Indian Healthcare Startup Ecosystem And Factors Affecting Its Sustainability Assignment
- Country :
Australia
Abstract:
India is having favorable demography, economic environment and government support. India is highly conductive to entrepreneurial activity. However, most of the startups fail in their first 5 year of operation, including some unicorns, which states Indias startup ecosystem has not achieved full maturity. Deep research on the reasons why most of the startups die in the infancy level, may give proper analytics to startup founders, investors and government bodies. Very less research is done on especially healthcare startup; data provided are for overall startups. This research can lead to detailed insight towards the challenges faced by healthcare startups and its solutions which would be helpful to develop a defined strategy and analytical tool for the betterment of startups and strengthen its sustainability. This review paper focuses on the objective i.e. understanding the most important factors playing negative role in Healthcare startups sustainability.
INTRODUCTION
India is a nation with more than 1.2 billion individuals, 31% of which i.e.379 million are between the ages of 18 and 35 (According to census report, 2011). In March, 2010, 12th President of India, Mrs. Pratibha Patil, reported the government vision by proclaiming present decade as Decade of Innovation (National Innovation Council, 2010).

The Indian Startup landscape has shown tremendous growth over the past decade and has become the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world. Over the past 7 years (2015-2022), there has been: The Startup India Action Plan was launched in January 2016 by the Honble Prime Minister. The vision of the action plan is to build a strong startup ecosystem that nurtures innovation, drives sustainable economic growth, and generates large-scale employment opportunities. Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the nodal department for startups in India, regularly engages with stakeholders to invite consultations on regulatory issues raised by startups, investors, and others in the ecosystem. These efforts are essential in easing and strengthening the regulatory environment in which startups set up and operate. These are playing an important role in boosting innovation and entrepreneurship in the country.
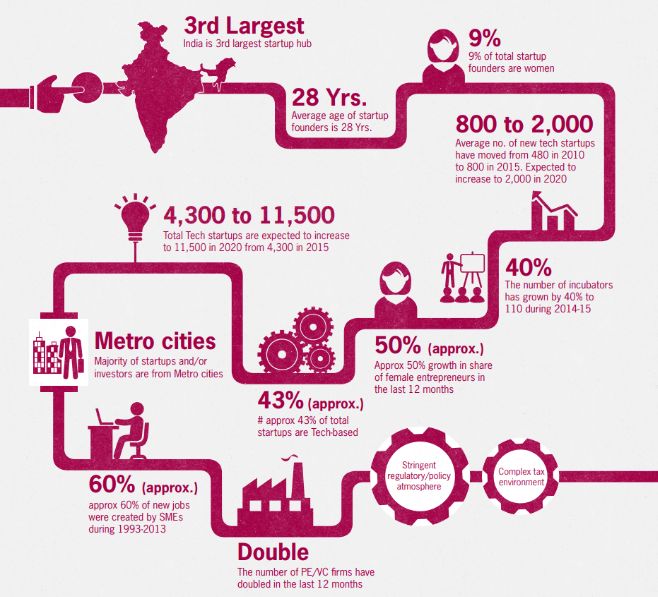
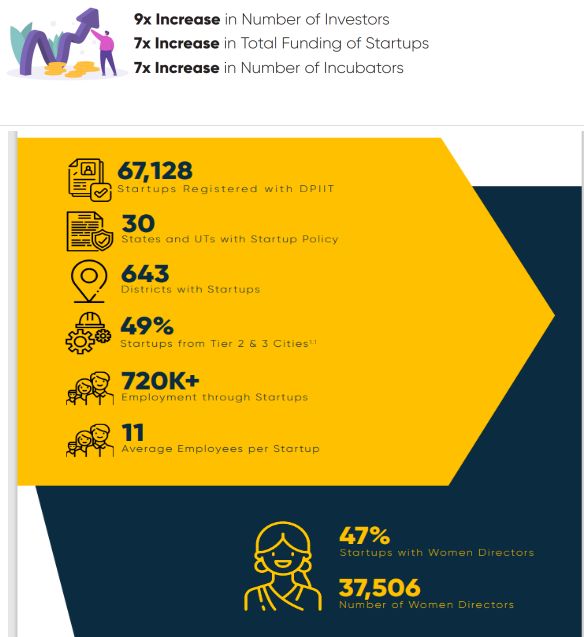
Tier 1 Cities include NCT of Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai Hyderabad, Kolkata, Ahmedabad and Pune. (3)
India has the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world, with over 60,000 startups and 65 unicorns (those that reach US$ 1 billion in valuation) in multiple industries. However, 90 per cent of these enterprises are likely to fail within the first five years, which makes it a difficult market to break into.
