Anatomy and Physiology of Communication and Swallowing Disorders HAP3045
- Subject Code :
HAP3045
Section 1: Structures of the Head, Neck, and Thorax
There are a number of structures in the head, neck, and chest that work together to produce sound when we speak or sing. These fall under power, source, and filter components.
Power: The lungs, diaphragm, and intercostal muscles provide airflow for speech; the diaphragm contracts to take air into the lungs and expels it via the vocal folds to produce sound.
Source: As air flows through the larynx, which houses the vocal folds, it generates sound. For John, Parkinson's illness produces muscular rigidity that results in hypophonia, that is, a breathy voice.
Filter: Sound goes via the pharynx, oral, and nasal cavies where articulators like the tongue and lips form it into speech. John's dysarthria occurs from inadequate tongue motions and lip seal that compromise speech intelligibility.
Speaking and eating include multiple linked systems that have to work together harmonically (Bassetti & Liberman, 2021). While the tongue forces food down during swallowing, with the epiglottis avoiding aspiration, the lungs and diaphragm create airflow for sound, formed into speech by the oral and nasal cavities.
Parkinson's disease causes malfunction in these systems that results in lower respiratory capacity, reduced strength and coordination of the face and tongue muscles, and impaired soft palate function, hence producing his hypophonia, dysarthria, and swallowing problems (Bacanoiu et al., 2020).
Section 2: Disruptions to Typical Anatomical and Physiological Functions
Table: Oral Motor Examination (OME)
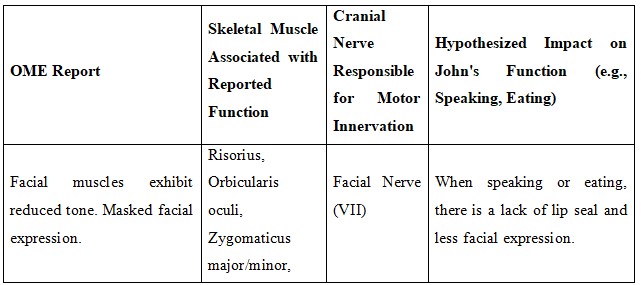
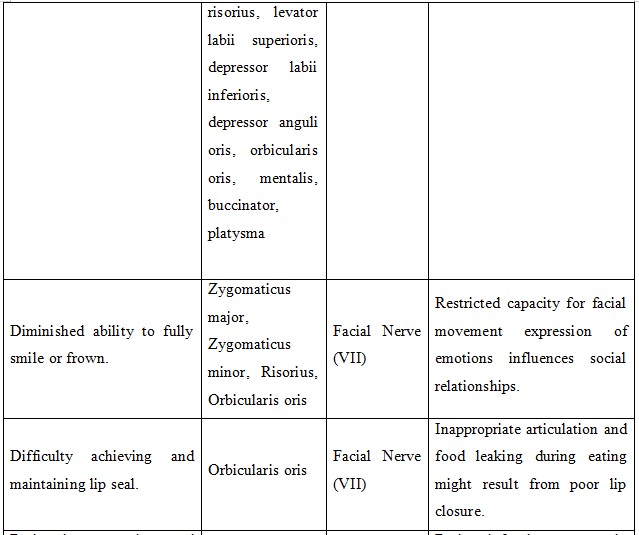
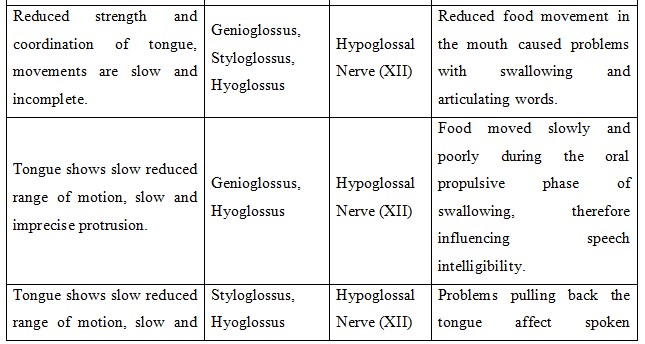
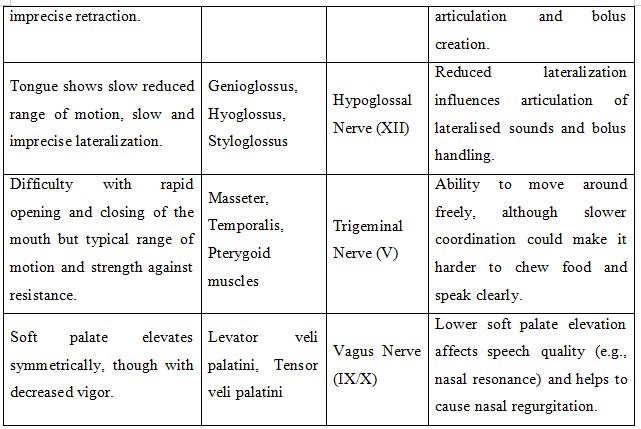
The Neuropathic Examination showed OME results of facial paralysis and poor lip seal that lowered cranial nerve VII function affecting speaking and swallowing (Liu & Zhong, 2020). As good communication involves his facial expressions and tones, the symptoms intensify his dysarthria, and as a result, reinforces his social withdrawal. Cranial nerve XII his hypoglossal nerve controls the tongue movement (Libreros-Jimnez et al., 2023) based on the dysphagia assessment he demonstrates reduced power, slowness and imprecision in the movement of his tongue in actions like protrusion, retraction and lateralization. Mostly with dry foods, such defects interfere with the motor and vocal functions of food conveyance and clarity of speech that defines oral preparation and propulsion stages. Vagus nerve dysfunction extends palatal elevation to a lower level so that nasal regurgitation risks rise and speech intelligibility drops.
Section 3: Central Nervous System (CNS) Structure and Function
Mostly affecting the substantia nigra, a region in the basal ganglia in charge of controlling voluntary motor control, Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative condition marked by the degradation of dopaminergic neurons (Sola et al., 2022). Reduced dopamine throws off the equilibrium between the substantia nigra and basal ganglia, which causes John's bradykinesia, muscular rigidity, dysarthria, hypophonia, and poor swallowing control.
In Parkinson's disease, dysphagia, that is, trouble swallowing, often comes from poor control of the pharyngeal and oral stages of swallowing (Schindler et al., 2021). John's poor motor control reduces his vocal projection because of weak breathing and raises his choking danger.
The blood flow of the brain via the circle of Willis nourishes important regions like the motor cortex and basal ganglia. Along with dopamine depletion, lower blood supply to these areas aggravates motor problems and compromises movement control.
Section 4: Integration of Typical and Non-Typical Functioning
Under a good swallowing mechanism, the food is taken and masticated and mixes with saliva to form a chunk of matter that can be swallowed (Sun-Waterhouse et al., 2021). The Parkinsons wheat John has leads to weakness of the tongue, poor coordination and restricted movement; this creates a barrier in the production of bolus and masticatory difficulties compounded by poor lip closure and difficulty in handling dry and tough textured meals. Normally, the tongue in term oral propulsive phase moves the bolus backward within the oral cavity (Matsuo & Palmer, 2023). Normal functioning of the tongue and soft palate as well as the pharyngeal muscle forms, propels and clears the bolus. These functions are however degraded by Johns Parkinsons disease making him vulnerable to bolus propulsion and clearance and increases the risk of aspiration and choking with hard or dry meals. In light of this, dysphagia in John is characterized by problems with specific meals, raise the risk of choking, and malnutrition resulting from an impairment at one or all the stages of swallowing.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

