COMP10002 To Implement A Simplified Community Detection Algorithm Assignment
- Subject Code :
COMP10002
- University :
The University of Melbourne Exam Question Bank is not sponsored or endorsed by this college or university.
- Country :
Australia
1 Learning Outcomes
In this assignment you will demonstrate your understanding of structures, linked data structures, and algorithm time complexity analysis. You will further extend your skills in program design and implementation.
2 The Story
In Assignment 1, we have tasted supervised learning, which is a major subcategory of machine learning that uses training datasets to derive parameters for mathematical models. In this assignment, we will try out another major subcategory of machine learning, unsupervised learning, in particular, clustering, which discovers data patterns by grouping a set of objects such that objects in the same group are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. Like before, you dont need to be an expert in machine learning for the assignment. We will guide you through the process step by step.
Social network apps, such as Facebook, Twitter, and WeChat, have become prevalent and are now part of our daily lives. A lot of opportunities and challenges arise from such apps. A challenge to look at in this assignment is called community detection, which aims to find groups of social network app users that are densely connected, that is, following each other (or, in a friendship). Figure 1 illustrates two communities (each enclosed by a red dashed curve) detected from a social network of 12 users u0, u1, . . ., u11, where two users connected by a line is considered to be in a friendship.
Figure 1: A social network example

The communities detected offer many opportunities. For example, the organizers of a product launch event may want to invite influences from every community to maximize the impact of the event, or they may analyse the interests of different communities and focus on those that are more likely to be their customers. As another example, social network platforms may detect groups of malicious users from the communities, e.g., accounts set up for spreading fake news or for political propaganda at election times.
3 Your Task
In this assignment, you will be given a small social network dataset, and your goal is to implement a simplifified community detection algorithm which has been broken down into a few stages like before. 1The given input to the program has three sections (a sample input is shown below):
- At least two and up to 50 lines of user profifiles. Each line represents a user, which starts with u[i] where 0 <= i < 50>
- An n n friendship matrix, where n represents the number of users (in the sample input, there are 12 user profifile lines, and so n = 12). The element at row i, column j of the matrix represents whether users ui and uj are in a friendship. If so, the element has a value of 1, and 0 otherwise. The friendship matrix in the sample input below corresponds to the social network in Figure 1, where user u0 is in a friendship with users u1, u2, and u3. Thus, in the friendship matrix, columns 1, 2, and 3 of row 0 are all 1s, while the rest of row 0 are all 0s. To simplify the discussion, this assignment assumes two-way friendships, that is, two users must follow each other at the same time (in a friendship), or they do not follow each other at all (not in a friendship). This means that the friendship matrix is symmetric.
- Two threshold values ths (a positive real number) and thc (a positive integer) separated by a whitespace character, which will be described and used in Stage 4.
u0 2018 #foodiesofinstagram #foodies #fresh
u1 2011 #local #togo #yummy #keyfooddeli #supportsmallbusiness #foodlover
u2 2013 #foodlover #yummy #dinner #foodies #togo
u3 2014 #foodies
u4 2017 #storemade #macncheese
u5 2022 #melbournedemons #richmondtigers #sydneyswans
u6 2021 #mcg #richmondfc #footy
u7 2014 #aussierulesfootball #melbournefc #aflfinals
u8 2019 #afl #footy #football #aussierules #aflw #sport #aussie #melb #syd #tas
u9 2017 #sydneyswans #nfl #aussie #melbournedemons #footy
u10 2018 #startreck
u11 2015 #starwars
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0.3 2
You may assume that the test data always follows the format above. No input validity checking is needed.
You will be given a skeleton code file named program.c for this assignment on Canvas. The skeleton code file contains a main function that has been partially completed. There are a few other functions which are incomplete. You need to add code to all the functions including the main function for the following tasks.
3.1 Stage 1: Read User Profifiles (Up to 5 Marks)
Your first task is to add code to the stage_one function to read the user profifiles. You need to define a struct named user_t to represent a user, and an array to store all user profiles. This stage outputs (1) thenumber of users read, that is, the value of n, (2) the user with the largest number of hashtags, and (3) the hashtags of the user. If there is a tie, print out the user with the smallest user number among the tied ones.
Hint: Use scanf with u%d to read a letter u and an integer, or use getchar to read the letter u fifirst.
Note the newline character n at the end of each line if using getchar. The output for this stage given the above sample input should be (where mac: is the command prompt):
mac: ./program < test0>
Stage 1
==========
Number of users: 12
u8 has the largest number of hashtags:
#afl #footy #football #aussierules #aflw #sport #aussie #melb #syd #tas
Like in Assignment 1, we will again use input redirection to feed test data into your program. Thus, you should still use the standard input functions such as scanf or getchar to read the data. You do not need to (and should not) use any fifile operation functions such as fopen or fread. Your program should not print anything except for the data requested to be output (as shown in the output example).
You can also modify the stage_one function to read all input in one go. You can (and should) create further functions to complete the tasks when opportunities arise.
