Mary Baker Case Study
- Country :
Australia
Questions
- Mary has now been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. What risk factors did Mary present with that would have contributed to the development of this disease?
Age (>45) 54 years old, therefore represents a higher risk
Hypertension- Having high blood pressure makes diabetes more likely to develop.
Family history- (genetically) father deceased aged 68 MI mother deceased aged 62, type 2 DM and stroke
Aboriginal and Torres strait Islander background most risky group
Inactive lifestyle- spents most of her day watching lifestyle.
Obesity BMI 34.3 (Female, Height 162cm, Weight 90kg) higher risk category
Passive smoking - Current smoker: 15 cigarettes / day, contributes to higher chances
Alcohol consumption- 3-4 alcoholic drinks per day, excessive intake can increase the risk - How does her pancreas and her body cells function differently to someone who has Type 1 diabetes?
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas stops producing insulin because the body's own immune system has destroyed its beta cells, but in type 2 diabetes, the pancreas either does not produce enough insulin or it is insufficiently effective to have the desired effect of allowing blood glucose to enter cells. - Explain the pathophysiology of ALL the assessment data reported:
- fatigue
- polyuria/polydipsia/nocturia
- tingling and numbness in both feet
- blurry vision
- BGL - 15.2mmol/L
- left foot is dusky and cool to touch, with sluggish capillary refill
- 3cm x 2.5 cm ulcer on her left heel, which has been there for at least 18 months, and will not heal
- develops pain in her left calf when walking around house
- reports chest pain and feels sweaty and anxious when ambulating for longer periods, i.e. walking around shops
- urinalysis showed positive for protein
FATIQUE
or exhaustion, happens when the body cells do not receive enough glucose to produce ATP, despite the fact that it is present in the blood. Insulin makes it easier for glucose (sugar) to pass from the blood into the body's cells. Her disease is the result of either a lack of insulin or its ineffectiveness.
POLYURIA
Because of the high blood sugar levels, the kidney is working harder to filter out the extra sugar in the blood, which causes more frequent urine.
POLYDIPSIA
As the body produces more urine in an effort to eliminate sugar from the blood, they get extremely thirsty as a result of the fluid movement. This causes the body to lose water, which causes dehydration and severe thirst.
NOCTURIA
A normal person's kidneys should produce less urine and urine that is more concentrated at night. However, in diabetes patients, the kidneys are actively trying to filter out too much sugar in the blood, which results in increasing urine outputs even at night.
TINGLING AND NUMBNESS
Long-term high blood sugar levels can induce diabetic neuropathy, which damages the peripheral nerve system severely and frequently results in numbness, discomfort, pain, and sensations like needles and pins. Microvascular injury can result in reduced tissue perfusion, which in turn might also cause oedema in her extremities.
BLURRY VISION
Blood that contains too much sugar destroys the retinal blood vessels in the eye, causing them to leak and cause diabetic retinopathy, which impairs vision.
BGL
When we take carbs, they are digested and transformed into glucose, which is taken into the bloodstream. Insulin is required to transport blood glucose into cells from the bloodstream; otherwise, blood glucose levels would continue to rise, resulting to Hyperglycemia, as in her situation.
LEFT FOOT DUSKY AND COOL TO TOUCH
They may display the symptoms mentioned above due to impaired blood circulation induced by high sugar levels causing damage to blood vessels such as constriction of blood vessels due to atherosclerosis resulting in Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD).
3CM X2.5CM ULCER
Decreased blood circulation (Peripheral Vascular Disease) to the site to aid healing, as well as elevated blood sugar levels, increase bacterial development and infection, further complicating the recovery and healingprocess.
DEVELOP PAIN IN Left calf
Decreased blood circulation and nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels, resulting in muscular soreness during activity and walking related to decreased blood flow, depriving cells of much needed nutrients and oxygen.
REPORT CHEST PAIN AND FELLS SWEATY
May be triggered by a number of causes such as exhaustion due to a lack of energy produced by insulin insufficiency, impaired blood vessels due to blood vessel constriction caused by atherosclerosis, which leads to cardio vascular disease and its related symptoms.
