Introduction to Ethical Theories: Examining Moral Foundations PHIL-1010
- Subject Code :
PHIL-1010
- University :
Other Exam Question Bank is not sponsored or endorsed by this college or university.
- Country :
Canada
ASSIGNMENT 1
Moushad Hussain Chowdhury
008015793
PHIL-1290-A05
Elena Rabinoff
1. Propositions
For the following sentences, list the
- sentential connectives,
- subjects,
- quantifiers,
- predicative connectives and v) simple
a) If all beers taste the same, then every stout is mild and
Ans-
- sentential connectives - If...then
- subjects - beers, stout
- quantifiers - all, every
- predicative connectives - is
- simple predicates - taste the same, is mild and
b) Either Sam will order you an Uber, or some person will drive you home
Ans -
- sentential connectives - Either...or
- subjects - Sam, some person
- quantifiers - some
- predicative connectives - will
- simple predicates - order you an Uber, drive you
2. Necessary and Sufficient Conditions
1.Name one condition that is unnecessary but sufficient for being ill.
Ans Eating expired food (Unnecessary but sufficient for being ill)
2.Name one condition that is necessary and sufficient for getting
Ans - Engaging in physical activity (Necessary and sufficient for getting exercise)
3. Name one condition that is necessary but insufficient for wearing
Ans- Owing jeans (necessary but insufficient for wearing jeans)
4. Name one necessary and sufficient condition for being drunk
Ans-Having a BAC above the legal limit (ecessary and sufficient for being drunk
3. Definitions
Provide a 4-step definition for each of the following terms. (Clearly label the 4 elements) a) Telephone b) Restaurant
Ans-
a) Telephone -
- Genus- A communication device
- Differentia- Transmits sound signals over a distance
- Example- A landline phone
- Non Example- A typewriter
b) Restaurent -
