Understanding Tourism Trends: Market Segmentation, Sociocultural Impacts, and Psychological Drivers
Part 1 -Brief Description
Weaver and Lawton's "Tourism Management" chapter 6 focuses its attention to the tourist and examines marketplace traits, destination, and segmentation of the market. The travel industry has developed from serving an industry for the masses to one that is an increasing number of specialized and personalized since 1950. At the beginning, travel grew easier to a larger populace as the country became more democratic. Basic market segmentation, which split travellers into major categories, started in the 1970s. These groupings had been further separated into more focused subcategories via multilayer division, which took into account a range of decisions and habits. The niche markets and "markets of one," which serve very particular or unique demands, were developed in the 1990s. The section also explores the method by which tourists select their locations, taking into consideration both external pull forces and their motivations and push factors(Weaver, David, and Laura Lawton, 2014). To successfully reach certain tourist categories, companies and destinations have to prepare the segmentation of the marketplace. The paper includes 8 segmentation concerns, which includes reliability, size, homogeneity, and measurability. Basic segmentation standards, which include geographic, sociodemographic, and psychographic functions, are addressed with an emphasis on their applicability in comprehending and serving an array of traveller agencies gender, age, family lifecycle, and variations between urban and rural regions. It is vital within the hospitality, tourism, and event management sectors that they have in-depth expertise of these tendencies and approaches for decision-making. In tourism, hospitality, and event industry segmentation elements including Family Lifecycle, Pet Ownership, Education, Race, Physical/Mental Condition, and Psychographics are significant. They assist organizations in better serving a huge range of purchasers by permitting them to personalise their offerings. Offering accommodation for tourists who are disabled encourages inclusion and will increase the customer base. Psychographic segmentation assists in developing customised encounters that increase customers' pleasure and loyalty through revealing reasons(Weaver, David, and Laura Lawton, 2014).
In order to improve comprehension and analytical potential, Chapter 10 addresses an extensive range of problems as it investigates the sociocultural and ecological impacts of tourism. Tourism sectors have gained recognition of Bhutan's preference for Gross National Happiness (GNH) beyond Gross National Product (GNP). GNH focuses its greatest emphasis on outstanding leadership, preservation of culture, preservation of the environment, and fair social growth. This strategy challenges the traditional emphasis on economic development exclusively. Bhutan strives for environmentally friendly tourism in accordance with GNH ideals by limiting the number of visitors and focusing a premium on quality rather than volume(Weaver, & Lawton, 2014). This strategy is well-received in the travel, hotel, and events industries as a paradigm for advancing sustainable development that transcends beyond simple financial projections, protecting culture including the environment, and encouraging holistic well-being. The demonstrative operation, prostitution, commercialization, and elevated rates of crime are only a few of the detrimental effects that tourism has on communities of destinations. The commercialization of indigenous cultures is known as "commodification," which has the potential to reason protests and authenticity loss. Because of variations in affluence and cultural assumptions, prostitution would possibly flourish in destinations for tourists. The effect of demonstrations explains how tourist have an effect on locals, which may also motive conflicts and cultural changes. Additionally, at the same time as the link between tourism & crime is various and complicated, it is able to arise at the identical time. In the tourism, hospitality, and event sectors, dealing with these sociocultural factors is crucial to the long-term sustainability of traveller locations and the psychological fitness of local groups(Weaver, & Lawton, 2014).
In Chapter 3, explore a strategic comprehend the demands for tourism. While psychologists research the complex psychological factors that impact travel decisions, the travel and tourism sector depends on pragmatic marketing strategies. Motivation interacts with aspects like the theory of positive psychology, fulfilment, and pleasure. Controlling the effects of tourism and improving the destination experiences is created less complicated with the aid of acknowledging and understanding those demands. Demand for tourism can be effective or nonexistent, relying on external, social-psychological, and financial elements. The studies of traveller motivation explore the shape of psychological factors that affect humans's decision to take journeys(Person, and Page, 2019). Motivation, according to Mountinho, is a subconscious call for that motivates humans to take behaviours in a good way to probably fulfil them. Comprehension of the demand for tourism that is prompted with the aid of an elaborate aggregate of social and financial actions requires a comprehension of those motives. Travel selections are motivated using each external and internal variable, which can be distinguished via an aggregate of external and internal variables. The demand of tourism is a prime instance of the way that humanitarian deamnd, while mixed with factors along with cultural immersion and talent improvement, develop the happiness that comes from travel, in particular in less developed areas.
Part 2 - Tourism theory and the tourism news item
The ABC tourism news article provides specific instances of how Maslow's Hierarchy of Individual Needs and the theories of Push and Pull forces affect the tourism and travel industry.
The push and pull factors theory
According to the push and pull factors theory, people are influenced to make travel decisions by both internal (push) and external (pull) forces. Pull factors are external inspires that attract people to particular locations, whereas push factors are internal incentives that encourage people to look out travel opportunities. There are numerous occasions in the tourism news item when both pull and push factors play an important part in shaping travel decisions(Prabawa, & Pertiwi, 2020).
