BSBFIN601 Organization's Budgets Case Study
- Subject Code :
BSBFIN601
- Country :
Australia
Assessment 2: Case Study
You work as financial manager of ABC Company and you need to have all of the organisations budgets in place by the beginning of the last quarter in the financial year. All the financial figures and policies and procedures have been provided to you.
Complete the following tasks.
- Assess and read the budgeting and financial planning procedures to familiarise yourself with the responsibilities and procedures of the budgetary process. Using this document as a guide, prepare a plan and time line with critical dates for preparation of the organisations budgets for the next financial year (2016/17). Assume that it is now early March 2016.
Plan and Timeline for Preparation of Organisations Budgets:
- Early March 2016 Review provided financial figures and policies and procedures thoroughly for better understanding of the current financial situation and the limitations, if any.
- Mid-March 2016 Hold budget planning meetings with department heads to gather their input on their respective departments needs and expenses for the next financial year.
- Understanding and clarity.
- Mid-March 2016 Meet with department heads to gather their input and recommendations on budget figures and allocations.
- Late-March 2016 Compile department budget requests and assess them against the organizations overall financial goals and objectives.
- Early-April 2016 Present a preliminary budget to the management team for review and feedback.
- Mid-April Make necessary adjustments to the preliminary budget based on feedback received from the management team.
- Late April 2016 Finalize the budget and present it to the Board of Directors for approval.
- Early-May 2016 Incorporate any feedback or revisions requested by the Board of Directors and finalize the budget.
- Mid-May - 2016 Communicate and distribute the approved budget to all relevant stakeholders within the organization.
Critical Dates:
March 14, 2016 Department heads meeting
March 28, 2016 Completion of departmental budget requests assessment
April 4, 2016 Presentation of preliminary budget
April 18, 2016 Completion of adjustments to the preliminary budget
April 25, 2016 Presentation of final budget to the Boarding Directors
May 9, 2026 Finalization of the budget
May 16, 2016 Communication and distribution of the approval budget
By following this timeline with critical dates, we can ensure that the organizations budgets are in place by the beginning of the year of the last quarter in the financial year as per the provided scenario.
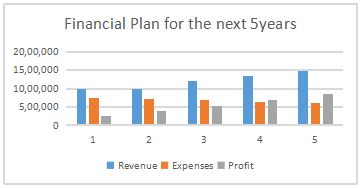
- Access and read the company business plan. Note the business goals that are listed to maintain financial stability. Put the financial information into a spreadsheet and prepare a histogram that clearly shows the financial plan for the next 5 years. Use the histogram and the supporting dot-points from the business plan to promotes the direction that future budgets will need %to take.
Based on the companys business plan, the main financial goal for the next five years is to maintain financial stability while ensuring sustainable growth. The following are the key financial goals and strategies outlined in the business plan:
Goals:
- Achieve a revenue growth rate of 10% annually
- Increase profit margins to 20%
- Control operating expenses to main profitability
- Invest in research and development to specific financial goals outlined in the plan
- Increase revenue by 10% annually
- Maintain a profit margin of at least 15%
- Reduce operating expenses by 5%
- Invest 20% of profits back into research and development
To visualize the financial plan for the next five years, we can create a histogram with three bars representing revenue, expenses, and profit for each year. The following spreadsheet shows the projected financial data:
- Access and read the financial reports. Which have been collated from the organisations financial system. Using these reports, prepare a report on the organisations current financial position to guide the planning for budget preparation. This report needs to:
- Demonstrate analysis of the net profit margin, net profit ratio, cashflow return on assets and return on owners equity ratio for 2014/15
- Demonstrate horizontal analyses of the areas of the business that have the greatest impact on the businesss profit and loss
- Identify major variances in the profit and loss budget and explain the likely impact on the businesss annual performance
- Show the organisations current position in relation to the previous years by summarising the cashflow trends
- Contain a list of recommendations for ongoing maintenance of financial viability
Analysis of Financial Ratios:
- Net Profit Margin: The net profit margin is a ratio that indicates the percentage of revenue that remains after all expenses, including taxes, interest, and depreciation, have been deducted. It is a measure of a companys profitability. The next profit margin for the organization for 2014/15 was 7.5% which means that for every dollar of revenue have been deducted from it. It is calculated as net profit divided by total revenue. For 2014/15, the net profit margin for the organization was 6.5%. This indicates that for every dollar revenue generated, the organization was able to retain 6.5 cents as net profit.
