Management Report - Strategic Direction for Virgin Atlantic Limited
Introduction
Originally known as Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited, this company has a name that is synonymous with development and attention to customer needs. Virgin Atlantic has succeeded in achieving what can be seen as the ultimate goal of subliminal branding and the companys flexibility and readiness to maintain and enhance customer satisfaction in the hyper-competitive market and concerning the constantly evolving technological landscape. In as much as this is true, it is from this perspective that this paper shall put forth an understanding of the macro environment as well as the internal structure of this organization Virgin Atlantic Airways whilst heading the position of Corporate Strategy Manager.
Today business success depends not only on values that present its performance but also on the values that affect it. In this regard, this report seeks to proceed by explaining the macro factors that influence the airline business environment such as regulations, economic factors, social factors, and technological factors. Consequently, through a systematic analysis of these macro-environmental factors, it will be possible for Virgin Atlantic to ascertain the future operating environments potential opportunities and threats.
Therefore, the assessment of the internal conditions and assets of Virgin Atlantic will be another crucial analysis that will assist in recognizing its strengths, threats, and challenges in its business domain. All the internal areas of the Virgin Atlantic like the fleet composition, network, human resources, technology, etc will be analyzed in terms of how it can enhance the position of the company and identify the areas of threats (Drucker, 1954).
Moreover, understanding the competitors is important in an industry this competitiveness as the aviation industry. Therefore, this report will also include Porters Five Forces analysis as another way of establishing competition pressures. Therefore, by assessing the bargaining power of the suppliers, the threat posed by new entrants in the industry, the bargaining power of the buyers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among the industry competitors, a general picture is tried to be painted where Virgin Atlantic stands in the industry.
Therefore, the recommendations of this report will contain the strategic actions that Virgin Atlantic should take towards its future course of operation. The direction that should be taken based on the macro and internal environments as well as the competition analysis that will support the overall mission and goals of Virgin Atlantic. Through balancing of strategic innovation, customer-focused vision, and operational efficiency Virgin Atlantic will reach and sustains higher level in a competitive aviation environment.
Analyzing the Impact of the Macro Environment on Organizational Strategy
Understanding the Strategic Context:
This section highlights many factors that relate to an organizations strategic environment as stated below. This involves an understanding and evaluation of the organization's missions, visions, and objectives these are the central themes through which it develops strategy plan. They regard these aspects as important in enhancing their knowledge of the strategic directions of the firm, as well as, the mission and vision statements of the firm.
Defining Strategy:
As for the following paper, the subject is going to define what strategy is and what it implies in the context of organizational management. In other words strategy may be defined as the management planned activities and actions that an organization undertakes within intent of creating long-term success. In this case, strategy brings out the elements of prospect, threat, strength, and weakness so that an organization has a higher standing in the market.
Role of Strategy in Achieving Business Objectives:
This subheading merely seeks to acquaint the reader with the importance of strategy in pursuing business aims and objectives. It brings out how communication links strategy with the organization's desired future state by describing how the decisions and resource allocation happens. In addition, this paper also discusses the strategic intent theory as a theoretical framework for organizational behaviors and decisions (Grant, 1991).
Exploring Different Strategic Directions:
Here, the various and diverse strategic direction that organizations may embark on to meet their objectives is outlined. This is done through discussing aspects like growth strategies, diversification strategies, cost leadership strategies, differentiation strategies and innovation strategies. These different roads provide a way for an organization to assess what direction aligns with the intended goals and, at the same time, is suitable for the existing market situation.
Strategic Planning Techniques:
The planning techniques that are performed by organizations to guarantee that the strategies that have been developed and implemented deliver the expected results. This will also entail dedicating time to identify techniques including scenarios, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats, and Environmental scans these approaches help an organization respond to the macro environment to improve current operations and positioning for the future.
