Dynamic Model Equation: Production Chemistry Assignment
- Country :
Australia
Q1
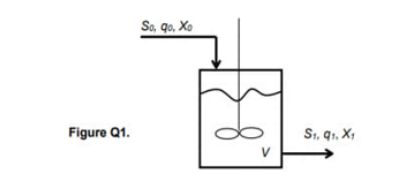
Bioethanol is produced in a continuous bioreactor containing suspended yeast cells that are capable of fermenting glucose to produce bio ethanol and carbon dioxide (Figure Q1). The biomass growth follows typical Mo-nod kinetics, with the rate of production of biomass (cells) and substrate represented by the following equations:
Rx=dx/dt= uX
u= uSmaxS/ Ks+S
R=-rx/Yx/s
where X is the biomass (cells) concentration (mg L-1), S is the concentration of limiting substrate, i.e. glucose (mg L-1), and the kinetic constants are mar= 0.55 h?1; and K, = 12 mg L-1.
It is assumed a yield of biomass to substrate, Y=0.85. The feed to the fermenter contains no cells. The substrate feed concentration is 60 mg L and the volumetric flow rate, qo= 20 L h^-1. The bioreactor is kept at a constant volume, V = 100 L.
- By writing the dynamics model equations, determine the transfer functions relating the concentrations X and St in the bioreactor outlet, to the concentration of substrate, So in the feed. Clearly state ALL relevant assumptions.
- Consider the case where the output biomass concentration, X, is controlled by manipulating the inlet substrate concentration, So. By analysing the time response to a sinusoidal input signal with a frequency equal to the natural frequency of the system, provide an analytical expression for amplitude ratio and determine if the process is stable. Set a proper simulation interval and explain how you calculated the natural frequency of the system. Provide the dynamic profiles of both input and output.
- Assume that the outlet biomass concentration is measured using an analyser with a delay time of 3 min. Design a PID controller using the Ziegler-Nichols tuning method. Compute the closed loop performance for a step change and compare the ultimate gain, frequency and tuning parameters of the PID controller estimated from the Simulink plot with those obtained by analytical solution.
- Identify a FOPDT model having a response as close as possible to the original process. Clearly state the gain, time constant and time-delay of the approximated model. Use the identified FOPDT to design a PID controller and simulate the closed- loop response of the system. Provide analytical solution for Z-N tuning parameters for the PID controller. Compare the tuning parameters obtained for the approximated model with those obtained for the real process in (c). Simulate the responses of the identified model and the original process, for the 4 different cases (plot the step responses on the same figure).
- The inlet (feed) substrate concentration, So, is subject to perturbations that can be approximated to a sine wave with a frequency was 0.5 rad/min. Simulate the Impact of the perturbation on the controller performance for the real system.
Determine the perturbation amplitude limit at which the controller performance degrades dramatically (when the output steady state error exceeds 10%). Propose and simulate a solution for mitigating the perturbation impact at this particular amplitude.
For question d, the expected 4 cases are 2 open loop systems (ordinal and FOPDT) and 2 closed loop systems (ordinal and FOPDT).

