Cross-Cultural Management and International Legal Systems in Global Business IBM4026
- Subject Code :
IBM4026
Question 1
Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions and Potential Issues for a British Multinational Company in China
Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Geert Hofstede coined the notion of cultural dimensions. He theorized it as a framework for dissecting the rudimentary cultural differences across countries.
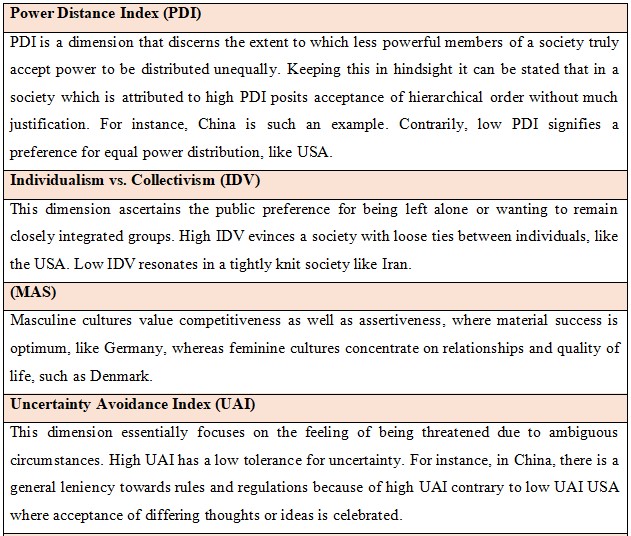


Hofstede's Research on the UK and China:
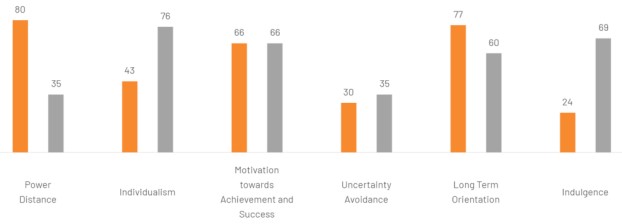
Figure: Graphical representation delineating Hofstedes cultural dimensions [Orange = China, Grey = UK].
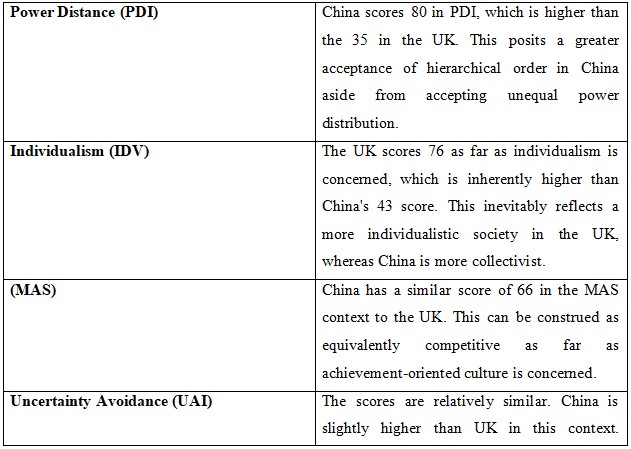
Potential Issues for a British Multinational Company in China:
1.Hierarchical Structures (PDI):
o Issue: British companies are well accustomed to low power distance. This is a point of contention with China's hierarchical corporate structure. As a result of this approach, the process of decision-making is quite slower as well as complicated in China since it essentially necessitates approval from higher authorities. British firms should look forward to adopting this hierarchical approach during operating in China. By respecting local customs and decision-making processes, the chances of the organization to gain favor from their Chinese counterparts is inevitable in nature.
2.Individualism vs. Collectivism (IDV):
o Issue: The UK's individualistic culture inherently clashes with China's collectivist mindset. In China, teamwork is a paramount aspect that every single organization should concentrate on accomplishing it. On the contrary, British firms are well acquainted with individual accomplishments which should be amended to thrive in this new ambience. A team-oriented ambiance should be encouraged which can concentrate on group accomplishment over individual success for the sake of aligning with Chinese cultural expectations.
3.Masculinity (MAS):
o Issue: The higher MAS in China is essentially construed as a competitive business ambiance that is aggressive in nature. suggests a more aggressive and competitive business environment. British firms are not at par with the Chinese market's competitiveness. The prevalent competitive stance of British companies should be more streamlined to harmonize with aggressive marketing to succeed in China.
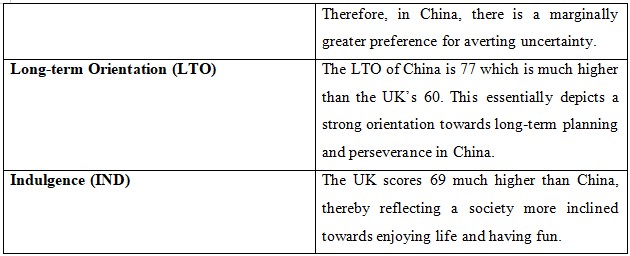
4.Uncertainty Avoidance (UAI):
o Issue: From an apparent vision the distinction between UK and China is not stark as far as uncertainty avoidance is concerned. However, British companies still face a daunting responsibility to align with the rules and regulations adhering to ambiance when it comes to conducting business across China. The first course of action that is imperative in this instance is to meticulously concentrate on maintaining compliance with local laws and regulations and be completely braced for extensive bureaucratic procedures.