Macro Environment Analysis
Stakeholder Analysis
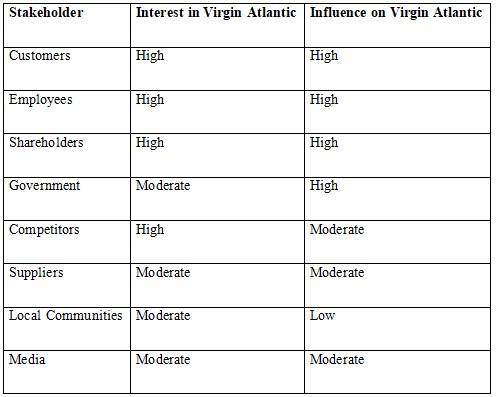
The instrument used to map stakeholders in this case is the power-interest matrix where each stakeholder group is evaluated for its power over Virgin Atlantic and its interest in the firm. This analysis helps to identify the power and affection of the different stakeholders and their potential impact on the organizational strategies and decisions (Wheeler & Sillanp, 1997).
Environmental analysis:
PESTLE
Political Factors: It where political factors that have to do with government policies and stability that are critical in the Virgin Atlantic business. They include factors such as changes in regulations affecting aviation, taxation, and trading policies that impact on overall cost structure of the airline operations and therefore its profitability and performance. For instance, the Brexit changes are likely to impact Virgin Atlantic operations because the changes in global regulation affect the operation of the business in the European markets and therefore require a change of strategy to undertake its operations legally.
Economic Factors: These macro-environmental forces influence Virgin Atlantic with references to GDP growth rates, inflation, and exchange rate rates. Fluctuations in fuel prices, exchange rates, and any form of economic shock can have a direct impact on the cost side, profitability, and traffic sensitivity of the airline. To a significant extent, Economic factors enable Virgin Atlantic to anticipate the conditions on the market and, accordingly, adjust the price and make the necessary decisions about the routes taken.
Social Factors: These factors concern elements like demographics, culture, and the rest of the social influences that affect the travel decision and behavior of consumers. Variations of the marketing-timing controls with customers behaviors, travels, and views towards the protection of our environment influence Virgin Atlantic directly in its marketing mix, network construction, and provision of services. For example, the expanding customer demand for passenger tourism products and services in an environmentally friendly way may necessitate the use of sustainable technologies in the air and appropriate supply of tourism within Virgin Atlantic (Grant, 1996).
Technological Factors: In this paper, Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited is examined concerning digital innovation and pertinent aircraft technologies that influence it. Services like online booking, the facility to self-entertain during a flight, and other business-related web applications enhance overall customer satisfaction and organizational effectiveness. Furthermore, product-related innovations in the aeronautical industry such as ways of fuelling planes most efficiently and efficient methods of maintaining planes are essential to Virgin Atlantic since they reduce operational costs and impact on the environment.
Legal Factors: Legal factors involve the legal constraints that govern the airline industry and the policies and regulatory measures that firms in this sector have to abide by. Aviation safety regulations, employment laws and regulations/standards, and environmental laws and regulations are legal elements through which Virgin Atlantic cannot afford to omit to operate legally to avoid legal risks. Another challenge that impacts Virgin Atlantic relates to the constantly altering data protection laws, passenger rights, and safety requirements; this means that the firm has to be on the lookout always, to ensure compliance with current laws.
Environmental Factors: Some of those that have stood out to be common but specific to the social aspect of Virgin Atlantic are the climate change factor, issues to do with sustainability, and impacts of legislation on the environment. Another question relates to the consequences of aviation industry activities and their impact on emissions, noise, and others, making Virgin Atlantic adopt Sustainable Aviation Technologies and Carbon Offset programs. Dealing with environmental issues will assist Virgin Atlantic in enhancing the perception of the public concerning the image of the company as an organizational entity that shows concern for the natural environment (Wheelen & Hunger, 2017).
