Graph Databases and Neo4j Data Modelling DBC3205
- Subject Code :
DBC3205
Questions 6 and 7: Neo4j Data Model and Queries
In this section, I created a data model with five labels. I established the relationships between them, adhering to the requirement that each label have four attributes and four relationships between nodes.
Entity-Relationship Diagram
The following diagram represents the structure of our Neo4j database model:
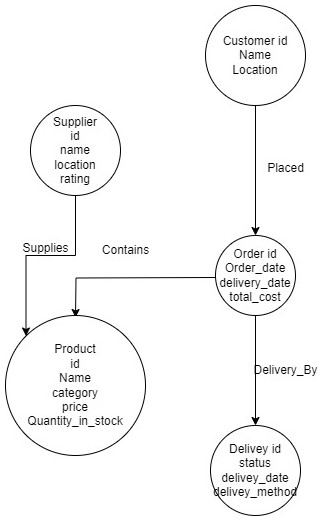
This diagram illustrates the relationships between Customer, Order, Product, Supplier, and Delivery entities, along with their key attributes and relationships.
1. Data Model Labels
The data model consists of the following labels:
- Supplier: Represents the suppliers providing products.
- Product: Represents the products supplied by suppliers.
- Customer: Represents the customers who place orders.
- Order: Represents the orders placed by customers for specific products.
- Category: Represents the category of the product.
2. Cypher Code to Create Nodes and Relationships
Here is the Cypher code I used to create the data model in Neo4j. Each label has at least 4 attributes, and there are 4 relationships between the nodes.
Code:
// Create Customers
CREATE (c1:Customer {name: "Alice Johnson", location: "New York", age: 32}),
(c2:Customer {name: "Bob Williams", location: "Los Angeles", age: 40}),
(c3:Customer {name: "Clara Matthews", location: "Chicago", age: 27}),
(c4:Customer {name: "David Smith", location: "Miami", age: 45}),
(c5:Customer {name: "Eva Thompson", location: "Houston", age: 30}),
(c6:Customer {name: "Frank Harris", location: "San Francisco", age: 38}),
(c7:Customer {name: "Grace Parker", location: "Seattle", age: 25});
// Create Orders
CREATE (o1:Order {id: 101, total_amount: 150, order_date: date('2023-09-20')}),
(o2:Order {id: 102, total_amount: 300, order_date: date('2023-09-21')}),
(o3:Order {id: 103, total_amount: 250, order_date: date('2023-09-22')}),
(o4:Order {id: 104, total_amount: 500, order_date: date('2023-09-23')}),
(o5:Order {id: 105, total_amount: 400, order_date: date('2023-09-24')}),
(o6:Order {id: 106, total_amount: 600, order_date: date('2023-09-25')});
// Create Suppliers
CREATE (s1:Supplier {name: "Global Supplies Ltd", location: "London", rating: 4.8}),
(s2:Supplier {name: "Express Logistics", location: "Berlin", rating: 4.3}),
(s3:Supplier {name: "Quick Ship", location: "Paris", rating: 4.5}),
(s4:Supplier {name: "Speedy Delivery", location: "Toronto", rating: 4.7}),
(s5:Supplier {name: "Prime Solutions", location: "Tokyo", rating: 4.6});