- Genus- Establishment
- Differentia- Serves food and drinks to customers
- Example- Smitty's
- Non Example- Grocery store
4. Validity
Explain why the following argument is invalid using either the counter-example method or the replacement method. Explain invalidity in your explanation.
- Anything for children is appropriate
- Most cartoons are for children
- There are no cartoons with violence
Ans - Argument:
- Anything for children is
- Most cartoons are for
- There are no cartoons with voilence
- Analysis:
- Premises (1) and (2) show that cartoons are for
- Premise (3) contains such opposite ideas, stating that children's cartoons do not contain brutal
- Counter-example: There is perhaps one counterstone that some people tend to exaggerate and underestimate the depiction of violance in cartoons that are clearly meant for
- Even though the premises could be true for an inaccurate conclusion, the argument becomes invalid from this
5. Lewis Carroll Diagrams
Use Lewis Carroll Models to determine whether the following arguments are valid. Show your work.
a)
- Some workers are underpaid
- Every underpaid worker is sad
- Someone is sad
b)
- John is both tall and a man
- John is either a tree or not a man
- John is a tree and a man
c)
- Most fruit are sweet
- Everything sweet has sugar
- Most fruit has sugar
Ans -
Explanation:
- Details:
- Certain workers do not get paid
- Every worker who is underpaid is
- Conclusion: Someone exists who is
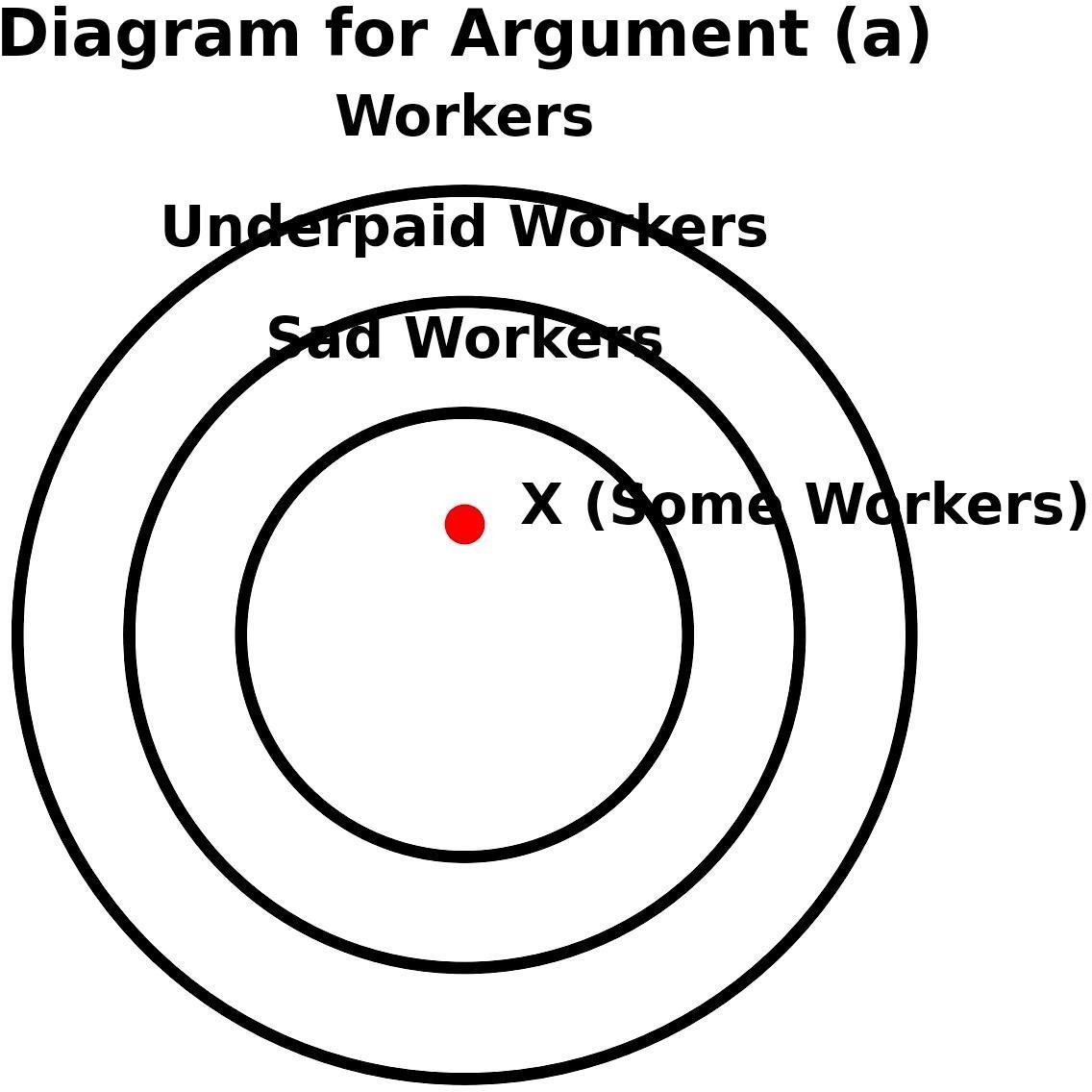
- Diagram Analysis:
- The outer circle signifies "Workers".
- Within, the smaller circle signifies "Underpaid "
- Further insde, a smaller circle stands for Sad
- There is a dot (X) in the circle of Underpaid Workers which
implies that one underpaid worker exist.
- Because all underpaid workers are sad, this dot must also reside
in the Sad Workers category.