Porters Five Forces model
1. Threat of New Entrants: A threat in the airline industry is the threat of new entrants, implying that competition can enter the business and secure a greater number of clients than the airlines. Other factors that are used in the threat of entry are capital intensity, government activity, and experience curve. Like other airline companies, Virgin Atlantic also possesses certain competitive advantages that act as forces preventing new entrants: product differentiation, brand name, customers loyalty, and valuable investments in fixed assets. On the other hand, strategic administration may face threats such as low-cost airliners and deregulation strategies in the future, which may give rise to the threat of new entrants and thus require serious strategizing (Johnson et al. 2016).
2. Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers on the other hand is the ability that the customers possess, which they exercise in agreeing on the price, service, and other conditions they have with the aircraft operators. Most of the airlines customers include individual passengers, corporate organizations, and travel companies. The key buyer power indicators include price sensitivity, the presence of substitute goods or services, and costs involved in switching from one brand to another. The intensity of the buyer power is moderately threatening to Virgin Atlantic because many other airline companies exist coupled with the fact that a buyer has many options to compare the price and services offered by one airline with those of the other. To this end, Virgin Atlantic intensifies focus on the satisfaction of the customers, strengthening the carrier-preferred programs, as well as the diverse services that may be offered to the passengers.
3. Bargaining Power of Suppliers: An analysis of the bargaining power of suppliers involves the position that aircraft suppliers, fuel providers, workforce, and other inputs for airline operations occupy in determining the operating costs and profitability. Another force that influences suppliers is the industrial buyers bargaining power which ranges based on factors such as the number of suppliers, the cost of searching for another supplier, and availability of other suppliers. The stakeholders that relate to Virgin Atlantic through material goods include airplane manufacturers like Boeing and Airbus, fuel providers, and employee unions. Nevertheless, the bargaining power of suppliers is still high because there are few propulsion manufacturers such as Boeing Airbus and Virgin Atlantic have been locked in long-term contracts and have first movers, economies of scale, and strategic supplier relationships.
4. Threat of Substitute Products or Services: The threat of producing a substitute product or service It deals with the vulnerability of the airport's business to be substituted by other modes of transport or other products that can serve the same purpose as air traveling. Some of the possible substitutes for aviation include rail transport, road transport, communication, and video conference. These cost factors include the price of the product and the ease of acquiring a substitute product. Other competitors like high-speed rail and video conferencing are in a moderate threat in covering short-haul flights but do not pose a significant threat to the long-haul international flight business thus reducing the threat to Virgin Atlantic. Substitute risks, on the other hand, need to be managed by staying sensitive to emerging technologies, the customers changing preferences, and their tastes.
5. Intensity of Competitive Rivalry: The intensity of rivalry refers to the intensity of competition that exists between the players in this market, the various airlines. The strength of rivalry comprises of number of competitors, the growth rate of the industry, and strategic differentiation. Virgin Atlantic is located in a rather unsteady business setting since there are competing international and local airlines. High competition results in fare reductions and other promotional measures together with unstable services in an attempt to attract the consumer. Competition pressure is specifically addressed by Virgin Atlantic through presenting differentiation between the airline and other competitors, focusing on customer-oriented services, and choosing routes that would enable the airline to firmly establish a position in the marketplace.
Strategic positioning: Ansoffs growth vector matrix
1. Market Penetration: Market penetration involves the increase in the current sales of the goods without changing the existing product portfolio by either approaching existing consumers for additional sales or look for other consumers with such potential. Market penetration strategies might be the following for Virgin Atlantic: Advertising a little lower fare than its competitors, offering bonuses for flying frequently and so on to keep its clients from straying to other airlines and also stealing customers from the competitors. In this way Virgin Atlantic wants to get a handle on a larger market share and additional revenues from the current market (Wright & McMahan, 1992).
2. Product Development: Product development commonly involves introduction of new products or services in the same market due to evolving needs of buyers. An example for Virgin Atlantic, product development key activities might be to add new destinations to be operated; introducing operational premium cabins; or to work on the product offerings on board. General from a strategic perspective Virgin Atlantic has sought to achieve competitive advantage through a process of innovation and refinement of the product offering to suit certain target customer segments to increase the market share and loyalty.
