Analysing the Influence of Microeconomic and Macroeconomic Components on Organizational Behavior and Addressing Global Issues: A Case Study of Tesco
Task 1:
Introduction
This report presents a detailed assessment of two prominent international businesses: Shein, an online fast-fashion retailer, and Tesco, one of the largest retail supermarket chains in the UK. The analysis focuses on each organization's legal structure, purpose, stakeholder influences, and environmental pressures, specifically emphasizing challenges following the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the report explores how digitisation has impacted each organisations decision-making, structure, and strategy, illustrating the crucial role of technology in modern businesses.
Organization 1: Tesco
1. Legal Structure:
Tesco is a public limited company (PLC), which means its shares are traded on the London Stock Exchange and owned by a diverse group of public shareholders. This structure allows Tesco to raise capital from the public, supporting its expansion and innovation efforts (Tesco PLC, TSCO: LSE SummaryFT.com, 2024).
2. Purpose:
Tesco aims to provide affordable, quality products to customers, aiming for value and convenience. Its mission is to be the customers champion, helping them enjoy a better quality of life through products that are both accessible and affordable. The vision is to be the most trusted retailer, with a focus on customer satisfaction, sustainable growth, and responsible business practices (Gavrilescu, 2023).
3. Stakeholders:
Tescos stakeholders include shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and the government. Each group has distinct needs and influences:
Shareholders seek profitability and returns on their investments.
Employees look for fair wages, job security, and growth opportunities.
Customers desire quality products, affordable prices, and convenience.
Suppliers depend on fair trade practices and timely payments.
Communities expect Tesco to operate responsibly and contribute to local welfare.
Government stakeholders require Tesco to comply with regulations and contribute to economic stability. Mapping stakeholder priorities is essential in addressing responsibilities and ensuring the companys actions align with both business and societal expectations (Rahman, 2023).
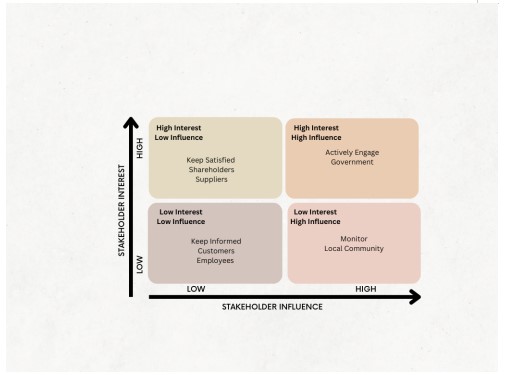
Figure 1: Tesco Stakeholder Mapping
(Self-illustrated)
4. Key Environmental Pressure:
Tesco faces competitive pressures from other retailers and the demand for sustainable practices. With a large carbon footprint and complex supply chain, Tesco is under pressure to implement environmentally responsible practices to reduce waste and carbon emissions (Chan, 2024).
5. Post-COVID-19 Challenges:
The COVID-19 pandemic led to significant operational disruptions for Tesco. It faced increased demand for online services, stricter health protocols, and supply chain bottlenecks. Additionally, it encountered staffing challenges, particularly as demand surged for certain essential items. Adapting to these changes required agile strategies to maintain product availability and manage costs (Khodoomi et al., 2023).
6. Use of Technology:
Tesco has integrated technology across its operations, from inventory management and online shopping to customer engagement. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics help Tesco analyse customer purchasing patterns, predict demand, and optimize stock levels. The introduction of self-checkout stations and online shopping platforms has improved customer convenience and streamlined store operations, showcasing how digitization enables more efficient, data-driven decision-making (Technology, 2023).
7. Leadership and Management Theories:
Tescos leadership strategy aligns with transformational leadership, emphasising change, and innovation to maintain competitive advantage. Transformational leaders inspire and motivate employees to embrace change, particularly in challenging retail environments. From a management perspective, Tesco incorporates systems theory, which views the organisation as an interconnected system where each part affects the whole (Kar et al., 2021).
8. Leadership Type:
Tesco's leadership style is largely transformational. Leaders focus on inspiring teams, fostering a sense of purpose, and encouraging employee engagement. This approach is evident in initiatives to boost customer satisfaction and sustainability. Transformational leadership supports Tescos adaptability, fostering an environment where employees are motivated to contribute to the companys vision actively, thereby enhancing overall performance (Transformational Leadership in Tesco: Challenges, Learning, Requirements, and Cross-Cultural Leadership, 2024).
Organisation 2: Shein
1. Legal Structure:
Shein operates as a private company with a unique global supply chain model, which has allowed it to bypass traditional retail channels and sell directly to consumers. This private structure allows Shein to have significant control over its operations without the scrutiny faced by publicly traded companies (Bhargava, 2024).
