Physics Assignment
- Country :
Australia
- On level ground, a child is pulling a sled with a rope that is inclined at above horizontal. The tension in the rope is 50 Newtons. The mass of the sled is 8 kilograms and the kinetic friction force between the sled and ground is 35 Newtons.
- What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the sled?
- What is the magnitude of the normal force of the ground on the sled?
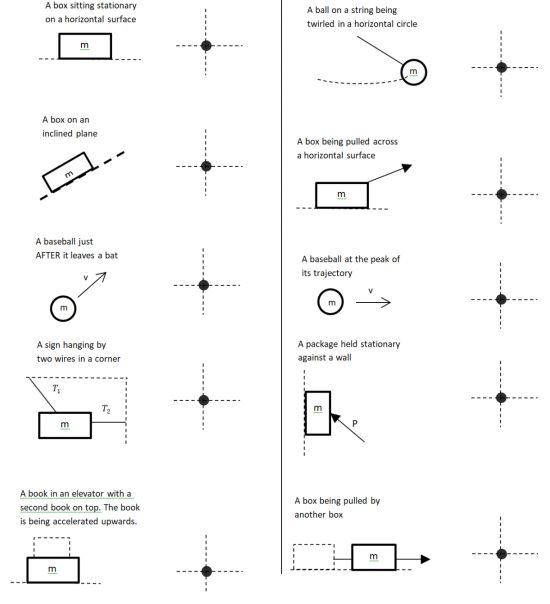
- A soft Nerf ball of mass 0.2 kg bounces off a wall at the angles shown in the diagram as shown in the diagram. The balls speed before it hits the wall is 15 m/s but the balls speed when leaves is only 10 m/s. The collision with the wall lasts 0.25 sec.
- What is the magnitude of the average force that the wall exerts on the ball? Hint: the force of the wall will consist of both a normal force and a friction force.
- What is the direction of this force? Give angle relative to horizontal.
- A 4 kg book is slid across a ceiling using the 100 N force directed as shown. The book speeds up to the right with a rate of .
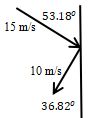
- What is the normal force between the book and the ceiling?
- What is the kinetic friction force between the book and the ceiling?
- Two boxes 3M and M are in contact with each other. There is a kinetic friction force on box due to the floor but the surface of box is smooth so the friction force between this box and the floor is negligible. A horizontal force P is applied to the larger block as shown. Assume .
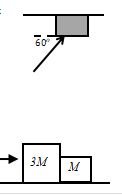
- Draw the free body diagram for the system of the two boxes, i.e., treat the two boxes as one object and show only the outside forces acting on the boxes.
- Draw the free-body diagram for each box individually. Remember that only forces that directly act on a box should be on the FBD for the box.
- Use the FBD of the system to determine the acceleration of the blocks. Check that your answer contains only the givens , and physical constants such as g. Make sure your answer is dimensionally correct. Note that symbols contain units in them so you should NOT write units in explicitly in symbolic answers.
- Use the FBD for one of the individual boxes to find the magnitude of the force of one block on the other in terms of the givens.
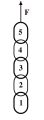
- A chain consisting of five links, each with a mass of 0.05 kg, is lifted vertically with a constant upward acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the magnitudes of the following forces:
- Force on link 1 due to link 2.
- Force on link 2 due to link 3.
- The force F of the person lifting the chain.
- A crate of mass 40 kg is pulled by a rope with tension at an angle = 22.62o above horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is 0.3 but the coefficient of static friction is 0.45. Use g = 10 .
- Draw the free-body diagram for the crate. Include a coordinate system showing +x and +y directions.
- Determine the normal force of the floor acting on the crate.
- Assume the crate does not move. Determine the friction force between the floor and the crate. Comment: usually the static friction force is not
- Now assume that the crate starts sliding. What is the acceleration then?
- A carnival ride consists of a hollow cylinder spinning about a vertical axis. As the cylinder spins around at a speed of v, a person of mass m rides the inside wall of the cylinder without slipping down (there is no floor). The distance of the center of mass of the person from the axis of the cylinder is r.
- Draw the free-body diagram of forces acting on the person during the ride. Show your choice for the +x and +y directions.
- Write out Newtons 2nd law for each direction in terms of the forces in your free body diagram.
- What is the normal force on the rider? What is the direction?
- What is the force of friction on the rider? What is the direction?
- The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rider is . What is the minimum speed that the rider can move without slipping down the wall?
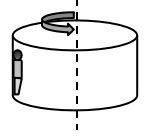
- When the three blocks in the shown figure are released from rest, they accelerate with a magnitude of 0.500 m/s2. Block 1 has mass M, block 2 has 2M, and block 3 has 2M. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between block 2 and the table?
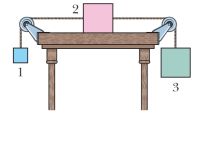
- Body A in shown figure weighs 102 N, and body B weighs 32 N. The coefficients of friction between A and the incline are and . The angle . Let the positive direction of an x-axis be up the incline. In unit-vector notation.
- What is the acceleration of A if A is initially at rest?
- What is the acceleration of A if A is moving up the incline?
- What is the acceleration of A if A is moving down the incline?
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back! Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects.
Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