3. Market Development: Market development is therefore the process of expanding the companys existing products or services into new markets. Possible market development activities may include Virgin Atlantic may decide to expand the geographical coverage of the company to areas that have not been fully explored, focus marketing efforts to new growth markets where travel demand is on the rise or enter into a joint venture with local airline companies to be able to penetrate such markets. By implementing the regional expansion and customers base expansion Virgin Atlantic intends to secure more opportunities than already exist in the USA, UK and Canada and meet its revenue goals (Kotler & Armstrong, 2010).
4. Diversification: On the other hand, market development is the strategy of searching for new markets with existing products or services that are unrelated to the business of the company. Therefore, diversity benefits may include associated activities such as travel agents, hotel services or transport services for Virgin Atlantic. Furthermore, diversification at Virgin Atlantic may entail direct purchase of other companies or outsourcing for firms offering similar services.
Internal Environment Analysis
Strategic Capabilities:
The strategic capabilities of a firm can be described as components of organization, which enable a firm like Virgin Atlantic to support strategic initiatives and construct a competitive advantage in a certain market. These capabilities involve many aspects of the organization with the attributes, skills as well as resources of the organization that help in accomplishing organizational goals and objectives.
Key Components of Strategic Capabilities:
Human Resources: Human capital represents one of the more crucial components of the strategic capability of the organization as abilities, competencies, and knowledge of employees are valuable for organizational strategies. Learner development and organization commitment, staffing methods, and workforce motivation make up the strategic components that help to create sound human resource capacity.
Technological Infrastructure: IT structure framework, software & hardware is an integral part of business technology in any organization. Technological advancements; information technology and other technology-related investments; and innovation help to develop technological competitiveness and to maintain organizations relevant to the dynamic environment.
Financial Resources: Suitable capital is crucial for supporting the implementation of strategic plans, and growth strategies, and investing in the main driving areas of development. The financial assets are capital acquisition techniques, budgeting and distribution strategies, financial risks and rewards, and financial profitability.
Physical Assets: Tangible plant assets such as buildings, machinery, and production facilities relate to the capacity or output delivery function of the organization. Managing and optimizing physical services are some of the interfaces in the efficient use of resources, which make up the strategic assets.
Organizational Culture: This paper posits that culture and the values adopted in the organization being considered are determinants of the strategic capability of an organization since they influence behavior, decision-making, and organizational performance. It is only when several cultural values are adopted that high strategic agility and market resilience are achieved; these cultural values include; innovation, collaboration, adaptability, and customer orientation (Rumelt, 2011).
Strategic Alliances and Partnerships: Externals like partners, suppliers, and other players in the environment enhance the creation of organizational competence because they provide additional resources, information, and even markets. Strategic alliances are useful in the creation of new ideas, markets, and competitive positioning.
Brand Reputation and Intellectual Property: They assist in building the brand and are strategic assets that set the organization apart from its competitors since they establish exclusive rights on certain symbols, names, inventions, or technologies. The need for the protection of legal rights about any idea, product, or service to ensure competitive advantage cannot be overemphasized (Porter, 1980).
These strategic components of the strategic capabilities help in the attainment of organizational goals, risk management as well as optimization of growth opportunities.
Resource-Based View Strategy for Competitive Advantage
Overview of Resource-Based View (RBV) Strategy:
RBV strategy refers to the resource-based view that is a management framework that attaches great significance to internal tangible and intangible resources and capabilities towards acquiring sustainable competitive advantage. RBV identified that firms have resources and abilities that can be leveraged to enhance Virgin Atlantic's performance in delivering value to clients. As opposed to the previous theories emphasizing outside environment pressures as the source of sustained competitive advantage, RBV points to internal conditions (Porter, 1985).
Key Principles of RBV Strategy:
Resource Heterogeneity: Therefore, RBV posits that resources and capabilities are heterogeneous and industry- and firm-specific, which has ramifications on the heterogeneity of competitive advantage. Managers must identify activity-specific sources, which are rare within the Virgin Atlantic context, unique and costly to relocate, and difficult for competitors to imitate.