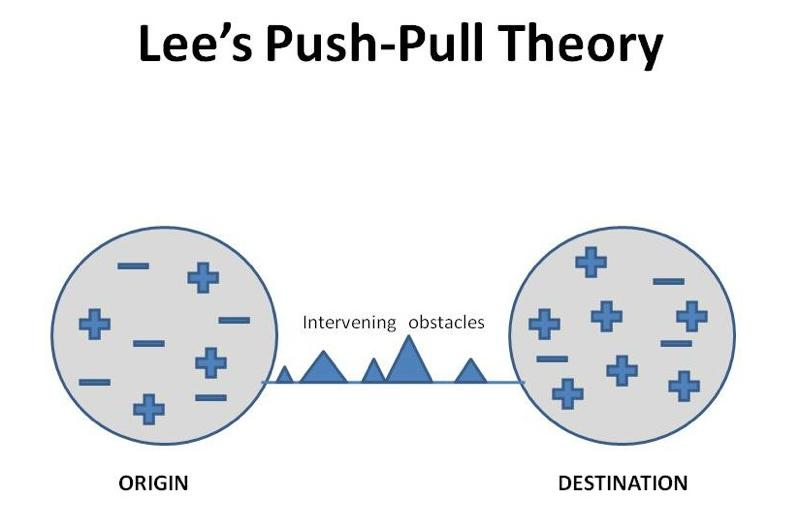
Figure 1: The push and pull factors theory
(Source: Prabawa, & Pertiwi, 2020)
For example, The ABC tourism news article on the tourist market's segmentation is consistent with the push and pull factors strategy. The article explains that market segmentation has changed over the years, moving from simple classifications in the 1970s to more specialised and tailored divisions in the present. This segmentation consists of pull factors consisting of outward attraction and travel destination features in addition to push aspects like travellers' internal motives and preferences. Through comprehension of these variables, organizations and places can also proficiently aim for precise tourist demographics and customise their services as a way to cater to the exceptional demand and possibilities of travellers. This is consistent with the Push and Pull elements concept, which emphasises how internal motives in addition to external attractions factors of interest interact to affect decisions regarding travel(Faulina et al. 2020).
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs theory
Maslow's hierarchy of needs serves as a framework for comprehending the reason why individuals behave the way they do. They involve a need for physiology, security, belonging and affection, self-actualization, and esteem. The theory was developed by Abraham Maslow, a psychologist. The news article on tourism affords data on approaches the industry fulfil these numerous needs (Zarotis, 2021).
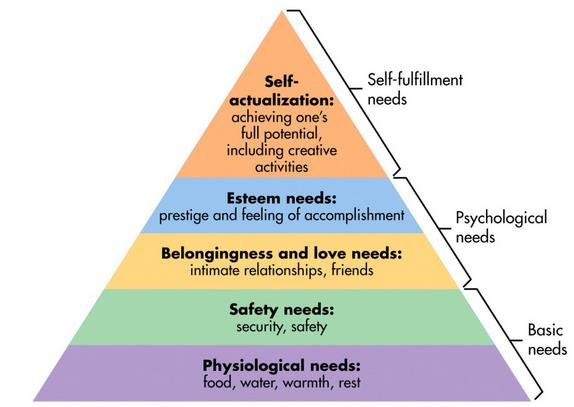
Figure 2: Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory
(Source: Bilousova, Borodavka, and Nurkevych, 2021)
For example, the ABC tourism news articles discussed how age, gender, and manner of life are just a few of the demographic and psychographic components which are taken into account while market segmenting the traveler commercial enterprise. From fundamental physiological demands like ease and accessibility to greater complex requirements like self-expression and personal fulfilment, this segmentation permits agencies and tour destinations to customize their services according to the extensive range of want and desires of travelers. Offering accommodation for travelers with disabilities, for example, fulfils their physiological demands for accessibility and comfort, whereas psychographic segmentation meets their more complicated necessities for self-expression in addition to personal fulfilment(Weaver, David, & Laura Lawton, 2014). The news iteams focus on environmentally fulfilment tourism methods also reflects a growing popularity of the importance of self-actualization via reviews that help renovate of way of life and safeguard the surroundings. This is consistent with Maslow's speculation, which proposes that human beings are seeking experiences that enable them to attain their maximum capacity and advance society(Bilousova, Borodavka, and Nurkevych, 2021).
Future Implications: Insights from Tourism Trends and Theories
This tourism news item forecasts a future filled with exceedingly customised studies, long-term viability and experiential tourism while blended with Push and Pull impacts and Maslow's Hierarchy of Individual Needs. Market segmentation will prioritise customisation at the same time as accommodating a extensive range of traveller preferences. Sustainable techniques that take into consideration cultural and ecological problems could be essential. Self-consciousness could be a pinnacle precedence for travellers which can be looking for life-changing encounters. Businesses that provide those needs through authentic, extensive interactions will succeed. This prediction shows a change inside the course of customised, moral, and pleasing travel stories, with a purpose to have an effect on the tourism area transferring ahead(Olusola et al. 2021).
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