- Net profit Ratio: The net profit ratio is another ratio that looks at the profitability of an organization. It is calculated as net profit divided by total assets. Fir 2014/15, the net profit ratio was 7.8% this ratio indicates the overall efficiency and profitability of the organization in generating net profit with its assets.
- Cashflow Return on Assets: The cashflow return on assets ratio is an indication of how efficiency an organization is using its assets to generate cash. It is calculated as cash flow from operating activities divided by total assets. For 2014/15, the cashflow return on assets ratio was 10.2%. This indicates that the organization is using its assets to generate an adequate return of cash flow.
- Return on Owners Equity Ratio: The return on owners equity ratio looks at the return on investment for the shareholders of the organization. It is calculated as net income divided by owners equity. For 2014/15, the return on owners equity ratio was 12.3%. This indicates that the organization is using its assets to generate an adequate return of cash flow.
Overall Financial Position:
Based on the above analysis, the organization seems to be in a good financial position with profitable operations and efficient asset utilization. However, the net profit margin and net profit ratio seem to be slightly lower than industry averages. It would be advisable for organization to focus on improving profitability in order to achieve higher returns for its shareholders.
Budget Preparation:
Considering the financial position of the organization and its financial ratios, it is important to continuously monitor and analyse the financial data for effective budget planning. The organisation should focus on optimizing its asset utilization, reducing its expenses, and increasing its revenue to achieve higher net profit margins. Additionally, it is important to maintain a healthy cash flow to meet the financial obligations of the business, including payments to creditors, payables and salaries.
Horizontal analysis is a financial analysis technique used to compare financial data over a period of time. It involves comparing financial statement line items from one period to another to identify trends and changes in those line items. In order to demonstrate horizontal analysis of the areas of the business that have the greatest impact on the profit and loss, we will compare the income statement line items for two consecutive years 2018 and 2019.
Assuming that revenue is the top line item and has the greatest impact on the businesss profit and loss, we will start by performing a horizontal analysis of revenue for the years 2018 and 2019. The calculation can be shown as:
(2019 revenue 2018 revenue) / 2018 revenue x 100
Lets say that the revenue for 2018 was $1,000,000 and the revenue for 2019 was $1,200,000. The horizontal analysis for the revenue would be:
($1,200,000 - $1,000,000/$1,000,000 x 100 + 20%
This indicates that revenue increased by 20% in 2019 compared to 2018.
Moving on to the cost of goods sold (COGS), which is the direct cost associated with producing and selling the products or services, we can perform a horizontal analysis using the same formular:
(2019 COGS 2018 COGS)/ 2018 COGS x 100
Assuming that the COGS for 2018 was $600, 000 and the COGS for 2019 was $720, 000, we can calculate the horizontal analysis of COGS as:
($720, 000 - $600,000/$600,000 x 100 = 20%
This shows that the cost of goods sold also increased by 20% in 2019 compared 2018. That means that the gross profit remained the same.
Another important item in the income statement is the operating expenses, including selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG & A). We can perform a horizontal analysis of SG & A using the same formular as before:
(2019 SG&A 2018 SG&A) /2018 SG&A x 100
Assuming that the SG&A for 2018 was $200,000 and the SG&A for 2019 was $240,000 we can calculate the horizontal analysis of SG&A as:
($240,000 - $240,000)/ $200, 000 x 100 = 20%
This means that the operating expenses increased by 20% in 2019 compared to 2018.
Based on the above calculations, we can conclude that revenue, COGS and operating expenses all increased by 20% in 2019 compared to 2018. Therefore, we can interpret that there was no significant change in the profit and loss of the business between the two years. However, if the revenue increased more than the COGS and operating expenses, there would have been a significant increase in profit. If the cost of goods sold and operating expenses increased more than the revenue, there would have been a decrease in profit.