Resource Immobility: RBV also notes that resources and capabilities could be inequitable or imitation which translates to sustainable competitive advantage. Historical conditions, the particular type of organizational culture, and complex social relations belong to the makeup of resource immobility that contributes to the character of resource stability.
Dynamic Capabilities: RBV also emphasizes the concept of dynamic capability, which is defined as the firms capability to alter, develop, and accumulate resources due to the changing circumstances in the economy and other competitors. Several reasons have been identified as mandatory at this stage, namely permanent learning and knowledge development, as well as management and organizational flexibility as factors that are prerequisites for competitiveness (Slack et al. 2018).
McKinsey's 7S Model as a Management Tool
Introduction to McKinsey's 7S Model:
In the context of Virgin Atlantic, McKinseys 7S model can prove to be a useful framework in management considering performance and integration. This is a strategic management model that was developed by the global management consulting firm McKinsey & Company and features seven interrelated processes that describe the strategy, design, processes, culture, people, methods, and workforce in an enterprise. By analyzing all these elements, Virgin Atlantic would be in a position to identify its strengths and areas of weakness towards the fulfilment of the company's strategic goals (McKinsey & Company, 2018).
Key Components of McKinsey's 7S Model:
Strategy: This paper, aims at providing Virgin Atlantic with a strategic management plan for achieving competitive advantage and satisfying strategic targets such as positioning, routes and network, fleet, and customer value decisions.
Structure: A formal and orderly arrangement showing subordination, assignments, authorities, and roles in Virgin Atlantic. This involves organization structures and functions such as the operations department, marketing department, finance department, and customer service department.
Systems: Business activities, procedures, and techniques; that is business operations refer to reservation systems, flight scheduling processes, security measures, and maintenance processes in Virgin Atlantic.
Shared Values: The basic postulates that capture the culture of Virgin Atlantic concerning the behaviors and activities to be pursued in the organization. They provide information on the companys brand, the relations with consumers, and the incentive schemes for the workforce.
Skills: Knowledge of Virgin Atlantic employees about the company, its operation, organizational culture, industry specifics, their past and potential experience, and their technical, communication, and leadership competencies (Virgin Atlantic, 2021).
Style: How the organizational culture, communication, and decision-making pattern of Virgin Atlantic has been developed, senior executives and key leaders possible by the leadership and management style that they adopted.
Staff: Virgin Atlantic people: these are the pilots, the cabin crew, the ground staff, and every other person who is an employee within the business organization we can refer to in the human resource aspect of the business. Applicants were active in striving for organizational goals as they utilized their skills, knowledge, and interests.
Application of McKinsey's 7S Model:
In the case of Virgin Atlantic, the use of McKinseys 7S model is an opportunity to study the situation in the field of organization and find out the measure of match or the issue of an off-match point, which is not suitable for the creation of reference point between the seven aspects. In so doing, Virgin Atlantic can organize strategy, structure, systems, cultural and leadership values, skills, style, and staff factors to frame organizational problem-solving activities to enhance organizational performance and deliver strategic initiatives. This type of model helps Virgin Atlantic to align corporate resources with outside opportunities and threats and ensure the sound and competitive future evolution of an airline company (Virgin Atlantic, 2021).
Analysis of Strategic Capabilities using the VRIO/VRIN Framework
Introduction to the VRIO/VRIN Framework:
In terms of Virgin Atlantic, next to Porters five forces model, the VRIO/VRIN analysis is used when evaluating the strategic assets of the airline. Developed by Jay Barney (1991), to understand whether and to what degree resources are Valuable, Rare, and Impossible to imitate and adequately coordinated for the exploitation of opportunities and unmasking of threats. This can be understood as guiding the strength that Virgin Atlantic has to bring to the table as a strategic direction.
Valuable Resources:
Some of Virgin Atlantics main resources are valuable and enable the company to gain a competitive advantage as follows: Some examples of value resources include the firms brand image in the airline industry, technological applications within the aircraft used, and an efficient customer-focused service delivery system. Additionally, Virgin Atlantic is useful for the organization to have good financial solutions as well as attractive associations with other channel partners.