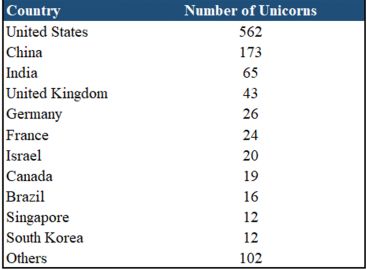
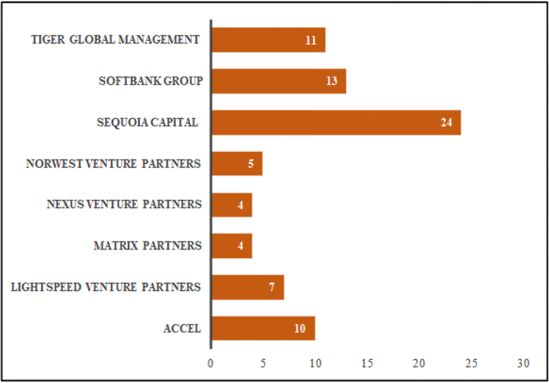
Source: CB Insights Global Unicorn List (as of 6 April 2022)
Figure 2. Number of Indian unicorns funded by major foreign investors
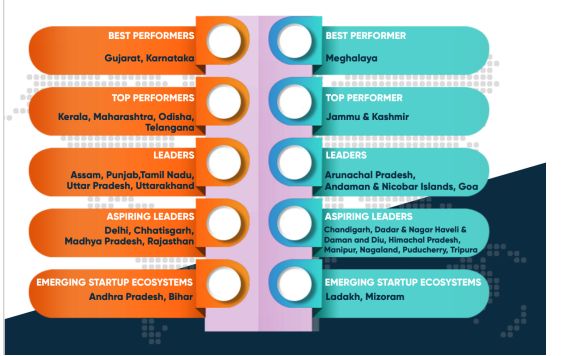
According to each States and UTs performance in the States Startup Ranking 2021, Category A5.1 and Category B5.2 States and UTs have been grouped as shown below
Number of programs undertaken to provide product showcase opportunities to startups (for corporates, industry associations, and other private sector stakeholders
The State has conducted close to 10 programs which include showcase days and national events to provide showcase opportunities for startups. The Department of Education, Government of Gujarat has supported the Entrepreneurship Development Centre at Parul University to conduct Startup Expo-Vadodara Startup Festival 2020, to provide startups with an opportunity to showcase their creativity and innovative ideas in the form of products and services during the event
HEALTHCARE STARTUPS
There is a significant demand in the quality of healthcare services in Tier II and Tier III cities which states that the people are recognising the need for specialty-care. The overall Indian healthcare market today is worth US$ 100 billion and is expected to grow to US$ 280 bn by 2020, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.9 percent.
- Online healthcare (Tele-medicine and Tele-Radiology) has increased the communication amongst multiple people. These startups connect healthcare providers with patients, and in a country like India where there is a rampant problem of uneven spread of doctors, such companies help in a major way. According to the World Bank, there are only 0.7 doctors per 1,000 people in India, and therefore, there is an acute shortage on the supply side.
- There is a growth in adoption of technology amongst doctors across diverse spectrum, which will enable them to deliver quality consultation to their patients.
- There is also significant advent of wearable medical devices and lifestyle tracking devices and applications.