2. Purpose:
Shein's primary purpose is to provide affordable, trendy fashion to a global audience. Its mission is to democratize fashion, making stylish and contemporary apparel accessible to people worldwide at low prices. The vision is to become the worlds leading online fashion destination by combining affordability, style, and convenience (Marketing, 2024).
3. Stakeholders:
Sheins stakeholders include its customers, employees, suppliers, logistics partners, governments, and communities where it operates.
Customers seek trendy, affordable clothing with fast delivery.
Employees look for job security and fair wages.
Suppliers and logistics partners require efficient collaboration and fair payment practices.
Governments expect regulatory compliance, especially with trade and labor laws.
Community is concerned with the environmental and ethical implications of Sheins fast-fashion model.
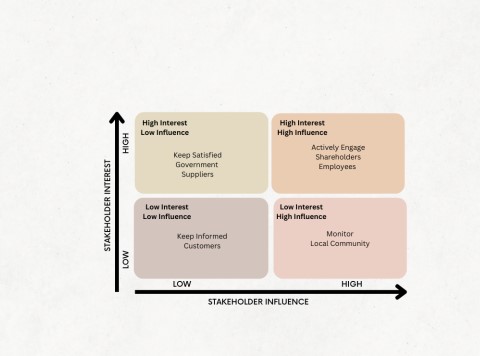
Figure 2: Shein Stakeholder mapping
(Source: Self-illustrated)
4. Key Environmental Pressure:
Shein faces scrutiny over its environmental practices due to the fast-fashion industrys reputation for waste and pollution. There is increasing pressure from both regulators and consumers for Shein to adopt sustainable practices, including reducing textile waste and enhancing transparency in sourcing.
5. Post-COVID-19 Challenges:
During the pandemic, Shein experienced supply chain delays and an increased demand for e-commerce. Like many businesses, it had to adapt quickly to logistical challenges and ensure the safety of employees in distribution centers. The companys reliance on international supply chains also exposed it to fluctuating costs and regulatory changes, necessitating agile operational adjustments (Qu, 2024).
6. Use of Technology:
Shein relies heavily on digital technology to drive its operations, from AI-powered trend analysis to targeted digital marketing. The company uses big data to identify fashion trends in real-time, enabling it to bring designs to market in a matter of weeks. Additionally, Shein has developed an efficient digital supply chain, where technology tracks manufacturing and shipping, ensuring low production costs and fast delivery (Qu, 2024).
7. Leadership and Management Theories:
Shein exemplifies transactional leadership, where leaders focus on structured processes and direct rewards for achieving specific goals. Given the company's focus on efficiency and scalability, transactional leadership aligns well with its operational goals. Shein also employs scientific management theory principles to optimize productivity through standardization and process efficiency, critical for managing its large-scale, fast-paced supply chain (Dong, 2023).
8. Leadership Type:
Sheins leadership style is transactional. Leaders emphasize meeting production and sales targets, and there is a strong focus on efficiency and productivity. This approach supports Shein's growth in a highly competitive market, allowing it to quickly adapt to trends and scale operations effectively (Ucha?ska-Bieniusiewicz & Ob?j, 2023).
Part 2: Microeconomic and Macroeconomic Impact on Tesco
1. Microeconomic Analysis of Tesco:
SWOT Analysis: Tesco's strengths include brand loyalty, extensive market presence, and strong supply chain management. Its weaknesses include reliance on the UK market and thin profit margins. Opportunities lie in expanding its online grocery services and adapting to sustainable practices, while threats stem from intense competition and fluctuating consumer trends (Pereira, 2023).
Porters Five Forces: Key forces influencing Tesco are high buyer bargaining power due to many retail options and intense competition within the supermarket industry. Additionally, the threat of substitutes is high, with many competitors offering similar products. The bargaining power of suppliers is moderate, as Tesco works with a diverse supplier base to mitigate dependency risks (Strategic Management: Analysis of Porters Five Forces Model for Tesco, 2023).
Value Chain Analysis: Tescos most valuable activities are its supply chain and logistics. By optimizing these, Tesco can minimise costs and improve product availability, enhancing customer satisfaction.
PESTEL Analysis: Politically, Tesco must navigate regulations around labor and competition in the UK. Economically, it is influenced by fluctuating consumer purchasing power and inflation. Socially, changing consumer preferences and demand for ethical practices shape Tesco's strategies. Technologically, innovations like online shopping platforms are integral, while environmental factors push Tesco towards sustainable practices (Shaw, 2024).
2. Macroeconomic Analysis of Tesco:
Tesco faces the challenge of balancing affordable pricing with the rising cost of resources and labor, impacting its ability to meet consumer demand affordably. Consumer demand for essential goods remains stable; however, fluctuations in demand for non-essential items affect inventory and pricing strategies. Tesco operates in an oligopolistic market, characterized by a few large competitors.