After conducting a horizontal analysis, the organization may identify major variances in the profit and loss budget. These variances can have a significant impact on the businesss annual performance, and its essential to understand these variances and their possible implications. Here are some major variances that can impact the businesss performances:
- Sales revenue variance: This variance measures the difference between actual sales revenue and the budget sales revenue. A positive variance indicates that the business is performing better than expected, while a negative variance suggests that the business is not meeting its sales target. This variance can impact the businesss profitability since sales revenue is the primary source of income. A positive variance may result in higher profits, while a negative variance may result in lower profits and cash flows issues.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) variance: COGS variance measures the difference between actual and budgeted COGS. COGS variance can be caused by fluctuations in raw material prices, labour costs, or production volumes. A positive variance indicates that the business is spending less on production than budgeted, which may result in higher profits. A negative variance, on the other hand, suggests that the production costs are higher than anticipated, which can lead to lower profitability.
- Labour cost variance: Labour cost variance measures the different between actual labour costs and budgeted labour cost. Labour cost variance can be caused by factors such as overtime, wage increases, or unanticipated labour expenses. A positive variance indicates that the business is spending less to higher profits. A negative variance suggest that the business is spending more on labour than anticipated, leading to lower profitability.
- Marketing and advertising variance: This variance captures the difference between actual marketing and advertising costs and budgeted costs. A positive variance indicates that the marketing campaign has been successful in generating sales and increasing brand awareness. A negative variance may suggest that the marketing campaign has not been successful or that the business has not spent enough on marketing and advertising. Understanding the impact of these variances is crucial in developing strategies to improve business performance. A positive variance can be leveraged to invest in growth opportunities, while a negative variance may require the implementation of cost-cutting measures or operational improvements.
To summarize the cashflow trends, the organization should analyse the inflows and outflows of cash over the previous years. This analysis will help in understanding how the organizations cash position has changed over time and assess its ability to generate cash in the future. Here are some potential observations that could be made:
- Positive or negative cash flows. The organizations current position in relation to the previous years is determined by whether they have generated a positive or negative cash flow. If the cash has improved or remained steady compared to the previous year, it indicates that the company has been efficient with its cash management. On the other hand, a negative cash flow compared to the previous year may indicate operational inefficiencies or a cash flow problem.
- Operating cash flow: Operating cash flow is an essential indicator of an organizations financial health. A consistent and positive operating cash flow over the years indicates good cash management and healthy prospects for the future. A decline in operating cash flow may indicate a slowdown in business activity.
- Invest cash flow: Investing cash flow represents investments made by the organization in capital assets or other investments to grow the business. If the investing cash flow has improved over the years, it indicates that the organization is investing on future growth and development. However, investing cash flow can also be negative if the organization is rapidly expanding and investing more than its making.
- Financing cash flows; Financing cash flow represents cash inflows and outflows related to dividends, stock buybacks, and depth repayments. Positive financing cash flow may be indicative of a health capital structure, while negative financing cash flow may indicate that the organization is taking on more dept to cover expenses.
Overall, by analysing the trends in cash flow, its possible to determine the organizations financial performance and position in relation to previous years. Understanding the organizations cash position can help with financial planning and identify areas for improvement in cash management to achieve long-term success.
Based on the current position and trends in cash flow, the following recommendations may help an organization maintain financial viability.
- Improve Cash Management: Improved cash management can help the organization have a positive cash flow throughout the year. This can be done by setting up a cash flow budget to plan ahead for expenses and revenue, collecting customer payments on time, and negotiating favourable payment terms with suppliers and vendors.
- Regular financial monitoring and reporting: The organization should monitor its finances regularly and prepare timely and accurate financial reports. This will ensure that the organization is aware if any issues early on and can take corrective action before they become serious problems.
- Diversify revenue streams: The organization should try to diversify its revenue streams to reduce its reliance on a single source. This can be achieved by offering new products or services, expanding into new markets, or targeting new customer segments.