USPs
- Health industry remains under-penetrated by technological innovation, thereby providing multiple opportunities for the new entrants.
- Healthcare portals are making it possible for people to browse through top doctors, read patient feedback and book their next doctors visit with the click of a button.15 Location Concentration
- Majority of these healthcare companies are located in the Tier 1 cities namely Mumbai, Delhi and Bengaluru.
- However, there is a demand for these companies in Tier-II and Tier-III cities as well.
OPPORTUNITIES
- Demographic factors:According to the latest UN report India with 356 million 10-24 year-olds have the largest concentration of youth population despite having a smaller population than China. India has a large domestic market and can be considered as a test bed before going global. The large population has also led to a consumer expenditure growth, which has in turn has propped up supply and production23
- Government support: Prime Minister Narendra Modi envisions India to be in the top 50 of the World Bank Doing Business ranking report as a part of his campaign to re-energize business and attract foreign investment. Currently, the country stands at 130th rank (out of 189 ranked economies). With the present government focused on making a difference in the countrys outlook, lot of opportunities exist even for the startup sector. On 16 January 2016, the Modi government announced capital gains, income tax sops for startups under its Startup India Action plan 2016. The Start Up India mission envisages promoting technology business incubators and creation of research parks. Also the Human Resource Development Ministry and the Department of Science and Technology are partners in an initiative to set up over 75 startup support hubs in the National Institutes of Technology (NITs), the Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs), the Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research (IISERs) and NIPERs or National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research.
- Internet Usage: Indian market provides tremendous opportunity for startups and brands willing to innovate. Internet penetration is high in urban markets and among professionals internet has become useful for innovations of startups & brands. As of 2014, India was the thirdlargest online market with more than 198 million internet users, ranked only behind China and the United States, 38 percent of those who use the internet at home or at work come from the 25-34 age bracket.
- High mobile penetration: Indias tele-density reached 76.55 percent with a subscriber base of 95.76 crore (2014). Growth in mobile penetration is transforming the way businesses and consumers communicate and work with increased productivity. For example, startups that develop mobile apps now have an ever increasing market to cater to.
- Rising number of global incubators: Startup incubators are companies that assist new startups in their initial phase of development by providing various services. Incubators share both tangible and intangible resources such as equipment, office space, services such as accounting, computing and legal services. They also assist startups in raising startup capital and perform various networking activities to reduce the financial burdens and resource issue. Incubators help entrepreneurs in building sustainable business environment while benefiting the broader corporate communities.
- Easy access to funding: The capital required can be accessed through various sources like VC/PE, Angel investors, banks, financial institutions and incubators. Entrepreneur group is supporting the development of other startups. M&A is witnessing increased momentum in India. Education: The state and central government is trying to tackle these issues by pumping almost INR 310 billion (approx. USD 5.7 billion) into improving school infrastructure and recruiting teachers. Right to Education Act is enshrining the rights of all children to free and compulsory education, increasing the enrolment and attendance levels.
CHALLENGES
But despite the optimism surrounding Indian startups, it is estimated that 90 per cent of them are likely to failwithin the first five years. Global investors are therefore looking for hidden pitfalls before they take the plunge.