Rare Resources:
Virgin Atlantic has some valuable resources of which some are rare within the airline industry as the following subtopics will expound on. For instance, it has some rights as the home airline to have some privileges in some terminals like Heathrow, whereas this airline enjoys better and other special strips during the traffic congested terminal. Also, identifying the specific airlines brand values and or its customer rewards programs is another valuable and scarce operating resource (Thompson et al. 2016).
Inimitable Resources:
Virgin Atlantic has also been known to come up with several resources that cannot be emulated by rivals within this industry. They have a very powerful brand image and this has been achieved through creatively designed advertisements and the use of celebrities in promoting its products. Similarly, the awareness of the airlines obligation to the employees and the consumer is yet another form of proprietary information that cannot be imitated.
Organized to Exploit Opportunities:
Virgin Atlantic has presented substantial evidence that shows it can efficiently harness its resources to capitalize on opportunities within the markets. For instance, the airline has leveraged its brand and customer database to expand point and hence, enter and capture new markets. In addition, contractual relationships with other airlines and other travel service providers exist within Virgin Atlantic to improve the service offering and point of sale for the customers.
Application of the VRIO/VRIN Framework:
Virgin Atlantic can apply the VRIO/VRIN analysis to compare which of the stakeholders activities is/are positively valued and which ones should be modified. All these can be helpful when it comes to strategic choices such as where to apply the available resources, where to expand, or where to locate in the given competitive context. Moreover, there is a continuous need to review and develop strategic capacities within Virgin Atlantic to maintain competitive advantage in the airline industry given its dynamism (Virgin Atlantic, 2021).
Benchmarking Strategic Capabilities and Value Chain Analysis
Introduction to Benchmarking and Value Chain Analysis:
Strategic benchmarking and value chain analyses are two significant approaches for assessing organizational performance, identifying for instance, an organization can assess its performance, evaluate its strengths and weaknesses, and determine where it stands against its competitors. They can prove of great use to Virgin Atlantic to improve its performance and maintain its viability in the airline business sector. Benchmarking is a system of comparing the data of different organizational and performance indicators with similar data of other organizations, while the value chain focuses on the centers of activity flow, creating or increasing the value of goods and services.
Benchmarking Strategic Capabilities:
Virgin Atlantic can go beyond the limits of strategic capability by evaluating such factors as productivity, efficiency, quality, innovation, customer satisfaction, et cetera with competitors or the most significant competitor. Virgin Atlantic can position itself with other companies or even leaders in this field so that it can understand its strengths and weaknesses as well as set goals for improvement. They can be done internally or externally or it can be a combination of both to gather more information.
Value Chain Analysis:
Value chain analysis in a nutshell means that different links within the value delivery system are examined to determine where cost could be driven down or where value could be created. Marketing and service being two of the elements in the value delivery net means that Virgin Atlantic can look at all the activities on the net and see in which area the company has a strong competitive advantage or which areas need improvement to deliver more value. However, it is in the coordination of activities up and down the value chain that Virgin Atlantic can either lessen or remove some of the activities and at the same time step up the level of satisfaction of customers while at the same time reducing costs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis:
Meanwhile, the cost advantage option is understood as cost efficiency is the comparative evaluation of the potential cost of the potential benefits of a project, plan, or decision. According to the cost-benefit analysis, Virgin Atlantic would get the quantitative information to evaluate the strategic plans including the cost of expanding the size of the fleet and the network as well as benefits that can be derived from technology opportunities. This way, Virgin Atlantic can negate bad decisions and is provided the ability to give it a method of ranking the pros and cons of trade-offs, investments, and resources needed in the organization.