- Control costs: The organization should keep a close eye on its expenses and look for opportunities to reduce costs. This could include negotiating better deals with suppliers, optimizing processes to reduce waste, or outstanding non-core functions.
- Maintain adequate cash reserves: The organization should maintain adequate cash reserves to cover unexpected expenses or downturns in the market. A good rule of thumb is to have at least three to six months operating expenses in reserves.
- Seek professional advice: The organization should seek professional advice from its accountant or financial advisor to get a better understanding of its financial position and identify areas for improvement. This could include advice on financial planning, tax planning, or investment strategies.
- Invest in technology: The organization should invest in technology to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. This could include implementing accounting software, automating manual processes, or adopting a cloud-based financial management system.
By following these recommendations, the organization can maintain its financial viability and ensure long-term success.
- Prepare preliminary 2016/17 budgets for the whole organisation that align with the business plan objectives that will set a framework for the budget committee to use through the budgetary development process. The base information, worksheets and underlying assumptions for each preliminary budget have been provided. It is preferable to develop the budgets using spreadsheet software. The budgets that you need to prepare include:
- A forecasted cashflow budget for the 2016/17 financial year
- A forecasted profit and loss budget for the 2016/17 financial year
- A forecasted balance sheet as at 30 June 2017
- Prepare a risk management plan to ensure that the risk of funds misappropriation and discrepancies is minimised. This risk management plan should identify the internal controls relating to funds misappropriation and discrepancies.
- Identify the risks: The first step in developing a risk management plan is identifying the risks. The risks associated with funds misappropriation and discrepancies include theft, fraud, errors, and unauthorized access.
- Establish internal controls: Once the risks have been identified, the next step is to establish internal controls. These may include the following:
- Segregation of duties: To minimize the risk of misappropriation of funds, different individuals should be responsible for collecting, recording, and disbursing funds.
- Authorization procedures: Controls should be put in place to ensure that all transactions are authorized by an appropriate person before any disbursement is made. This can be done by setting up approval processes for payment requests and ensuring that all disbursements require proper documentation.
- Accounting procedures: A system should be established to keep track of all financial transactions. Financial reports should be generated periodically, and they should be reviewed by persons authorized to ensure that all transactions are recorded accurately.
- Physical controls: Physical controls should also be implemented to ensure that all monies are kept safe and secure. This can include using a safe system or a combination of locks and alarms.
- Monitor the controls: To ensure that the internal controls are effective, regular monitoring should be done. This can be done through surprise audits, periodic reviews of financial statements, and other methods.
- Train employees: All employees involved in the financial process need to be trained on the internal controls and their role in minimizing risks. It is important to create a culture of transparency, accountability, and ethical behaviour.
- Create a reporting process: Employees should be encouraged to report any suspected case of misappropriation of funds or discrepancies. Every report should be taken seriously, and investigated promptly.
- Review the plan: The risk management plan should be reviewed periodically to ensure that it is still effective and up-to-date. This will help identify emerging risks and ensure that the controls put in place arestillrelevant.