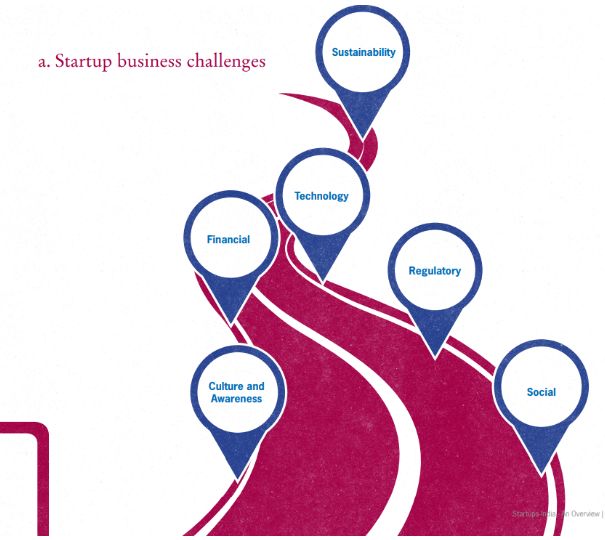
The 2016 World Bank Ease of Doing Business (out of 189 economies) ranks India at 130 where starting a business rank for the country is even lower at 155.22 Policies and regulatory environment has been criticized for starting up business in the country. Taxation, multi window clearances, red-tapism and bureaucracy are some of the issues associated with the country. Moreover, historically the governments role has been fairly limited to providing the funding in terms of grants and loans but recently with the Prime Minister Narendra Modis government, it is taking up a more active role enabling the right environment for this sector. According to a survey by Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI) industry body, growth, talent management and funding are the top three challenges faced by startups
Talent:
- For a startup in India, it is difficult to attract and hire the right talent and skilled workers at a time when the economy is witnessing a booming private sector with a plethora of multinationals setting shop and hiring talent
- Culture issues associated with taking risks and dealing with failures have prohibited people from venturing out with an entrepreneurial spirit. People are conscious about risks and rewards, India being a price sensitive market. In addition, not everyone is flexible enough to work in a startup A startup often cannot match the compensation packages offered at larger companies nor is a startup job seen as a steady one b.
Funding:
- Challenges in raising funds remain the primary concern, especially during the starting stage, given no credit history or track record of the company. Also, there is limited number of credit rating firms for small and medium enterprises
- Over the past few years, investors have put in billions of dollars into hundreds of startups, many of which have grown into thriving businesses. However, many analysts believe that raising funding in later stages of business could become difficult to sustain their operations.
- Many Internet companies delay putting in efforts for revenue generation and focus more on raising investment from different channels. As a result, once the funding halts, trouble looms large with low revenue figures
- Effective cash management is an issue in the short and long term. Cash being the primary channel of payment, electronic payments are still not popular owing to absence of complete penetration to Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
Management
- Flawed business models and revenue strategies lead to failure of many startups
- Appropriate IT infrastructure is a current need given growing number of consumers coming online. Without an impetus to the right and timely technology in the country, growth of businesses will not happen. Cyber risks and lack training of employees on security platforms are acting as roadblocks for startups to prosper
- Mentorship of talent is very important as a lot of these startups are having a young workforce with some very unique ideas that needs direction for reaping effective results. There is lack of formal mechanism to mentor startups in the country and help them grow beyond the setup stage
- Lack of an effective branding strategy is another issue that hampers startups from flourishing speedily
- Indian market is highly unorganized and fragmented, acting as a big hurdle for startups to succeed
- Lack of awareness of potential that exists for their startup businesses prohibits growth Some of the other challenges in this sector include managing business with intense competitive environment, maintaining a sustainable business, technology design, regulatory framework, and intellectual property rights. According to the IAMAI survey, issues such as regulatory framework and monetisation of business model are not bigger concerns for startups as compared to the primary problem of raising funds.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Starting a venture is a well planned and disciplined exercise with due consideration of both internal and external factors that may impact the sustainability of the venture.
- The idea behind the venture, market size, revenue and profit targets are some of the important factors that need to be clearly defined before embarking on the journey.
- Time, team work and tenacity are important elements which determine entrepreneurial success.
- Infrastructure, government regulations and availability of finance at various stages of growth could be some of the challenges for startups.
- In fact, history is replete with examples of startups which began with big fanfare but ended as damp squibs within a short span of time due to various reasons.
- Barba Sanchez (2017) mentioned that in order to examine how motivation and entrepreneurial skills affected the decision to remain self-employed from the perspective of the Expectancy Theory of Motivation, they established a series of working hypotheses on the mechanisms that trigger human actions or behavior.
- Thomas Baron (2017) book brings together the research fields of start-up ecosystems and diaspora entrepreneurship. The author interprets the results of semi-structured interviews with four diaspora entrepreneurs and four experts in Berlin, as well as observations from field studies and the analysis of secondary sources. The findings prove impacts of diaspora ventures on the dynamics of the Berlin start-up ecosystem and are applied to a modified version of the ANDE toolkit.
