BEM2037 Leadership Challenges and Practice Course Outline
- Subject Code :
BEM2037
- University :
University of Northampton Exam Question Bank is not sponsored or endorsed by this college or university.
- Country :
Australia
BEM2037 assignment brief 2024-25
Deadline: 27th March 2025
The overall word count is 3000 +/- 10%
OVERVIEW
This assignment is focused on the application of Pedlers leadership practices to real world leadership challenges. We are looking for you to demonstrate your learning from the module and show your understanding of the models and theories we have discussed. It is important to choose to focus on issues which hold the greatest interest and relevance to you.
The assignment is composed of two separate sections.
Section 1 focuses on your own leadership and how you have applied the practice of self-leadership.
Section 2 features a case study and asks you to identify and critically discuss how leaders can use other leadership practices to address significant challenges in the organisation.
In his book Pedler argues that Leadership begins with a challenge. It happens when someone does something useful in a challenging situation (Pedler et al, 2010. P.13). He identifies 14 challenges of leadership, the challenges he feels are most often found in organisations The 14 challenges of leadership are those organisational problems and opportunities of the day requiring our best efforts at leadership.
These are shown here along with the seven practices. These are the tools and techniques leaders use to address the challenges.
You can find out more about these in the core text, which you can access through the reading list on ELE
You will be expected to present coherent arguments for and against the topic, presenting evidence on both sides.
You should draw on theories and models discussed in the lectures bringing together different perspectives from the module.
You should show that you have conducted some research from outside the lectures to substantiate your arguments.
Make sure you give preference to analytical depth over descriptive breadth.
Choose carefully how you complete the assignment. Make sure your answer is carefully structured and written in a professional, academic tone.
You must cite any sources, throughout your essay and include a full list of references in alphabetical order at the end of the essay (this does not form part of your word count). You must use the APA 7th edition Referencing System.
Section 1 Personal Leadership Reflection
Word count 1500 +/- 10%
This section is focused around the application of Pedlers leadership practices to challenges you have faced your own real world leadership experience.
Many graduate job application forms require applicants to reflect on their own understandings and experiences in order to demonstrate leadership skills. This assignment is your chance to practice this kind of reflection within a theoretical framework.
Choose ONE of these challenges and critically reflect on how you have exercised leadership to address this challenge. You can use a challenge from any aspect of your life. It does not have to be from a formal leadership position; it really can be any incident that gave rise to a challenge. It may be the challenge of group work at school or university, the challenge of overcoming personal limitations, the challenge of work; anything where you felt you addressed a personal challenge.
For example, this may be about you making a significant change in your life (Making Major Change) or using social media to lead others (Leading Through Networks) or creating your own, personal strategy (Developing Direction and Strategy).
You will need to focus on the practice of Self-leadership in this section. Include a brief description of your experience of self- leadership as a response to the challenge (you can include more detail in your appendices if you want).
Make sure you include theories on self-leadership to explore how you responded to the challenge. Your response might have been successful or unsuccessful but you should include theory to evaluate your response.
Then draw on some of the other practices to show how you led in this situation. You may consider your use of power, or how you managed risk or how you asked challenging questions.
You will need to underpin your reflection with theoretical perspectives. This will allow you to demonstrate your understanding of the theories we discussed in the module by showing how you applied the theory to address your challenge. Use one of the models for reflection we discussed in the module to help structure your reflection.
You will need to refer to Pedler et al (2010) and briefly review the 14 challenges. You will need to consider
Which challenge you are addressing?
What is the critical incident that gave rise to this challenge?
Why did you need to practice leadership in this situation?
How did you use Self-leadership??
Which other of Pedlers practices did you use?
Why did you use these?
What was the result?
What have you learned from this?
Structuring section 1
The section should be structured with an introduction, a main body and a conclusion. You can use headings and subheadings to help with the structure of your assignment. Sub-headings will help to show where each opinion piece starts and ends
You must include a reference list at the end of the piece. This must be in APA 7 format.
The reflection can be written using the first person. So you can use I and we, for example.
Introduction
The introduction sets the context for the reflection, making it clear why you think this is a leadership challenge. Provide some brief background to the challenge you intend to discuss. You do not need to describe the challenge in detail; just give enough background and context so the reader understands what was happening.
Main body
This is where you develop your reflection. Use one of the reflective templates we discussed in the module to help structure the reflection.
Try to think deeply about the issue and reflect on how you felt at times during the challenge. The feelings you experience will influence your behaviour, so understanding this will help you develop your leadership skills.