5.Indulgence (IND):
o Issue: The UK's higher indulgence score can be translated as a more relaxed approach when it comes to conducting business, which is not at par with China's more restrained culture. British firms should adapt to a more restrained approach. This can be actualized by emphasizing discipline and adherence to social norms.
Question 2
Legal Systems and Their Characteristics
1. Common Law System
Characteristics:
- Precedent-based: Legal decisions are delineated on the grounds of prior court rulings (stare decisis). Since it furnishes consistency as well as predictability. Based on these verdicts, judgments are formulated.
- Adversarial System: The contribution of Judges plays a passive role, acting as referees while lawyers for each side present their case.
- Flexibility: Judges can interpret and adapt the law based on the evolving landscape of new circumstances.
- Jury System: Cases are extrapolated by a group of peers, who are well versed with the scenario.
Instances:
- The United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia are just a few instances of such legal systems.
2. Civil Law System
Characteristics:
- Codified Laws: Comprehensive written statutes attributed with codes are the preliminary sources of law.
- Inquisitorial System: Judges dissect the facts before relating them to a case and applying the law.
- Less Reliance on Precedent: Judicial decisions do not hold the equivalent binding authority as in common law systems.
- Systematic Approach: Systematically laws are organized into codes that entail diverse facets of the legal system.
Examples:
- France, Germany, Japan, Brazil
3. Religious Law System
Characteristics:
- Based on Religious Texts: Sacred texts and religious teachings are the source of the laws.
- Integration of Religion and Law: Legal as well as moral rules are intertwined, with a heavy annotation on the religious authorities - who generally undertake the role in legal interpretation.
- Community-Based: It is imperative under such circumstances to maintain the moral and social fabric of the community.
- Limited Flexibility: Stringent adherence to religious doctrines inherently limits adaptability to new issues.
Examples:
- Islamic Sharia law in countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and parts of Indonesia
4. Customary Law System
Characteristics:
- Traditional Practices: Laws are articulated based on customs, conventions, and practices that are passed down through generations.
- Community Enforcement: Community leaders play a role in enforcing and interpreting customary laws.
- Oral Tradition: Laws are not always written down, since oral transmission ar still relevant.
Examples:
- Indigenous legal systems in Africa, the Pacific Islands, and among Native American tribes
Legal Framework of the United States
The United States primarily operates under the Common Law System.
- Judicial Precedent: The decisions formulated by the Court establish binding precedents for future cases. This not only affirms consistency but also validates the stability as far as the legal system is concerned across the United States.
- Federal and State Laws: The U.S. has a dual system of federal and state laws, with the U.S. Constitution as the supreme law of the land.
- Separation of Powers: The legal system is meticulously grounded on the principle of separation of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
- Bill of Rights: The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution protect individual freedoms and rights.
Importance of Understanding Different Legal Systems for International Trade and Investment
Theory of International Legal Environments
The theory of international legal environments revolves around concentrating on the gravity of dissecting the legality associated with the way a business can operate in a global diaspora.
- Legal Environment as a Determinant of Business Success: The first action course that an organization should concentrate on while conducting business on an international platform is to differentiate the legal environment which can immensely impact the operation as well as profitability of a farm if adequate management measures are not incorporated. Therefore, it can be stated that the relationship between the legal ambiance of a nation is inherently connected with the risk management strategies formulated by the organization. Firms that navigate legal complexities effectively gain a competitive advantage if they adhere to the rudimentary legislation delineated under the Companies Act as well as the USA Model Business Corporation Act.
- Dynamic Nature of Legal Systems: Legal systems often nation eventually experience evolution as time elapses. This is predominantly due to the influence of sociopolitical amendment as well as drastic changes in the economic ambiance. International agreements essentially inculcate necessary amendments through which the legal system is also bound to make certain amendments over time. From this perspective, it can be stated that as far as farm business management is concerned, it is always imperative to stay well-versed in the legal development of a nation in which it operates to remain ahead of its competition and refrain from getting entangled in lawsuits due to incompliance with legality.
- Cross-border Legal Risks: Firms engaged in international trade and investment face cross-border legal risks. This risk often falls under a continuum ranging from distinction in legal interpretation to misinterpretation of enforcement mechanisms where regulatory standards differ. Keeping this in hindsight, it is always prudential to efficaciously dissect the legality - so that compliances are not only stringently adhered to but simultaneously respected across all strata of the business operation as a part and parcel of efficacious risk management strategies.
Conclusion
To concur, it can be inferred that the legal system underpinning the U.S. is primarily based on the common law system. Since it is attributed to judicial precedent, as well as federal and state laws. For firms involved in international trade and investment, knowledge of different legal systems is invaluable. It not only affirms legal compliance but looks for effective contract enforcement, with adequate appropriate dispute resolution. That is why it is always prudent to gain cognizance of the theory of international legal environments to grasp the dynamic and complex nature of legal systems, thereby emphasizing the need for firms to stay informed and adaptable in the global marketplace.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