- Dr.Gopal Das (2018) states that the startup arena has lot of challenges ranging from finance to human resources and from launch to sustaining the growth with tenacity. Being acountry with large population, the plethora of opportunities available are many for startups offering products and services ranging from food, retail, and hygiene to solar and IT applications for day to day problems which could be delivered at affordable prices.
- Bocken (2015) said that the Sustainable start-ups can find opportunity in sustainable business model innovation, new technology and funding platforms and develop the multiple business cases for their businesses to be successful beyond the green customer base.
- Cantamessa (2018) developed a SHELL model, which appears to be a powerful model, especially if applied to a large database, because it allows the development of a standard model or survey for the autopsy of the startups failed, allowing to define a sort of taxonomy useful to identify the more frequently patterns.
- Ghezzi (2020) Provides two main contributions to the existing knowledge. On the one hand, this study frames in the academic literature two well-known popular tools among practitioners: the Business Model and the Lean Startup Approach. Our theoretical framework show that BMD and LSA should be included in the strategic entrepreneurship literature field, since their founding elements are linked with the strategic literature and the entrepreneurship literature too.
- Gopal Krishnan (2017) Developed some methodologies for better team work and simulation.
- Gupta (2016) says there has been an increase in number of startups, or entrepreneurial ventures that have come into existence. Despite the risks involved, many of them have charted through unfavorable circumstances and flourished mostly through innovation of modern technology.
- Herrera (2015) The study uses case studies to build a framework that describes factors leading to successful corporate social innovation (CSI).The study focuses on social innovations that create social value and competitive advantage.
- Holland (2022) examines the difference between policies in start-up decisions versus persistence decisions. The analysis of the decisions of 135 entrepreneurs indicates that the manner in which entrepreneurs use expectancy and value in persistence decision policies is significantly different to the way that they use expectancy and value in general opportunity pursuit decision policies.
- Hyder (2016) methodology is a survey research applying the Lussier Model of business success and failure with a sample of 143 small businesses to better understand the reasons of their success or failure using logistic regression statistical analysis.
- Jacob (2019) analyzed survey responses from 34 startup representatives to investigate the relationship between prototyping practice, startup success, and perceived difficulty of startup tasks. K-means cluster analysis shows three distinct groups, differentiated by (1) their amount of available funding, (2) their use of prototyping best practices, and (3) their reported difficulty in startup tasks. High-performing startups reported having the highest funding, experiencing less difficulty in startup tasks, and using prototyping best practices more frequently than their peers.
- Javier (2022) reported the statistical analysis of a bibliographical sample of 60 recent articles. It defines a core of seven practical business success factors supported by the academic literature (Core-7 SF). This core makes it possible to identify the intersection between success in business practice and academic research. It shows that the most important variable to predict the success of a start-up is the Idea, followed by the CEOs Leadership, the Business Model, the Marketing approach, and the Entrepreneurial Team
- Jo Royle (2013) discusses a lack of specific technical skills; a need for best practice guidance on evaluation metrics, and a lack of intelligent future proofing for dynamic technological change and development are skills gaps currently challenging the communication industry. However, the challenge of integrating digital marketing approaches with established marketing practice emerges as the key skills gap.
- Kotsch (2017) analyzed a series of interviews with twelve startup founders from three different regions (the province of North-Rhine Westphalia in Germany, Budapest in Hungary and the state of California in the US).
- Krishna (2016) have proposed a method to predict the outcome of a startups based on many key factors like seed funding amount, seed funding time, Series A funding, factors contributing to the success and failure of the company at every milestone.
- Maina (2016) has studied the existence of a positive relationship between entrepreneurship training and success of youth business start-ups. It concludes that the relationship between access to finance and business development services towards the success of youth business start-ups was statistically significant.
- Mauricio (2017) states that the experience previous start-up of the founding team and government support factors affect the seed stage; the venture capital factor affects the early stage; the clustering, technological/business capabilities of the founding team and venture capital factors affect the growth stage; and the clustering factor affects the expansion stage.
