Unlocking Hypertension Control: Examining Risk Factors, Medication Adherence, and Self-Management in Rural China
1.1 Aims and Objectives
This study intends to describe patterns of risk factors and demographics and to identify the relationship between risk factors and HTN knowledge, treatment and control. Further, it examines the mediating effect of medication adherence and self-management on this relationship in HTN patients.
The study objectives are as follows:
- to examine the demographics and risk factors characteristics in a rural area in China
- to investigate the effect of risk factors on participants HTN knowledge, treatment and control
- to assess risk factors relationship with medication adherence and self-management
- to evaluate the mediating effect of medication adherence and self-management on the relationship between risk factors and HTN knowledge, treatment and control.
1.2 Research Questions and Hypothesis
1.2.1 Research questions.
- Is there any relationship between behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) and HTN knowledge, treatment and control?
- Is there any relationship between behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) and medication adherence and self-management?
- Do medication adherence and self-management mediate the relationship between behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) and HTN knowledge, treatment and control?
1.2.2 Hypotheses.
Alternative hypothesis 1: Behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) are believed to have an effect on participants HTN knowledge, treatment and control.
Null hypothesis 1: Behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) are believed to have no effect on participants HTN knowledge, treatment and control.
Alternative hypothesis 2: Behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) are believed to have an effect on participants medication adherence and self-management.
Null hypothesis 2: Behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) are believed to have no effect on participants medication adherence and self-management.
Alternative hypothesis 3: Medication adherence and self-management are believed to mediate the relationship between behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) and HTN knowledge, treatment and control.
Null hypothesis 3: Medication adherence and self-management are believed to have no mediating effect on the relationship between behavioural risk factors (dietary habits, smoking, drinking and physical exercise) and HTN knowledge, treatment and control.
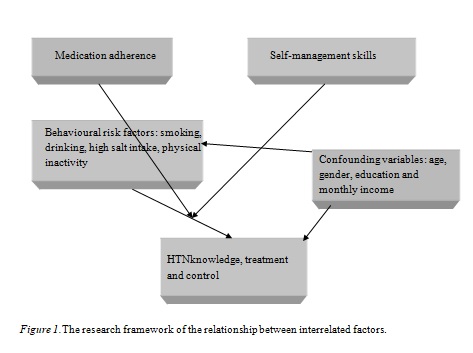
1.3 Research Framework (Conceptual Framework)
Based on the literature review, behavioural risk factors such as smoking, drinking, physical inactivity and excess salt intake affect the likelihood of HTN and HTN knowledge, treatment and control. Further, HTN knowledge, treatment and control could be influenced by the mediating effects of medication adherence and self-management. Effective BP control can be achieved in most people with HTN through lifestyle modifications and antihypertensive drugs (Shaw & Bosworth, 2012). However, even when under the care of the most diligent clinicians, patients can only achieve HTN control if theyadhere to their medication regimen and practise self-management skills. Broadly speaking, medication adherence is an aspect of HTN self-management (Lin, Jueng& Tzu, 2009). HTN self-management has been reported to be more effective at lowering BP in a study conducted by McManus et al. (2010). People with HTN who maintain high levels of medication adherence and self-management skills are expected to have better rates of HTN knowledge, treatment and control. Several studies have explored the intertwining relationships between risk factors and HTN knowledge, treatment and control,although this was notexamined inthis study; however, the mediating effect of medication adherence and self-management has not been examined in the literature. Figure 1 depicts how the important factors in the current study are interrelated. The study conceptualises that HTN knowledge, treatment and control are negatively related to risk factors including smoking, excessive drinking, high sodium intake and physical inactivity. Further, medication adherence and self-management are anticipated to mediate the effects on the relationship between risk factors and HTN knowledge, treatment and control.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