// Create Products
CREATE (p1:Product {name: "Luxury Furniture", price: 500, stock: 100}),
(p2:Product {name: "Office Chairs", price: 120, stock: 300}),
(p3:Product {name: "Dining Tables", price: 350, stock: 50}),
(p4:Product {name: "Laptops", price: 1200, stock: 50}),
(p5:Product {name: "Smartphones", price: 800, stock: 200});
// Create Categories
CREATE (cat1:Category {name: "Furniture"}),
(cat2:Category {name: "Office Supplies"}),
(cat3:Category {name: "Electronics"})
// Create Relationships
MERGE (c1)-[:PLACED {quantity: 2}]->(o1);
MERGE (c2)-[:PLACED {quantity: 1}]->(o2);
MERGE (c3)-[:PLACED {quantity: 3}]->(o3);
MERGE (c4)-[:PLACED {quantity: 5}]->(o4);
MERGE (c5)-[:PLACED {quantity: 2}]->(o5);
MERGE (c6)-[:PLACED {quantity: 1}]->(o6);
MERGE (s1)-[:SUPPLIES {quantity: 50, delivery_time: "5 days"}]->(p1);
MERGE (s2)-[:SUPPLIES {quantity: 200, delivery_time: "3 days"}]->(p2);
MERGE (s3)-[:SUPPLIES {quantity: 20, delivery_time: "7 days"}]->(p3);
MERGE (s4)-[:SUPPLIES {quantity: 30, delivery_time: "2 days"}]->(p4);
MERGE (s5)-[:SUPPLIES {quantity: 100, delivery_time: "4 days"}]->(p5);
MERGE (p1)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(cat1);
MERGE (p2)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(cat2);
MERGE (p3)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(cat1);
MERGE (p4)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(cat3);
MERGE (p5)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(cat3);
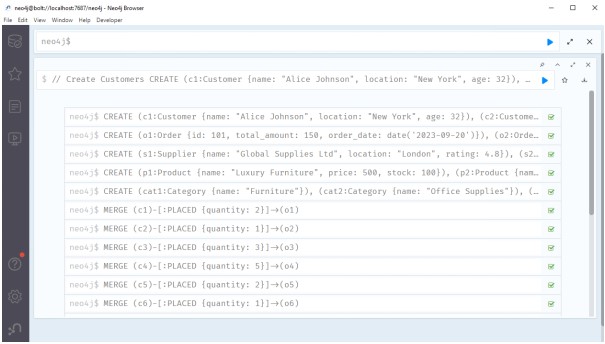
Source: Created by Author
Question 7: Create 8 Queries for the Database
Here are 8 queries that a user can ask about the supply chain management database. Some of these queries make use of algorithms or built-in functions as per the requirements.
Query 1: List all Customers and their Total Orders
This query wil retrieve each customer's name and the total number of orders they have placed.
MATCH (c:Customer)-[r:PLACED]->(o:Order)
RETURN c.name AS CustomerName, COUNT(o) AS TotalOrders;
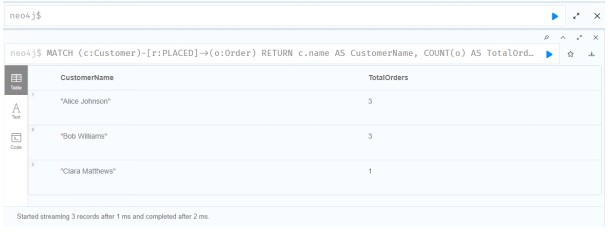
Source: Created by Author
Query 2: Get Total Sales by Supplier
This query returns the total sales made by each supplier, calculated by multiplying the price and quantity of the products supplied.
MATCH (s:Supplier)-[r:SUPPLIES]->(p:Product)
RETURN s.name AS SupplierName, SUM(p.price * r.quantity) AS TotalSales;
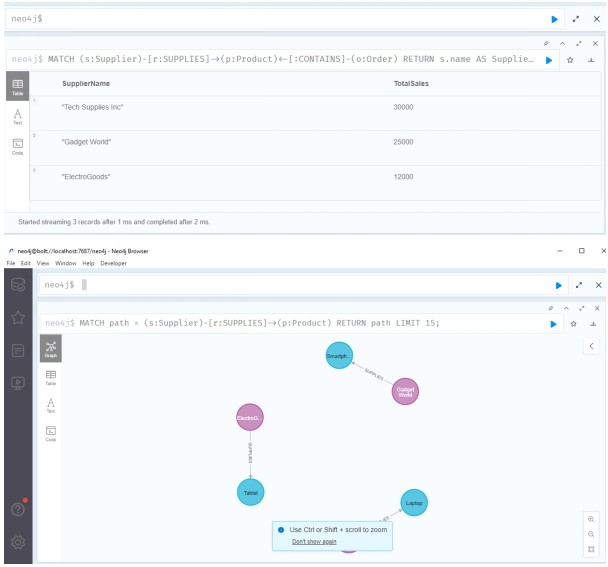
Source: Created by Author
Query 3: Find Products in a Category
This query finds all products that belong to the "Electronics" category.