- Pugliese (2016) analysis reveals an imbalance in the use of variance-based empirical approaches to study the process-based phenomenon and some misalignments in the use of non-process-based empirical approaches to improve a process-based theory.
Macmillan et al (1987) investigated the major differences between a successful and nonsuccessful venture by investing 150 ventures as per 5 major criteria. This study found two factors insulation from competition and demonstrated market acceptance of product responsible for the venture's success.
Bosmaet al (2004) had concluded that an investment in human and social capital tends to increase the performance of the entrepreneurs. At the same time they established importance of innovations used towards improving the performances of human and social capital. The study also reveals that a skillful individual entrepreneur is more likely to perform better in the industry over others.
Astebro and Bernhardt (2003) explored negative the relationship between fresh ventures and bank loans and positive relationship between non-banking loan and venture survival. This whole study was conducted on small businesses launched in US 'between' 1987-1991. A lot of female entrepreneurs are also venturing in the business and giving tough fight to their peers. Female investors are working and their stock picking skills are good and they generally invest in financial market.
Shukla, 2018 mentioned the need of broadening the concept of the leadership in case of startups and stressed upon the emergence of the shared leadership suitable for the expansion and extension of start-ups.
Pearce et al (2006)also describes the perks of shared leadership over the vertical leadership and how it has an edge in reference to descriptive value. It suggests that the high-profile cases of success of reckless start-ups, whose different way of innovation and creativity, are mere stories, rather than the actuality. Innovation has always been one of the main aspects for the startup to flourish and with the changing needs and demands, some new innovations and more optimized form of working and constant need of changing is an important aspect. Success of products largely depends upon management of distribution channels in the target market. Company has to upgrade the product over the time to meet the expectations of customers
(Appu & Balaji, 2018). Kumar (2015) analyzed the suitable environment for startups within India and other countries and found India as one of harshest environment for the start-ups to grow. Government had also taken various measures and simplified the various rules and procedures to smoothen the process for setting up a start-up.
However, due to lack in breakthrough innovation, there was some hesitation in initial findings for the startups. Incubator and accelerator culture had somehow, provided the relief to the start-up ecosystem within India.
Ritesh Dwivedi (2019) has analyzed employee issues, funding pattern and challenges, government support, credit and taxation problems, reasons of failure etc. have been identified and covered in this study. Study analyzed prevailing challenges and vulnerabilities to explore and develop better ecosystem for startups.
Richa Chaturvedi (2020) explored the variables of environment and strategy that effects Indian startups. The sample size was consisting 89 startups from all sectors. Although, the present study made an attempt to understand the innovation phenomena in context withorganization design, however, the innovation in startups is ambiguous and still remainsto be defined.
Kai Buehler (2021) researched one study conducted in Germany in 2019 and then again in 2021 in Germany, Israel, USA and China. In both studies startups were asked to rate themselves in the aforementioned 4 main categories through a set of 20 questions to calculate their individual 4T Score (scores between 1 and 100).
PROBLEM STATEMENT
India is having favorable demography, economic environment and government support. India is highly conductive to entrepreneurial activity. However, most of the startups fail in their first 5 year of operation, including some unicorns, which states Indias startup ecosystem has not achieved full maturity.
Deep research on the reasons why most of the startups die in the infancy level, may give proper analytics to startup founders, investors and government bodies. Very less research is done on especially healthcare startup, data provided are for overall startups. This research can lead to detailed insight towards the challenges faced by healthcare startups and its solutions which would be helpful to develop a defined strategy and analytical tool for the betterment of startups and strengthen its sustainability.
OBJECTIVES
- Understanding the most important factors playing negative role in Healthcare startups sustainability.
- Development of well defined strategy to strengthen the sustainability of healthcare startups.
- Development of an analytical tool which can be helpful to startup founders, investors and government body for analyzing the startup in detail and predict its sustainability.