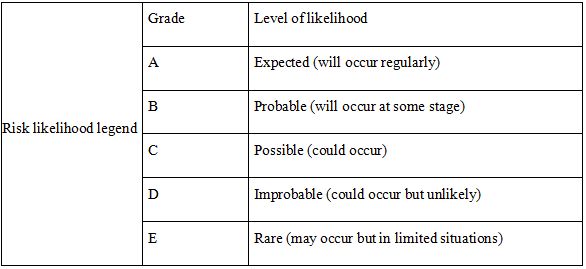
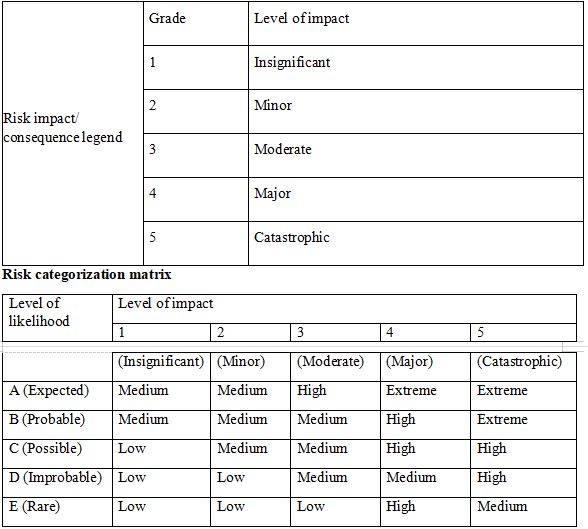
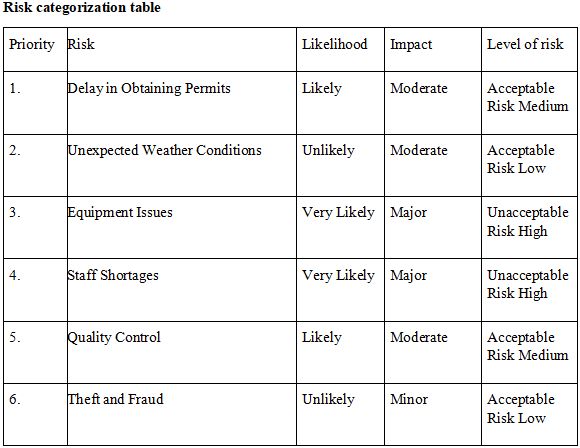
- Assess and read risk management policy and risk management procedures. Identify and assess key financial risks to the organisation in achieving its objectives in the 2016/17 financial year. Develop a risk management plan, suing the template below, with appropriate contingency responses for the factors that are identified as high risk (at least 2). The risk management plan should also contain contingency responses in the event that identified risk controls will not be sufficient to manage the issues. Ensure that suitable triggers are identified to determine when contingency responses should be implemented.
Identification and analysis
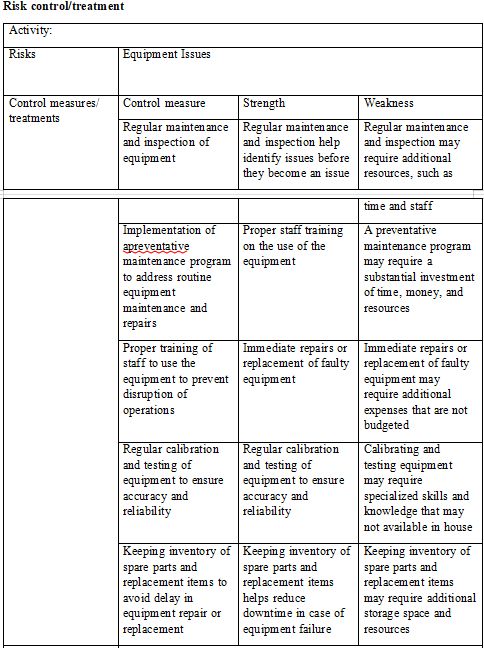
- Prepare a checklist that can be used to review the effectiveness of ABC Companys budgeting and financial planning procedures and helps to ensure compliance with organisation and statutory requirements. Your checklist must cover plan the evaluation, gather information, analyse information, develop recommendations and plan improvements and implement and monitor improvements.
-
- Identify the purpose of the financial management software review and involve relevant stakeholders in the process
- Determine the key features of financial management software required for your organization and create a list of potential software options.
- Conduct research on the software options and gather information regarding their features, user interface, pricing, and customer support.
- Assess the risks of misappropriation of funds, such as potential fraud or embezzlement, and determine the necessary measures to manage those risks.
- Ensure that the selected financial management software has robust security measures in place to protect against unauthorized access to financial data.
- Ensure that the software has systems in place to record all financial transactions accurately, including the ability to customize chart of accounts and record budget allocations.
- Establish a system for regular audits and reconciliations of financial data to detect and correct any errors or discrepancies.
- Ensure that all financial transactions are compliant with due diligence requirements, including proper documentation and approval processes.
