of this inventory was unsold by Goanna Ltd at 30 June 2018. (e) Goanna Ltd sold land to Numbat Ltd in December 2018. The land had originally cost Goanna Ltd $20 000 but was sold to Numbat Ltd for only $16 000. To help Numbat Ltd pay for the land, Goanna Ltd gave Numbat Ltd an interest-free loan of $9 000, and the balance was paid in cash. Numbat Ltd has as yet made no repayments on the loan.
(f) On 1 July 2017, Goanna Ltd rented a spare warehouse to be used jointly by Numbat Ltd and Galah Ltd with each company paying half the agreed rent to Goanna Ltd. The rent paid to Goanna Ltd in the 201718 year was $300 while the rent paid in the 201819 year was $350.
Question 11.4 Intragroup transactions
Emu Ltd owns all of the shares of Cassowary Ltd. In relation to the following intragroup transactions, all parts of which are independent unless specified,prepare the consolidation worksheet adjusting entries as at 30 June 2019. Assume an income tax rate of 30%.
(a) Emu Ltd sold inventory to Cassowary Ltd on 1 September 2018 for $27 000. This inventory had cost Emu Ltd $18 000. One-third of the inventory was sold by Cassowary Ltd to Goanna Ltd for $13 000 and one-third to Galah Ltd for $13 200.
(b) Emu Ltd manufactures certain items which it then markets through Cassowary Ltd. During the current period, Emu Ltd sold items for $18 000 to Cassowary Ltd at cost plus 20%. Cassowary Ltd has sold 75% of these transferred items at 30 June 2019.
(c) During June 2019, Cassowary Ltd declared a $2 000 dividend. The dividend was paid in August 2020.
(d) In January 2019, Cassowary Ltd paid a $4 500 interim dividend.
(e) Emu Ltd sold a warehouse to Cassowary Ltd for $150 000. This had originally cost Emu Ltd $123 000. The transaction took place on 1 January 2018. Cassowary Ltd charges depreciation at 5% p.a. on a straight-line basis.
Question 11.5 Intragroup transactions
Platypus Ltd owns all of the share capital of Wallaby Ltd. In relation to the following intragroup transactions, all parts of which are independent unless specified,prepare the consolidation worksheet adjusting entries as at 30 June 2019. Assume an income tax rate of 30%.
(a) During the year ending 30 June 2019, Wallaby Ltd sold $55 000 worth of inventory to Platypus Ltd. Wallaby Ltd recorded an $8 000 profit before tax on these transactions. At 30 June 2019, Platypus Ltd has one-quarter of these goods still on hand.
(b) Platypus Ltd manufactures items of machinery which are used as property, plant and equipment by other companies, including Wallaby Ltd. On 1 January 2019, Platypus Ltd sold such an item to Wallaby Ltd for $52 000, its cost to Platypus Ltd being only $45 000 to manufacture. Wallaby Ltd charges depreciation on these machines at 20% p.a. on the diminishing balance.
(c) A non-current asset with a carrying amount of $1 200 was sold by Wallaby Ltd to Platypus Ltd for $900 on 1 January 2019. Platypus Ltd intended to use this item as inventory, being a seller of second-hand goods. Both entities charged depreciation at the rate of 10% p.a. on the diminishing balance on non-current assets. The item was still on hand at 30 June 2019.
(d) Platypus Ltd issued 1 000 10?bentures of $100 at nominal value on 1 October 2018. Wallaby Ltd acquired 300 of these. Interest is payable half-yearly on 31 March and 30 September. Accruals have been recognised in the legal entities accounts.
(e) On 25 June 2019, Platypus Ltd declared a dividend of $8 000. On the same day, Wallaby Ltd declared a $4 000 dividend.
Module 3 Non-controlling interest
Question 12.1 Full and partial goodwill methods
On 1 July 2019, Rainbow Ltd acquired 80% of the issued shares of Lorikeet Ltd for $165 000. At this date, the equity of Lorikeet Ltd was

At acquisition date all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Lorikeet Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to fair value. At 30 June 2021, the equity of Lorikeet Ltd consisted of:

During the 20202021 year Lorikeet Ltd recorded a profit of $15 000.
Required
Calculate the goodwill and prepare the consolidated worksheet journal entries at 1 July 2019 and 30 June 2021 for Rainbow Ltd assuming:
(a) At 1 July 2019, the fair value of the non-controlling interest was $40 000 and Rainbow Ltd adopts the full goodwill method.
(b) Rainbow Ltd adopts the partial goodwill method.
Question 12.2 Full goodwill and partial goodwill methods
Swamp Ltd acquired 90% of the shares (cum div.) of Tortoise Ltd on 1 July 2018 for $237 000. At this date, the equity of Tortoise Ltd consisted of:
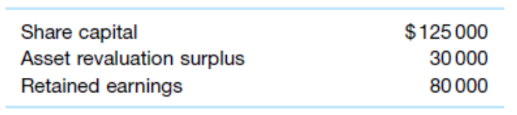
At acquisition date all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Tortoise Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to fair value. Tortoise Ltd had recorded a dividend payable of $10 000, which was paid in August 2018, and goodwill of $5000.
At 30 June 2019, the equity of Tortoise Ltd consisted of:

During the 201920 year Tortoise Ltd recorded a profit of $20 000.
Required:
Calculate the goodwill and prepare the consolidated worksheet entries at 1 July 2018 and 30 June 2020 for Swamp Ltd assuming:
(a) At 1 July 2018, the fair value of the non-controlling interest was $25 000 and Swamp Ltd adopts the full goodwill method.
(b) Swamp Ltd adopts the partial goodwill method.
Question 12.3 Partial goodwill method, gain on bargain purchase
Black Ltd acquired 90% of the shares of Swan Ltd for $107 600 on 1 July 2019. At this date the equity of Swan Ltd consisted of:

At acquisition date all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Swan Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to fair value.
At 30 June 2020, the equity of Swan Ltd consisted of:

During the 201920 year Swan Ltd recorded a profit of $15 000. The transfer to general reserve was from retained earnings existing at 1 July 2019.
Required
Calculate the goodwill at 1 July 2019 and prepare the consolidated worksheet entries 1 July 2019 and at 30 June 2020 for Black Ltd assuming Black Ltd adopts the partial goodwill method.
Question 12.5 Partial and full goodwill methods
On 1 July 2019 Sugar Ltd acquired 90% of the shares of Glider Ltd for $435 240. At this date the equity of Glider Ltd consisted of share capital of $300 000 and retained earnings of $120 000. All the identifiable asset and liabilities of Glider Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to fair value except for:
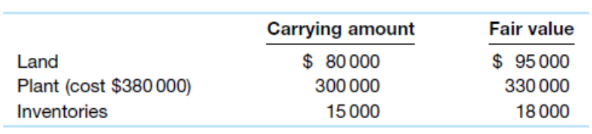
The plant was considered to have a further 10-year life. All the inventory was sold by 30 June 2020. The tax rate is 30%. Sugar Ltd uses the partial goodwill method.
During the 201920 period Glider Ltd recorded a profit of $30 000.
Required
(a) Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries for the preparation of the consolidated financial statements of Sugar Ltd at 30 June 2020.
(b) Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries if Sugar Ltd used the full goodwill method, assuming the fair value of the non-controlling interest at 1 July 2019 was $47 700.
Module 4 Associates and joint ventures
- What is an associate entity? (LO1)
- Discuss the similarities and differences between the criteria used to identify subsidiaries and that used to identify associates. (LO1)
- What is meant by significant influence?
Question 14.1 Adjustments where investor prepares and does not prepare consolidated financial statements
Piano Ltd has a 30% interest in a joint venture, Mandolin Ltd, in which it invested $50 000 on 1 July 2017. The equity of Mandolin Ltd at the acquisition date was:

All the identifiable assets and liabilities of Mandolin Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to their fair values. Profits and dividends for the years ended 30 June 2018 to 2020 were as follows:

Required
(a) Prepare journal entries in the records of Piano Ltd for each of the years ended 30 June 2018 to 2020 in relation to its investment in the joint venture, Mandolin Ltd. (Assume Piano Ltd does not prepare consolidated financial statements.)
(b) Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries to account for Piano Ltds interest in the joint venture, Mandolin Ltd. (Assume Piano Ltd does prepare consolidated financial statements.)
Question 14.2 Accounting for associate/joint venture by an investor
Violin Ltd acquired a 40% interest in Drum Ltd in which it invested $170 000 on 1 July 2018. Violin Ltd has signed a joint venture agreement with the other investors in Drum Ltd providing joint control to all investors. The share capital, reserves and retained earnings of Drum Ltd at the investment date and at 30 June 2019 were as follows:

At 1 July 2018, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Drum Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to their fair values.
The following is applicable to Drum Ltd for the year to 30 June 2019:
(a) Profit (after income tax expense of $11 000): $39 000
(b) Increase in reserves
- General (transferred from retained earnings): $15 000
- Asset revaluation (revaluation of freehold land and buildings at 30 June 2019): $100 000 (c) Dividends paid to shareholders: $15 000.
Violin Ltd does not prepare consolidated financial statements.
Required:
Prepare the journal entries in the records of Violin Ltd for the year ended 30 June 2019 in relation to its investment in the joint venture, Drum Ltd.
Question 14.3 Inter-entity transactions where investor has no subsidiaries
Lute Ltd acquired 20% of the ordinary shares of Sitar Ltd on 1 July 2017. At this date, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Sitar Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to their fair values. An analysis of the acquisition showed that $2 000 of goodwill was acquired. Sitar Ltd was judged to be an associate of Lute Ltd.
Lute Ltd has no subsidiaries, and records its investment in the associate, Sitar Ltd, in accordance with AASB 128/IAS 28. In the 201819 period, Sitar Ltd recorded a profit of $100 000, paid an interim dividend of $10 000 and, in June 2019, declared a further dividend of $15 000. In June 2018, Sitar Ltd had declared a $20 000 dividend, which was paid in August 2018, at which date it was recognised by Lute Ltd. The tax rate is 30%.
The following transactions have occurred between the two entities (all transactions are independent unless specified).
(a) In January 2019, Sitar Ltd sold inventory to Lute Ltd for $15 000. This inventory had previously cost Sitar Ltd $10 000 and remains unsold by Lute Ltd at the end of the period. (b) In February 2019, Lute Ltd sold inventory to Sitar Ltd at a before-tax profit of $5 000. Half of this was sold by Sitar Ltd before 30 June 2019.
(c) In June 2018, Sitar Ltd sold inventory to Lute Ltd for $18 000. This inventory had cost Sitar Ltd $12 000. At 30 June 2018, this inventory remained unsold by Lute Ltd. However, it was all sold by Lute Ltd before 30 June 2019.
Required:
Prepare the journal entries in the records of Lute Ltd in relation to its investment in Sitar Ltd for the year ended 30 June 2019.
Question 14.5 Accounting for an associate across two years with inter-entity transactions
On 1 July 2018, Key Ltd acquired 25% of the shares of Board Ltd for $400 000. The acquisition of these shares gave Key Ltd significant influence over Board Ltd. At this date, the equity of Board Ltd consisted of:
At 1 July 2018, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Board Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to their fair values except for:

The plant was considered to have a further useful life of 5 years. The land was revalued in the records of Board Ltd and the revaluation model applied in the measurement of the land. The tax rate is 30%.
At 30 June 2020, Board Ltd reported the following information:
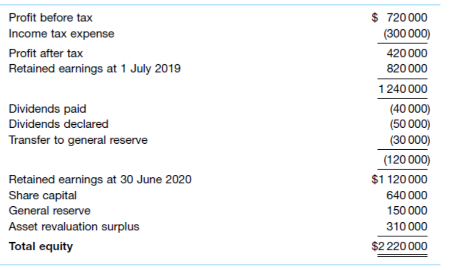
Board Ltd also reported other comprehensive income relating to gains on revaluation of land of $10 000. Assume also that the following inter-entity transactions occurred.
(a) On 1 July 2019, Key Ltd holds inventory sold to it by Board Ltd at an after-tax profit of $20 000. This inventory was all sold to external entities by 30 June 2020.
(b) During the 201920 period, Board Ltd sold inventory to Key Ltd for $100 000 recording an after-tax profit of $15 000. One-third of this inventory is still held by Key Ltd at 30 June 2020.
(c) On 1 January 2019, Board Ltd sold a vehicle to Key Ltd for $40 000. The vehicle was recorded at a carrying amount of $38 000 by Board Ltd at the date of sale. The vehicle is estimated to have a further 2-year life.
(d) From 1 July 2018, Key Ltd rented a warehouse from Board Ltd and paid rent of $15 000 p.a., the rent being paid in advance each year.
Required
Prepare the journal entries for inclusion in the consolidation worksheet of Key Ltd at 30 June 2020 for the equity accounting of Board Ltd.
Module 5 Segment reporting
The following segment information is presented for Manny Ltd:
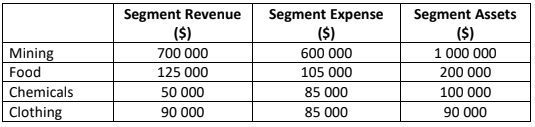
Required:
Determine which segments are reportable according to the guidelines provided in AASB 8Operating Segments.