Global Issues:
Two critical global issues affecting Tesco are sustainability and ethical supply chain management. Tesco has implemented policies to reduce plastic use and support fair labor practices, reflecting its commitment to environmental and social responsibility. As consumer expectations continue to evolve, addressing these global issues will be crucial for maintaining Tescos market reputation and fostering long-term growth.
Task 2:
Key Components of Microeconomics and Macroeconomics in Organizational Behavior and National Economy
Microeconomics: The Theory of Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are one of the fundamental components of microeconomic theory, which explains how prices are determined in the market and how organisations would modify their own production and pricing strategies according to the behavior of consumers (Pinkasovitch, 2024). It largely impacts organisational behavior, especially in retail industries like Tesco, where operational adjustments are driven based on changes in demand. When the demand for goods from customers becomes high, Tesco increases its stock holding, reduces the chances of running out of stock, and can also increase its price to show that the demand is high. During low demand times, Tesco may offer a discount to attract sales. On the national level of the economy, supply and demand affect the distribution, production level, and economic stability. Demand across multiple sectors drives job creation and consumer spending with economic growth. Conversely, when demand declines, production slows, affecting employment rates and potentially leading to economic contraction (Fukase & Martin, 2020).
Macroeconomics: The Theory of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy, another essential component of macroeconomic theory, refers to government decisions on spending and taxation to influence the economy. Through fiscal policy, the government can stimulate economic growth during a recession or curb inflation during periods of excessive growth (Hayes, 2024). For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many governments increased spending on healthcare and social welfare programs while providing financial aid to businesses, including retailers like Tesco. Fiscal policy impacts organizational behavior by affecting disposable income, consumer spending patterns, and organizational costs (Hayes, 2024).
In Tesco's case, an increase in disposable income due to tax cuts can lead to higher consumer spending and drive sales. Conversely, higher corporate taxes can lead Tesco to streamline operations, reduce expenses, or re-evaluate expansion plans. Fiscal policy also plays a significant role in employment, as government-funded programs and tax incentives encourage organisations to create jobs.
Global Issues: Cultural Diversity and Ethical Decision-Making
1. Cultural Diversity
In a globalised world, organisations like Tesco operate in diverse markets, employing people from different cultural backgrounds and serving customers with diverse preferences. Effective management of cultural diversity at work increases employee well-being, innovation, and customer relationships (Ponomareva et al., 2022). Tesco has implemented inclusive practices to accommodate the diversity of the workforce. For example, diversity training programs help to create an inclusive work environment whereby employees have a sense of value and worth.
Cultural diversity management is not just the benefit of Tesco but also has wider social impacts. It promotes social cohesion, reduces bias, and encourages businesses to play a role in addressing problems of inequality (Raithel et al., 2021). Diversity is thus an economic issue at the level of the nation because it has positively affected creativity, productivity, and more importantly, the competitiveness of the workforce (Raithel et al., 2021).
2. Ethical Decision-Making
Ethical decision-making has becomeanimportantelementforsustainingpublic trust and meeting the regulatory standardsoforganisations. In an era where consumers are increasingly aware of social and environmental issues, businesses are expected to demonstrate responsibility in their practices (Joseph, 2020). Tesco has faced ethical challenges, including criticism over labor practices and environmental impact, and has responded by implementing policies aimed at transparency, fairness, and sustainability. Ethical decision making also has economic implications. Organizations that adopt ethical practices can avoid costly regulatory penalties, enhance brand reputation, and gain competitive advantages (Casali & Perano, 2020).
Tescos Approach to Managing Cultural Diversity and Ethical Decision-Making Cultural Diversity in Practice
Tescos approach to cultural diversity goes beyond mere compliance; it actively seeks to foster inclusivity and representation within its workforce. By implementing diversity training and inclusive hiring practices, Tesco promotes a work environment where employees of different backgrounds feel respected and valued. The company's leadership recognizes that a diverse workforce brings unique perspectives, which can enhance creativity, problem-solving, and employee morale (Tothld, 2023). On the customer side, Tesco tailors its product range to cater to the cultural preferences of various demographics, ensuring that its offerings resonate with local communities. These initiatives help Tesco establish itself as a culturally aware brand, which strengthens its market position and aligns with the expectations of a globalized consumer base (Tothld, 2023).
Ethical Decision-Making in Practice
Tesco's ethical promise is quite visible in its programs about sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR). For instance, Tesco has progressed significantly toward minimising environmental effects by reducing plastic packaging and restraints on greenhouse gas emissions. It has set ambitious goals, like attaining net zero by 2050 and bringing its long-term strategies in line with global standards for the environment (Pereira, 2023). Additionally, Tesco involves itself in ethical sourcing for the support of fair labor practices; hence, the company works closely with its suppliers while ensuring that they maintain standards on fair wages, as well as safety in their working conditions. Tesco transparently reports on its initiatives of CSR, which then enhances the confidence of consumers and accountability (VanDerHeyden, 2024).
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