3.2 Stage 2: Compute the Strength of Connection (Up to 10 Marks)
Add code to the stage_two function to read the fifirst two rows of the friendship matrix. These two rows represent the users who are in a friendship with the fifirst two users, u0 and u1.
Then, calculate the strength of connection between u0 and u1 with the following equation:
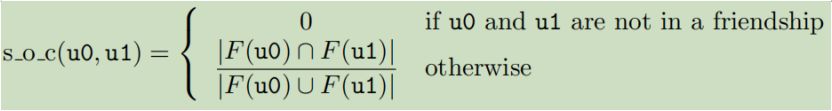
Here, F(u0) and F(u1) refer to the sets of users who are in a friendship with users u0 and u1, respectively; operator ? takes the intersection of two sets; operator ? takes the union of two sets; and | | returns the number of members of a set (not the abs function as in Assignment 1). Intuitively, two users with more shared friends will have a larger strength of connection, and s o c(u0, u1) ? [0, 1].
In the sample input, the set of users who are in a friendship with u0 is F(u0) = {u1, u2, u3}; the set of users who are in a friendship with u1 is F(u1) = {u0, u2, u3}; F(u0) ? F(u1) = {u2, u3} (2 members); F(u0) ? F(u1) = {u0, u1, u2, u3} (4 members). Thus, s o c(u0, u1) = 2/4 = 0.5.
The output for this stage given the above sample input should be (using %4.2f for output formatting):
Stage 2
==========
Strength of connection between u0 and u1: 0.50
3.3 Stage 3: Compute the Strength of Connection Between All Pairs of Users (Up to 15 Marks)
Add code to the stage_three function to fifinish reading the friendship matrix. Then, compute the strength of connection between every pair of users. The output for the stage is a strength of connection matrix, where the element at row i, column j is s o c(ui, uj). You need to generalise Equation 1 for the computation.
Hint: You may also choose to read the full friendship matrix and compute the strength of connection matrix in Stage 2. For marking purposes, you should still follow the output requirement of each stage.
Given the sample input above, the output of this stage is shown in the next page (using %4.2f for output formatting). As the output shows, the strength of connection matrix is also symmetric. For example, theelement at row 0, column 1 (that is, s o c(u0, u1)) and the element at row 1, column 0 (that is, s o c(u1, u0)) are the same, which are both 0.5 as calculated above.
Stage 3
==========
0.00 0.50 0.40 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.50 0.00 0.40 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.40 0.40 0.00 0.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.50 0.50 0.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.17 0.33 0.14 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.17 0.00 0.40 0.00 0.17 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.33 0.40 0.00 0.33 0.33 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.33 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.17 0.33 0.14 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
3.4 Stage 4: Detect Communities and Topics of Interest (Up to 20 Marks)
Stage 4.1 (3 marks)
Add code to the stage_four function to read the strength of connection threshold ths and the core user threshold thc.
We say that two users are close friends if their strength of connection is greater than ths. For example, when ths = 0.3, u0 and u1 (or u2, u3) are close friends, as their strength of connection 0.5 is greater than 0.3 as shown in the Stage 3 output, while u5 and u6 are not close friends as s o c(u5, u6) = 0.17 < 0>
Further, we say that a user is a core user if the user has more than thc number of close friends. Counting the number of close friends of a user ui is simple - just count the number of elements at row i of the strength of connection matrix that are greater than ths. In the Stage 3 output matrix shown above, row 0 has 3 elements greater than ths = 0.3, and so u0 has 3 close friends which is greater than thc = 2. Thus, u0 is a core user. In total, the sample input (as plotted in Figure 1) has four core users: u0, u1, u2, u3, and u7.
Write a function that takes a user (or user number) as its input and test whether the user is a core user. Each core user forms a community together with the close friends of the user. For example, u0 forms a community with u1, u2, and u3; u1 forms a community with u0, u2, and u3; u7 forms a community with u5, u6, u8, and u9. Technically, when two communities have shared users, they should be merged together and considered as a single community. For simplicity, in this assignment, we omit this merging process and just treat each community formed by a difffferent core user separately.
Now, add code to the stage_four function to go through each user and check if the user is a core user, by calling the core user testing function you just wrote. If so, compute and output the close friends of the user, in ascending (increasing) order of the user numbers.
Stage 4.2 (for a challenge, 2 marks)
Further compute and output all unique hashtags of the users in the community form by each core user, sorted in alphabetical order (5 hashtags per line). To compute the unique hashtags, modify the given linked list code and the insert_unique_in_order function to insert the unique hashtags into the list and maintain the list nodes in alphabetical order. Then, you just need to go through the list and print out the data (that is, a hashtag) in each node, by adding code to the print_list function. This step aims to test your learning of linked lists. There may be more efficient solutions for this step, which you can implement but should not be included in your assignment submission.
At the end of your submission file, you need to add a comment that states the time complexity of your algorithm for Stage 4.2, and explains why it has that time complexity, assuming that there are U users, C core users, H hashtags per user, and a maximum length of T per hashtag