Make sure you include a future focus in your reflection. You must show how you can apply what you have learned from this challenge. Try to be as clear as you can be about this and include some actions you can take to improve your leadership in the future.
The arguments and the points you make must be supported with evidence from good academic sources. You should use academic journals, books and databases to provide the evidence. All sources of evidence should be referenced using APA7th edition.
Conclusion
The conclusion is where you draw together all the points you have discussed together.
Section 2 Real World leadership
Word count 1500 +/- 10%
Read the case study carefully.
Identify 1 challenge from Pedler et al (2010) the organisation in the case study is facing. You may identify several challenges, but you need to focus on just one.
Then critically discuss how leaders are addressing the challenge using the leadership practices. You can choose which practices you wish to focus on but you must apply at least TWO of the practices.
Again, refer to Pedler at al (2010). You will need to consider:
What is the challenge the organisation is facing and how does this relate to Pedlers framework?
Why is the organisation facing this challenge?
Which practices is the organisation using to address the challenges? You must choose at least two, but you can discuss more.
Critically analyse how the organisational leadership is applying these practices to address the issue.
What else could the organisation do
Structuring section 2
The section should be structured with an introduction, a main body and a conclusion.
You can use headings and subheadings to help with the structure of your assignment. Sub-headings will help to show where each opinion piece starts and ends
You must include the AI declaration coversheet at the start of the document
You must include a reference list at the end of the piece. This must be in APA 7 format.
Introduction
The introduction sets the context for each piece, making it clear why you think this is interesting or important. Provide some brief background to the organisation, the issue and the leader(s) you intend to discuss. The introduction must include a clear statement of your main argument.
Main body
This is where you develop the arguments to support the main aim from the introduction. The arguments and the points you make must be supported with evidence from good academic sources. You should use academic journals, books and databases to provide the evidence. All sources of evidence should be referenced using APA7th edition. Build your argument logically, analysing and evaluating the evidence as you go so that your overall conclusion is clearly supported by your discussion.
Conclusion
The conclusion is where you draw together all the points you have made n order to reach an overall conclusion.
References and Word Count
Referencing must conform to APA 7th guidelines details on the ELE2 site
Each section must have its own reference list
Each section has a word count of 1500 words, +/- 10%. So, the overall word count is 3000 words, +/-10%
The overall word limit is 3000 words, +/- 10%.
The word limit includes in-text citations but does not include your reference list or any appendices.
You can include appendices if you want. These may provide supporting information you think is relevant but which cannot be included in the text. However, these will not be marked.
Additional Reading
Please note that for this assignment, you will be expected to read more widely than the core text and the readings provided in the lectures. This is where the reading list provided early in the module will come in useful.
You will be expected to conduct your own literature search to find suitable readings which help you to better understand and/or critique the leadership issues which you are discussing. You are strongly encouraged to access the University Library https://www.exeter.ac.uk/departments/library/ and the Journal search facility
Introduction
Boeing, a leading aerospace company known for its innovation and engineering prowess, has faced numerous challenges in recent years that have significantly impacted its business operations and reputation. This case study examines some of these key challenges and the complexities of the aerospace industry.
History
Boeing was founded in 1916 by William Boeing in Seattle. Boeing started by building military seaplanes and then expanded into commercial aviation, becoming one of the largest aerospace companies. The Boeing 247 was one of the first modern airliners, introduced in the 1930s. In 1970, Boeing introduced the 747, the Jumbo Jet, which has become one of the most successful commercial aircraft, bringing in the era of mass long-distance travel.
Boeing is also a major influence in defence and military aerospace, producing many military aircraft including the F22 Raptor, in partnership with Lockheed Martin. Boeing also develops and builds a range of autonomous systems, including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) such as the ScanEagle and the MQ-25 Stingray.
Boeing has a long history of space development, in partnership with NASA. They have supported every major U.S. space programme and is the lead contractor for NASAs Space Launch System (SLS), a super-heavy lift rocket forming part of the Artemis programme, which aims to return humans to the moon. In June 2024, Starliner, Boeings crewed spacecraft, delivered 2 astronauts to the ISS but following problems with propulsion systems, Starliner returned to earth uncrewed, leaving the two astronauts on the ISS. It is planned to return them to Earth aboard the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft later this year.