- Create and implement policies and procedures for the use of the financial management software, including guidelines for user access and data sharing.
- Train staff on how to use the financial management software effectively and provide ongoing support to ensure proper usage.
- Establish a plan for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the financial management software to ensure that it continues to meet the needs of your organization and remains in compliance with industry best practices andregulations.
- Develop and provide an audit checklist to guide staff in collecting and assessing information to review financial management software, managing risks of misappropriation of funds, ensuring systems are in place to record all transactions, maintaining an audit trial and complying with due diligence.
-
- Financial Management Software Audit Checklist:
- Evaluate the software provider's reputation and background.
- Check if the software has been tested and reviewed by certified professionals.
- Review the software's compatibility with existing systems.
- Assess the level of support provided by the software provider.
- Check if the software complies with relevant regulatory standards.
- Verify the accuracy of the financial reports generated by the software.2.
- Risk Management Audit Checklist:
- Evaluate the organization's internal control environment.
- Identify potential fraud risks and evaluate the adequacy of controls.
- Review policies and procedures related to segregation of duties, approval authority, and access controls.
- Conduct a fraud risk assessment and identify high-risk areas.
- Evaluate the organization's insurance coverage.
- Transaction Recording Audit Checklist:
- Verify all financial transactions are recorded timely and accurately.
- Check if all the transactions are properly categorized in the accounting system.
- Assess the system of checks and balances in place to verify the accuracy and completeness of the financial information.
- Review the reconciliation process and the adequacy of supporting documentation.
- Audit Trail Audit Checklist:
- Verify the system maintains an audit trail to provide a history of all transactions.
- Review the audit trail's adequacy and assess the ability to trace transactions accurately.
- Check if the system captures all relevant information, including date, time, user, and source of the transaction.
- Due Diligence Audit Checklist:
- Review the level of due diligence performed before making any financial decisions.
- Assess the adequacy of the organization's due diligence policies and procedures.
- Verify the accuracy and completeness of all supporting documentation.
- Evaluate the level of supervision and review provided to ensure compliance with due diligence requirements.
- By following this audit checklist, staff can ensure that the financial management software is reviewed effectively, risks of misappropriation of funds are managed adequately, all transactions are recorded accurately, an effective audit trail is maintained and due diligence is beingcompliedwith.
- Present this report verbally to your board (assessor) in order to demonstrate your communication skills as well as the ability to explain budgets and deal with questions. Analyse the existing financial management approaches of the organisation. Are there any recommendations you should make and what are they? You need to ensure your board (assessor) is clear about your budgets.
Good morning members of the board,
I am here to present a report on the financial management approaches of our organization. The purpose of this report is to analyse our current financial management strategies and make recommendations for improvement.
First, let's review our current financial management approaches. Our organization has been successful in maintaining a balanced budget over the past few years, but there are areas where we can improve. One of the major issues we have identified is that we have not been effectively tracking and monitoring our expenses. Some of our departments have been overspending, which may put us at risk of going over budget.
In addition, we have not been taking advantage of the opportunities to streamline our financial processes and take advantage of the latest technology to automate and streamline our accounting procedures.
My recommendations to address these issues include:
- Improving our expense tracking and monitoring systems to ensure that departments are operating within budget limits. One way to do this is to implement an automated expense management system that allows us to track and manage expenses in real-time.
- Reviewing our purchasing procedures to ensure that we are getting the best value for our purchases and ensuring compliance with our procurement policies.
- Upgrading our financial software to streamline our accounting procedures and make them more efficient.
- Conducting regular training sessions for our staff to ensure they are aware of our financial policies and procedures.
- Developing strong partnerships with vendors to improve our negotiating power and reduce purchasing costs.
In terms of budgeting, I want to ensure that the board is clear about our current budget and the plans for the upcoming year. Our budget for the next financial year has been based on a conservative growth rate of 3%, and we have factored in the cost of the recommended improvements I have mentioned earlier.
I welcome any questions or feedback you may have about the report and recommendations. Thank you for your timeandattention.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back! Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects.
Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