- Therefore at least one person is sad, making the conclusion
- Invalid
- John is both tall and a man
- John is either a tree or not a man
- John is a tree and a man
Explanation:
- Details:
- John is a man and
- John is a tree or not a
- Conclusion: John is a man and a
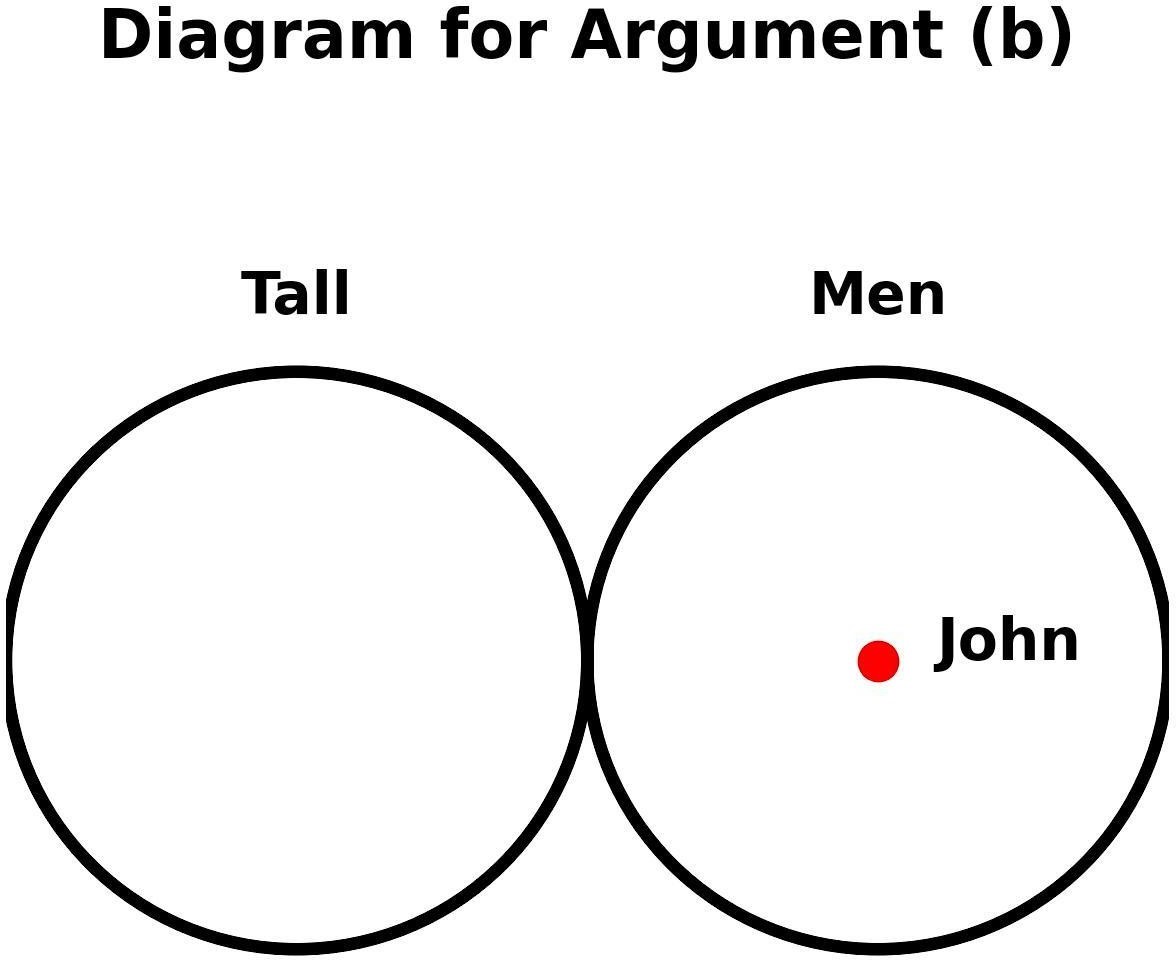
- Diagram Analysis
- Two separate circles, one labeled Tall and one labeled Men.
- John is inside both circles since he is tall and a
- The second premise states John is a tree or not a man, e., he may be a tree OR merely not a man.
- But the conclusion makes John a tree AND a man at the same time.