URINALYSIS SHOWED POSITIVE FOR PROTEIN
The pancreas produces enough insulin in a person with type 2 diabetes, but the body cannot utilize it properly. High blood sugar levels may strain the kidneys as they filter the blood, causing kidney injury. Protein (albumin) can leak into the urine as a result of this injury.

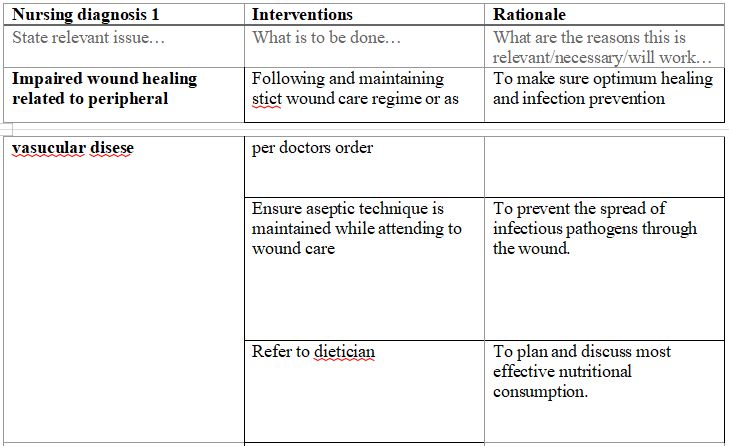
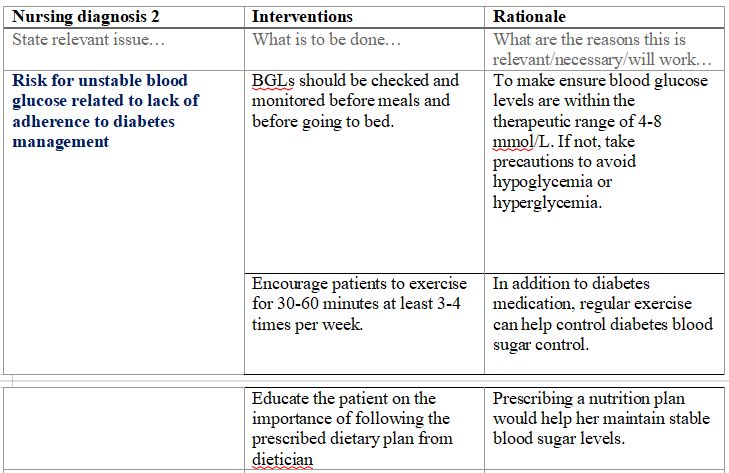
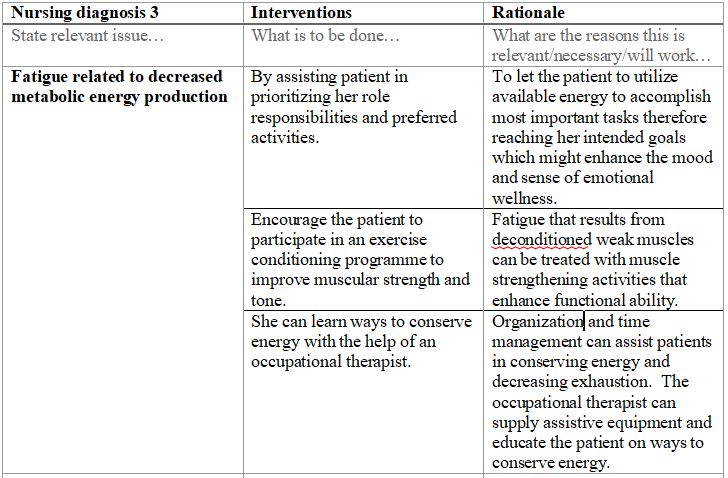
- Identify three nursing diagnoses related to Mary. These could be something that she is at risk of or something she already has. Remember a nursing diagnosis is not a medical diagnosis. Think of it terms of the problems she is experiencing or may experience related to her medical problems. For each diagnosis, list three nursing interventions, each with a rationale (reason why the intervention will work), you would implement to help this client. Use three separate plans one for each nursing diagnosis.