Major challenges
Boeing is currently facing a number of complex challenges:
1. Competition: Boeing is operating in an intensely competitive environment in all its areas of operation including aviation, defence and space. There are several other aerospace manufacturers, like Airbus, which has gained market share and is introducing new, innovative aircraft designs. This competitive pressure complicates Boeing's ability to maintain pricing power and attract new customers. New aircraft manufacturers are emerging around the world, threatening the Boeing Airbus duopoly. These include COMAC in China and United Aircraft Corporation in Russia.
In the defence sector, Lockheed Martin poses a significant challenge for Boeing with the F-35 programme. Boeing is a key player in the space industry and has strong ties to NASA. Boeing is developing the Starliner spacecraft for crewed missions but is facing competition from SpaceX and other space exploration companies.
Boeings ability to address competition is key to its survival and growth. A focus on innovation, strategic partnerships and improving customer relationships and trust may help them maintain their competitive edge.
2. Quality Control: The company has been criticized for lapses in quality control, particularly following the 737 MAX incidents. This scrutiny has led to increased regulatory oversight and a need for Boeing to enhance its safety and inspection protocols, which can be costly and time-consuming. It has also had a negative effect on the trust relationship with customers and the public.
To address quality control issues, Boeing is working to rebuild trust with stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to safety, transparency and accountability. Sharing data, insights and changes to processes with regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) will reassure stakeholders of Boeings commitment to safety. Boeing has also increased funding for employee training around safety and compliance in an attempt to build a better safety culture in which employees take ownership of their work. (Boeing, 2024c)
3. Aircraft Production: Boeing has experienced delays in aircraft production, particularly with the 737 MAX and 787 Dreamliner models. These delays have stemmed from both internal issues and external factors such as supply chain disruptions, leading to dissatisfaction among airlines waiting for deliveries.
The global supply chain has been disrupted by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to shortages of critical components. Boeing's reliance on a vast network of suppliers makes it vulnerable to these disruptions, affecting production schedules and delivery timelines.
By investing in automation to speed up assembly, Boeing can address some of the delays to delivery of new aircraft. Combined with better training, this can help increase output and decrease errors.
Culture
Boeings corporate culture is characterized by a traditional, hierarchical structure, typical of legacy aerospace companies, reflecting its long history. The decision-making process tends
to be slow, with multiple management layers ensuring that protocols are followed meticulously.
Boeing has a risk averse culture as historically Boeing prioritized safety and regulatory compliance over rapid innovation, especially in its commercial aviation and defence sectors. This means they are less likely to engage with high-risk ventures. Whilst Boeing was seen as an innovative company in the early days of jet aviation, it is now more likely to be seen as conservative in its approach to technology and business models. Innovation tends to be incremental rather than disruptive.
Boeing has a Unionised workforce and labour relations are a significant part of Boeings internal culture.
However, this culture has also contributed to issues, most notably the 737 MAX crisis, which highlighted internal pressures to prioritize profit over safety. Reports surfaced that Boeing's shift towards a more profit-driven mindset under certain leadership regimes led to lapses in communication, transparency, and accountability. The fallout from the crashes, coupled with pandemic-driven layoffs, damaged employee morale and trust within the organisation. (Englehardt et al., 2021)
Strategy
Boeing's strategy has historically focused on incremental innovation and long-term stability. As a legacy aerospace company, Boeing prioritizes safety, regulatory compliance, and cost-efficiency. Boeing's commercial aircraft development, for instance, tends to be conservative, focusing on upgrades to existing models like the 737 series rather than introducing disruptive new designs. Its defence contracts, particularly with the U.S. government, contribute to steady, predictable revenue streams.
However, Boeing's reliance on legacy models led to a crisis with the 737 MAX. The pressure to reduce costs and speed up development resulted in safety compromises, damaging Boeings reputation and finances. Moving forward, Boeing will need to rebuild trust, focus on operational excellence, and re-emphasize its safety-first approach while balancing the demands of a competitive market.
Boeing has a diverse portfolio with many revenue streams. It operates through three main segments: Defence, Space and Security and Global Services. Boeing claims to be one of the largest, most diversified aerospace and defence companies in the world (Boeing, 2024b).
Boeing is working on several strategies to compete in the aviation industry. Boeing is investing heavily in R&D to improve the performance and efficiency of its aircraft and introduce advanced technologies. Boeing is also seeking to diversify its product line to include new aircraft variants allowing different configurations for different markets. Boeing also hopes to capitalise on expanding services and support solutions. For example, Boeing operates a maintenance, repair and overhaul service (MRO), as well as aircraft storage, at several locations around the world. Boeing also offers aircraft leasing and fleet management solutions, pilot and crew training and advanced data analytics to optimise airline operations.