- The diagram does not illustrate this as necessary, making the argument
- Valid
- Most fruit are sweet
- Everything sweet has sugar
- Most fruit has sugar
Explanation:
- Details :
- Most fruits are
- All sweet things have
- Conclusion: Most fruits contain
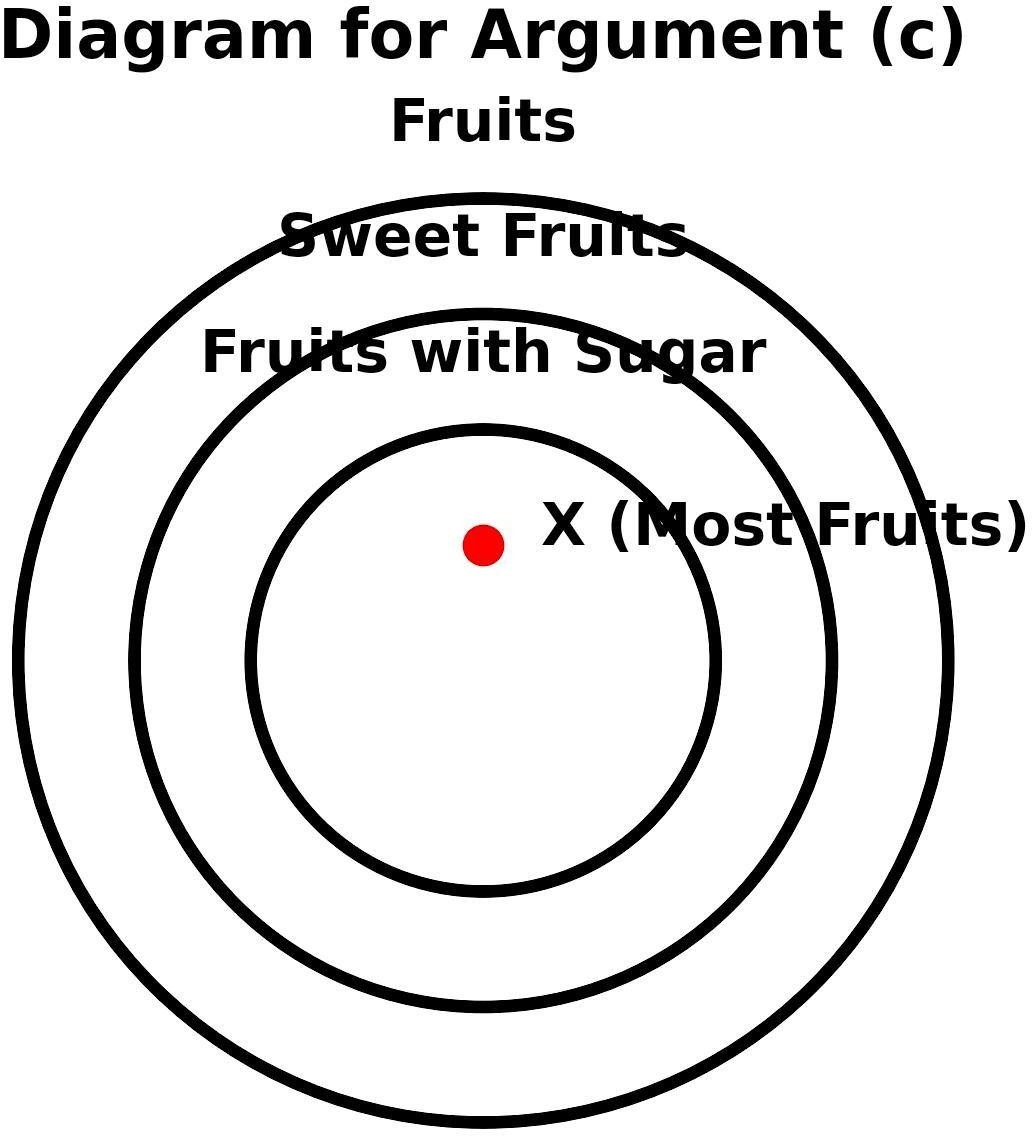
- Diagram Analysis:
- The largest circle is labelled Fruits.
- Within it is smaller circle for Sweet
- Inside this, there is an even smaller circle for Fruits with
- Since most fruits are sweet, a significant part of the Fruits circle overlaps with the Sweet Fruits circle.
- Because everything sweet contains sugar, the Sweet Fruits circle fits within the Things with Sugar circle.
- Since most fruits are sweet and sweet things have sugar, it logically follows that most fruits have
- This makes the argument