Application of Benchmarking and Value Chain Analysis:
Strategic benchmarking and value chain analysis can be of special utility for Virgin Atlantic to improve results and deliver more value to clients, as well as take better advantage of its resources. Therefore, with the help of the industry leaders and comparing different activities of the value chain, Virgin Atlantic can establish the potential for enhancing competitiveness and ensuring long-term success in the continuously changing airline industry. The significance of cost-benefit analysis as a strategic tool is that, it provides Virgin Atlantic with a proper framework for financial prognosticating on organizational decisions to ensure that any decision the firm decides to undertake is valued by the stakeholders and more importantly, is strategic for the achievement of the firms intended goals and objectives. Altogether, these strategic instruments help Virgin Atlantic to work, evolve, and maintain the leadership position of the airline (Virgin Atlantic, 2021).
Analytical Tools and Models of Analysis
Introduction to Analytical Tools:
Another critical success factor of strategic management systems is that analysis tools and frameworks provide the means for assessing the industry, the competitive forces and actors impacting the organization, and the stakeholders in the organization. Such tools help organizations like Virgin Atlantic to analyze the conditions of the market, identify the most effective opportunities for entering, and select proper business strategies. Taking this into account, the following can be referred to as the most popular assessment instruments: the BSC, Porters Five Forces model, and stakeholder mapping to assess and use the results in decision-making (Virgin Atlantic, 2021).
The Balanced Scorecard:
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework that translates Virgin Atlantic's vision and strategy into a comprehensive set of performance metrics across four key perspectives: The four primary areas are financial, customers, internal business processes, and learning and growth. Virgin employs objectives, measures, targets, and initiatives of the BSC to accomplish performance measurement, goal implementation, and strategy conveyance based on these multiple viewpoints. It offers an inclusive insight into organizational performance as it captures both the financial and non-financial indicators and it also supports organizational learning and organizational congruency throughout all the layers of the organization (Bowman & Faulkner, 1999).
Competitive Analysis using Porters Five Forces Model:
Used for the analysis of the airline industry and the airline attractiveness of these sectors, Porters Five Forces model is a force to be reckoned with. The model examines five key forces that shape industry competition, these are the threat shown by new entrants, the buyers bargaining power, the suppliers bargaining power, the threat posed by substitutes, and the intensity of competitor rivalry. Through the evaluation of these forces, Virgin Atlantic will be in a position to identify areas of opportunities for gaining competitive advantage and more importantly, the level of competition to look for ways of reducing competition. Porters five forces model assists in determining the competitiveness of the forces that act on a particular industry to inform Virgin Atlantic of its entry and positioning strategies based on the markets and resources available for the business (Porter, 2008).
Stakeholder Analysis:
Stakeholder mapping is a technique of analyzing its major stakeholders interests, power, and stake in Virgin Atlantic Airline. It focuses on categorizing the stakeholders based on their power and interest and assessing their knowledge of issues relevant to the organization and possibly associated risks. By understanding the key actors involved, Virgin Atlantic will be able to prioritize which of the stakeholders its communication must be targeted at; the power of the stakeholder, the extent of their interest, how vulnerable they are, and if Virgin Atlantic is likely to share common ground with them or not. Virgin Atlantic stakeholder information shows that the needs of these stakeholders assist the company in exhibiting better relations, a better business image, and credibility in the market.
Application of Analytical Tools:
Analytical frameworks such as the Balanced Scorecard, the Five Forces model, and stakeholder mapping enable Virgin Atlantic to evaluate the business factors, competitors, and stakeholders. As a result, Virgin Atlantic will be able to leverage tools for realizing strategic opportunities, threats, and general strategies congruent with the organizational objectives, and favorable to Virgin Atlantics sustainable success in its chosen market. These analytical tools provide clues that make it easier to come up with optimal solutions to accomplish mission visions and objectives and to manage organizational capital optimally (Kaplan & Norton, 1992).
Strategic Directions Evaluation
Porters Generic Strategies
In the case of Virgin Atlantic, Porters generic strategies play a significant role in finding out a competitive advantage among the airlines. Such approaches include cost-driven strategy, differentiation, and focus to provide solutions to various market segments.