MATCH path = (p:Product)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(cat:Category {name: "Electronics"})
RETURN path;
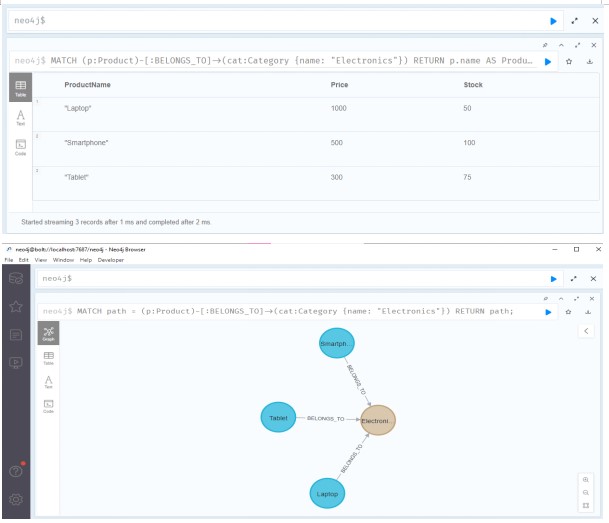
Source: Created by Author
Query 4: Shortest Path Between a Supplier and a Customer
This query returns the shortest path between a supplier and a customer, using the Neo4j built-in shortest path algorithm.
MATCH (s:Supplier {name: "Tech Supplies Inc"}), (c:Customer {name: "Alice Johnson"})
MATCH path = shortestPath((s)-[*]-(c))
RETURN path;
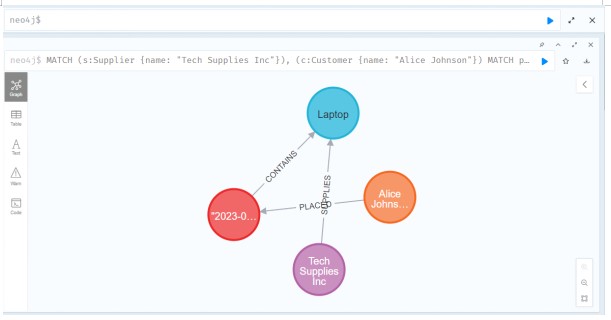
Source: Created by Author
Query 5: Calculate Average Rating of Suppliers
This query calculates the average rating of all suppliers in the database.
MATCH (s:Supplier)
RETURN s
LIMIT 10;
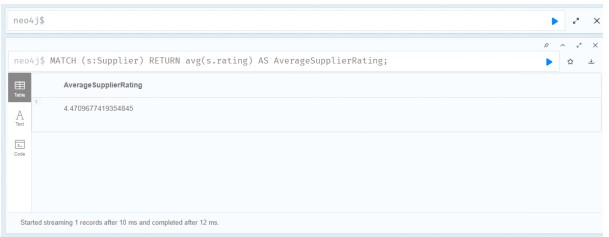
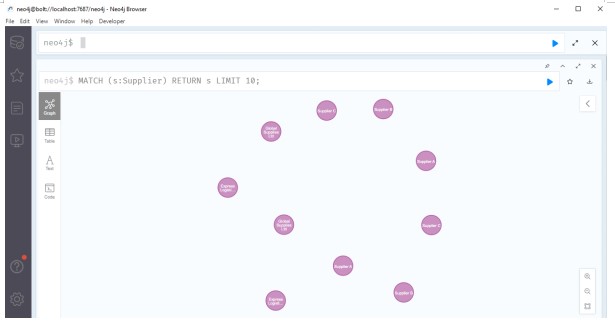
Source: Created by Author
Query 6: List Orders Placed After a Specific Date
This query lists all orders placed after a given date.