- Mary is commenced on oral hypoglycaemic therapy. Describe in simple terms the different ways these drugs work. You do not have to list their different names but you must explain how they help maintain stable BGLs.

- This morning, before breakfast, you go to assess Mary and find that she is pale and sweaty, irritable and restless. You take her BGL and the reading is 3.5mml/l. What nursing interventions will you provide immediately? What follow up interventions will you implement depending on how she responds?
We would treat her for hypoglycemia given her BGL is less than 4 mmol/L; she is conscious, we could give her 6-7 jellybeans OR 1/2 can of ordinary soft drink OR 1/2 glass of fruit juice OR 3 tablespoons of sugar or honey OR Glucose tablets equivalent to 15 grams carbohydrate. Checkherblood sugar again after 15 minutes to see if blood sugar is above 4 mmol/L. If not, you can repeat the above process up to the equivalent of 15 grams of carbohydrates. Snacks containing long-acting carbohydrates such as 1 slice of bread, 1 glass of milk, 1 piece of fruit, or 2-3 dried apricots, figs, or other dried fruits if your blood sugar is above 4 mmol/L or feed. or 1 cup low-fat natural yogurt or pasta or rice. - Mary confides in you that she is having difficulty coping with her diagnosis. List three factors that may impact on her self-esteem. She has chronic illnesses such as diabetes that require her to take medication andmonitorher diet for the rest of her life.
The condition has developed physical limitations that limit her capacity to complete everyday tasks and meet her job responsibilities, causing pain and tiredness. - Recognizing the vulnerability she would be to complications such as a foot ulcer that may not heal easily and problems with her eyes.
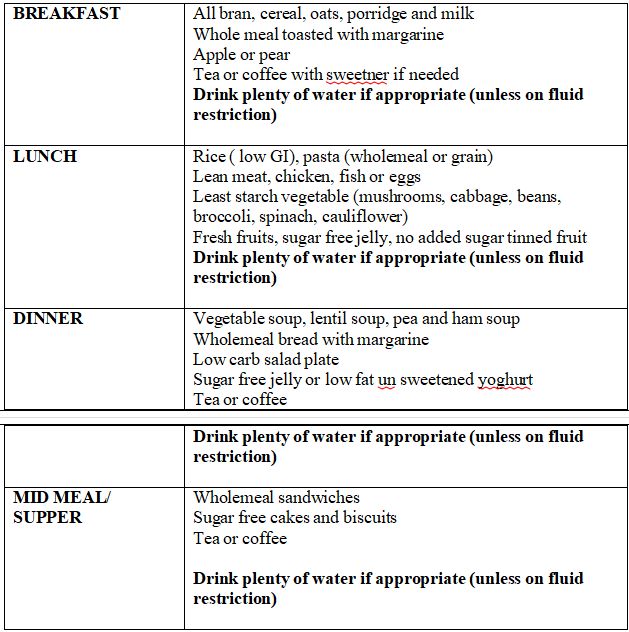
- In the RACGP hand book for general practice Management of type 2 diabetes it is recommended that patients should be advised to eat according to the Australian dietary guidelines (Eatforhealth, n.d.). Using these guidelines develop a detailed meal plan for one day that you could give to Mary as a dietary guide to use upon discharge.
- List two organizations that could provide support to Mary and detail the support that they provide. Ideally should be an Australian organization that Mary could contact directly.
- What education will you proved to Mary to ensure that her diabetes is well managed and to reduce her risk of her complications worsening. List all the information that she would need to know to manage her condition well, e.g. diet, medications, lifestyle changes, sick days, complications, monitoring etc. Use 300-500 words for this section.

- Marys sister is living in outback Australia. Explain the environmental and social factors contributing to diabetes in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations

Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back! Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects.
Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