Cost Leadership Strategy
Virgin Atlantic could try for a cost leadership strategy to make the cost of operation lower than the cost incurred by all other airline organizations. Cost efficiency would include process efficiency or rationalization of costs, scale cost factors, and attaining the optimum level of cost at every segment of the value chain. Pricing policies also is advantageous to Virgin Atlantic since they can capture price-sensitive consumers in the market.
Differentiation Strategy
It could also choose a distinct market focus where Virgin Atlantic offers a product or service in the market that cannot be sourced from other firms. This could include investment in innovations like the level of entertainment during a flight, a luxurious experience, or personalized services. In this way, Virgin Atlantic can set high prices and build customer loyalty for those travelers who always want to receive something new and exciting in the sphere of airline companies (Hitt et al. 2017).
Focus Strategy
In a focused strategy, the Virgin Atlantic Company directs its marketing attention towards a single, distinct group in the market, such as business travelers or luxury travelers. Thus, if Virgin Atlantic concentrates on satisfying these segments needs and wants, the airline is capable of achieving great value for its services and gaining these valuable consumers. It also enables Virgin Atlantic to work effectively and achieve maximum profitability within the predetermined market segment.
Bowmans Strategy Clock:
Virgin Atlantic also has several opportunities for action which include positions identified by the extended model of Bowman & Faulkner's (1997) strategy clock beyond Porters four generic strategies and that encourages the understanding of hybrid strategies and the fine-grained positioning strategies.
Hybrid Strategies
However, it is essential to note that Virgin Atlantic might try to implement both the cost leadership and the differentiation strategies, at least to some degree. For example, in addition to avoiding high ticket prices to capture the market, as Virgin does, it could also offer other extra special services or amenities that many single-value strategy-adopting firms would not have.
Nuanced Positioning Strategies
Hence, positioning can not be excluded from Virgin Atlantics strategizing since positioning essentially defines the means of attaining a special place in the market. It can suggest the growth of specific products available to specific consumers, the enhancement of technology utilized during flying, or the extension of the gap from competitors by using trends like green tourism.
Conclusion
As such, the analysis made has provided appearances of the position that Virgin Atlantic has in the industry of airline. From the analysis of the macro and internal environment having identified the competitive forces and probable strategies, the following could be deduced. First of all, Virgin Atlantic has been very aggressive in realizing the principles of customer service and satisfaction and has taken a significant step forward to redefine the flying experience in the highly competitive world today. It also came up with other issues such as increased competition, changing customer demands, and other regulatory factors, which should be resolved to ensure further growth and profits.
The following strategic recommendations are proposed for Virgin Atlantic Limited based on the analysis made in this study. First of all, Virgin Atlantic should continue to dedicate efforts to customer-centered strategies aiming at enhancing satisfaction and loyalty. This can create pressure to adopt customer-oriented business models, digital and physical value propositions, and sustainable solutions for modern consumers. Also, Virgin Atlantic should pay attention to improving its innovation capabilities in all available domains: the Aerodynamics of the aircraft and its technologies, the route network, and the services provided to the clients.
There is one more issue to discuss, namely, the problem of the development of strategic partnerships which is one of the crucial sources of financing for Virgin Atlantic, especially when it comes to expansion of the geographic reach of the company and its access to new markets. I have found out that for Virgin Atlantic airline to increase its coverage in any region, it is possible to partner with other airlines, travel agents, and hotels to enhance the connectivity, consumer reach, and effectiveness of routes. In the same regard, strategic alliances would be useful in operations such as sharing of costs, marketing initiatives, and, in most cases, shipping to optimum utilization of resources towards sales generation.
Are you struggling to keep up with the demands of your academic journey? Don't worry, we've got your back!
Exam Question Bank is your trusted partner in achieving academic excellence for all kind of technical and non-technical subjects. Our comprehensive range of academic services is designed to cater to students at every level. Whether you're a high school student, a college undergraduate, or pursuing advanced studies, we have the expertise and resources to support you.
To connect with expert and ask your query click here Exam Question Bank