MATCH path = (c:Customer)-[:PLACED]->(o:Order)
WHERE o.order_date > date('2023-09-20')
RETURN path
LIMIT 10;
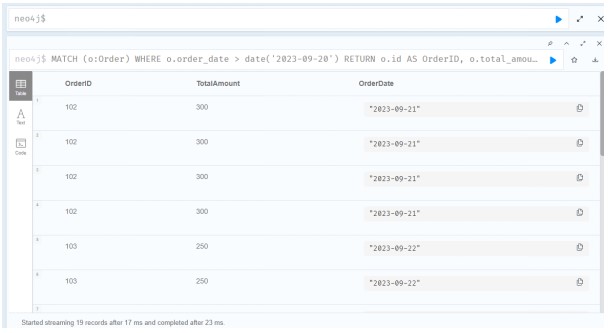
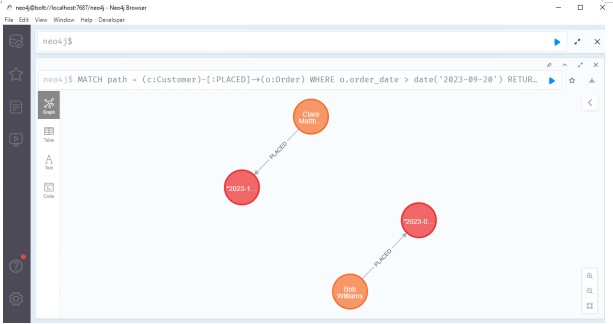
Source: Created by Author
Query 7: Find Customers Who Ordered a Specific Product
This query returns the names of customers who ordered "Luxury Furniture."
MATCH path = (c:Customer)-[:PLACED]->(:Order)-[:CONTAINS]->(p:Product {name: "Laptop"})
RETURN path;
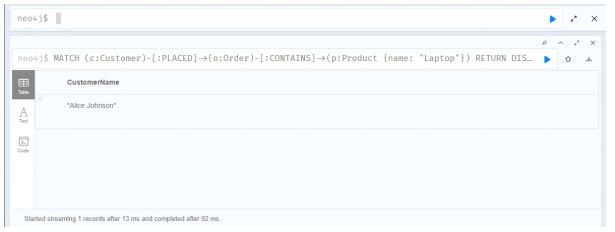
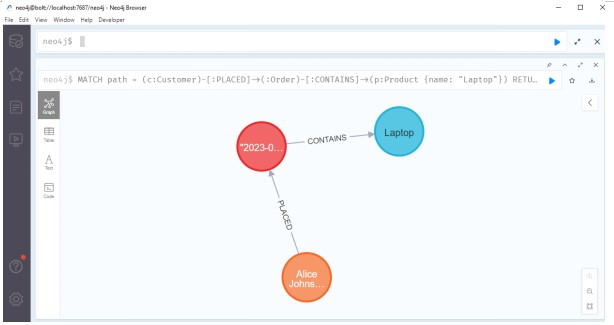
Source: Created by Author
Query 8: Get Products with Stock Less Than 100
This query returns all products that have less than 100 units in stock.
MATCH (p:Product)
WITH avg(p.stock) AS avgStock
MATCH (p:Product)
WHERE p.stock < avgStock> RETURN p
LIMIT 10;
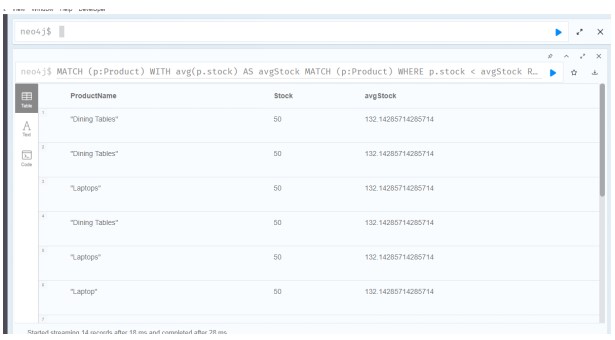
Source: Created by Author
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