The most important factors affecting the startup sustainability
The following part will provide an overview of the most characteristic factors causing a startups failure or success regarding to literature review.
The factors which determine startup companies categorize into two main factors and following sub-factors too.
According Postmortem analyses show that startups fail due to a number of internal and external factors.
1. INTERNAL FACTORS
- Personality of entrepreneurship:
- The character or passion of the founder represents his commitment to the project or idea of company (Mauricio, 2017).
- It is decisive of the founder is a person like, how he handles his employees, how he negotiates with other companies; and on the other hand, because of the founders influential position, his interpretations of subjective elements lead the way.
Entrepreneur is the one who, in the end, makes a strategic decision based on his sense of reality (Kotsch, 2017). - Digital Marketing Skills
- Digital marketing Skill is an ability to use of the internet, mobile devices, social media, search engines, and other channels to reach consumers.
- Some marketing experts consider digital marketing to be an entirely new endeavor that requires a new way of approaching customers and new ways of understanding how customers behave compared to traditional marketing (Barone, 2019).
- Teamwork
- To studies in several principle entrepreneurs and deduced that mobilization of team bases is one of the aspects needed for establishing a profitable venture (Muoz-Bullon, 2015).
- The composition of teams and confidence levels of teams impact firm performance (Liozu, 2015).
- Innovation Product or new idea of product
- Innovation product is a degree in which new innovative products and/or services are introduced (Mauricio, 2017).
- Innovation is one of a novel solution to problems of startup. it requires the creation and application of new knowledge that leads to new capabilities amongst diverse stakeholders (W.H. Voorberg, 2015).
- Timing
- The standing of the right timing for market entry is most normally discussed in the technology industry.
- According to Gross, he stated that the 200 companies that the factor time accounted for either success or failure in 42% of the cases (Kotsch, 2017). The right timing is everything.
- Waiting too long to start acting on ideas is not something that you should do, but jumping into the whirlpool of entrepreneurship when the timing is wrong will kill not only your enthusiasm very fast, but will also destroy your business, self-esteem and sometimes even your reputation (Thepitcher, 2016).
2. EXTERNAL FACTORS
- Consumer Behaviour
- However, by adoptiong digital marketing, the challenge of capturing and using data effectively highlights that digital marketing requires a new approach to marketing based on a new understanding of consumer behavior.
- Around 89% of all consumers now begin their search for product information on the internet (Alfrey, 2019). This is, arguably, the stage at which digital marketing can be most powerful.
- Venture capital
- Venture Capital is the entrepreneurial capital that consists of financing startup in the phase of growth with high potential and risk (Bocken, 2015).
- Venture capital is a form of private equity and a type of financing that investors provide to startup companies and small businesses that are believed to have long-term growth potential.
- Governement Support
- Governments in advanced countries have always been interested in fostering entrepreneurship in order to generate innovation, economic growth, and job creation.
- Government policy should attributed to start-ups for shift in policy to focus more strongly on such high-growth firms or startup (Baron, 2017).
- Government supporting is the financial sponsorship of the government, through seed capital, in the initial stage of startup, are also support programs made, especially for startup (Mauricio, 2017).
- Initiatives of non-profit organizations and governments often provide grants, loans or other financing plans that support the startup landscape in a given region (Kotsch, 2017).
- Technologies
- Technology have been changed the size of business. Technological and managerial skills, aptitudes and knowledge required to gain competitive advantage (Mauricio, 2017).
- Nowadays, there are many startups that have emerged by exploring new and innovative technology and are dedicated to further their growth using the same.
- With extensive market research, many entrepreneurs have been able to pinpoint current trends that could help in developing that kind of technology for both businesses and consumers (Gupta, 2016).
CONCLUSION (EXPECTED OUTCOME OF RESEARCH)
These detailed findings of research and developed strategy will give proper roadmap to startup founders to evaluate their journey and an insight to what may lead to their startup failure.
Analytical tool would be helpful to startup funders to evaluate their own mistakes, it will be helpful to government bodies as well as investors to evaluate a promising startup properly before funding it.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back! Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects.
Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