Stakeholders
Boeings key stakeholders include customers, employees, investors and regulators. Boeing has a broad focus on commercial airlines and defence, as well as space exploration. The aerospace environment for Boeing is mature market, with a long history of relationships with regulators and investors. However, competition is increasing in all of Boeings markets as new entrants emerge around the world. They are also facing increased competition from a number of newer entrants into the space industry, particularly SpaceX.
Key Stakeholders
Boeing:
1. Customers: Airlines, defence contractors, government agencies.
2. Employees: Engineers, assembly line workers, and corporate staff.
3. Investors: Shareholders who expect returns and growth.
4. Suppliers: Companies providing materials and components for aircraft and defence products.
5. Regulators: FAA, NASA, and international aviation authorities ensuring safety and compliance.
6. Community: Local communities affected by Boeings operations, including job creation and environmental impact.
4. Suppliers: Boeing's reliance on a vast network of suppliers makes it vulnerable to these disruptions, affecting production schedules and delivery timelines.
Ethics and Sustainability
Boeing operates in an environment in which ethics and sustainability are key issues. Their ability to address these issues are key to their long-term sustainability as CSR becomes more and more important to investors and stakeholders.(Boeing, 2024a)
For Boeing, aviation is one of the largest contributors of greenhouse gases (Statista, 2024) and Boeing is under pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. Boeing focuses on improving the operational efficiency of their aircraft, developing Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) and investing in developing new technologies. However, the aviation industry's overall environmental impact remains a critical ethical concern, especially as air travel grows.
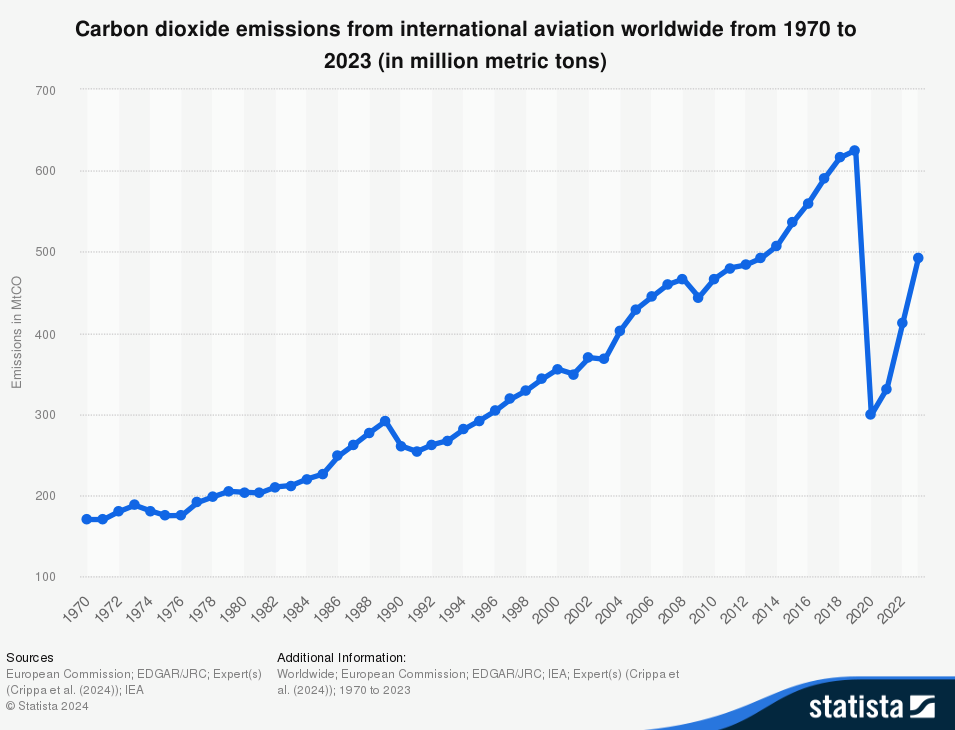
Statista (2024)
Another ethical concern for Boeing is around safety and compliance. Following the crashes of two Boeing 737 Max Aircraft, the fleet was grounded across the globe. The following investigations revealed some deep issues with safety culture at Boeing and how employees were being treated. There were also issues with the regulation by the Federal Aviation Authority (FAA), the body responsible for regulating aviation in the USA. Boeing was alleged to have too big a role in the certification process, with little oversight from the FAA.
These ethical issues have tarnished Boeings reputation and damaged its stakeholder relationships.
(Note: ChatGPT 4.0 was used in the research and development of this case study

