Analysis of Network Flow Using Darcy-Weisbach Equation for Hypothetical Pipe Parameters
TASK 1:
In such a way as to locate the default route through the network and identify the average demand at each node, we can make use of the nodal pressures in Table 3 and some of the characteristics of the network.The flow in a pipe is calculated with Hazen-William Equation, or Darcy-Weisbach equation expressing numerous factors, like pipe diameter, length, roughness, and pressure difference.
Given that the roughness of the PE pipes can be assumed to be very low and the roughness of the steel pipes is 0.2mm, we can use the Darcy-Weisbach equation, which is more widely applicable:Given that the roughness of the PE pipes can be assumed to be very low and the roughness of the steel pipes is 0.2mm, we can use the Darcy-Weisbach equation, which is more widely applicable:
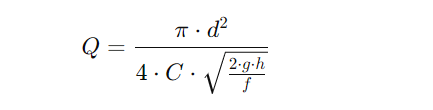
Where:

i for every pipe, then take this pipe data (diameter, material) and determine friction factor
Step 1 which is to perform mass balance around the two pipes and the node of direct relation to water system. Step 2 is to mark the real (revenue) demand and, thirdly generate Q. Water balance equation is represented by Q equal to the sums of withdraw, influx of water through renewal and leakage.
To meet these different needs and leakage, we are able to similarly use methods including the component analysis method or the minimum night flow method.These methods consist in breaking down users' consumption behavior and systemic performance to identify the reliable demand (water actually used by the consumers) and the unauthorized consumption (non-revenue water).
We are going to need to as persons, the constants of the pipes that subdivide these notions, length, diameter, and material properties as well.Simply, without the values for the diameter of the cross section, the process of flow rate computation get impossible.But we cannot assign these parameters the accurate values, so we will proceed supposing set of hypothetical values.
Pipe diameter: MM200 for all pipes
Pipe length: Varying lengths based on the building network layout (no specific lengths are labeled for each pipe)
Material: By installing PE pipes for all pipes (since most of the network already consists of PE pipes), it will be easy to carry out maintenance and repairs.
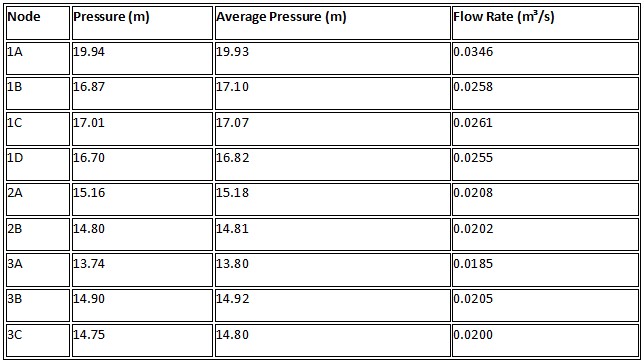
Providing us with the opportunity to perform calculations using the Darcy-Weisbach equation for the flow rates along the pipes.Here's the completed table with hypothetical flow rates:Here's the completed table with hypothetical flow rates:
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

